WR1 - Surface anatomy & inguinal canal Flashcards
The abdomen & pelvis area can be divided into 4 quadrants
What are these and what divides them?
Right & left upper & lower quadrants
Transumbilical line divides upper and lower
Median line divides left and right
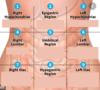
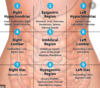
What are the 9 abdominopelvic regions?
What divides them?
Upper:
- R&L Hypochondriac
- Epigastric
Middle:
- R&L Lumbar
- Umbilical
Lower:
- R&L iliac
- Hypogastric
Divisions in Vertical plane are the midclavicular lines
Divisions in horizontal plane the Subcostal line & Transtubercular line

For each of the abdominal regions, name the major organs that are contained within each region
What muscles make up the anterior abdominal wall and what are their individual actions?
External oblique:
- Compress & support abdominal viscera
- Flex & rotate trunk
Internal oblique:
- Compress & support abdominal viscera
- Flex & rotate trunk
Transversus abdominis:
- Compress & support abdominal viscera
Rectus abdominis:
- Flexion of trunk (lumbar vertebrae)
- Compresses abdominal viscera
- Stabilises pelvis
Identify the muscles in the diagram below


What innervates each of the anterior abdominal muscles?
External oblique:
- Ventral rami T7-T11
- Subcostal nerve (T12)
Internal oblique & Transversus abdominis:
- Ventral rami T7-T11
- Subcostal nerve
- First Lumbar nerve
Rectus abdominis:
- Ventral rami T7-T12
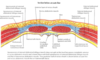
From outermost to innermost - list the layers of the anterolateral abdominal wall
Skin
Subcutaneous tissue (superficial fascia)
Muscles & their aponeuroses - with deep fascia covering each muscle
Endoabdominal fascia
Extraperitoneal fat
Parietal peritoneum
What is the rectus sheath?
Explain how the arrangement of the abdominal muscles & rectus sheath changes as you move down the abdominal wall
Rectus sheath formed from the interlaced aponeuroses of the flat abdominal muscles - External & Internal obliques + Transversus abdominis
Superior to the Umbilicus:
- Rectus abdominis muscle lies between the 2nd & 3rd aponeuroses that make up the sheath
Inferior to the Umbilicus:
- The innermost aponeurosis passes anterior to the Rectus abdominis - meaning all 3 aponeuroses are together
Identify the different layers
Is this section above or below the umbilical (arcuate) line?

Inferior to Umbilicus
Identify the labels
Is this from above or below the umbilicus?

Above the umbilicus

What level is the umbilicus at and why is this a useful landmark?
What dermatome is it?
L3/4
Aorta bifurcates at this level
Dermatome = T10
What is the inguinal ligament?
What does it do?
The inguinal ligament:
A band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal

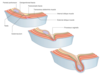
What is the inguinal canal?
A canal formed from the layers of the anterior abdominal wall as they push through the wall obliquely
- This pushing through occurs during the relocation of the gonads during fetal development
It is approximately 4cm long and lies parallel to and above the medial half of the inguinal ligament
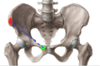
On this lovely pelvis here - mark the attachments of the Inguinal ligament
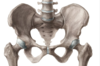
Anterior superior iliac spine - ilium
Pubic tubercle - pubis
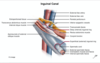
What structures contained within the inguinal canal?
Males - the Spermatic cord conveying the ductus deferens
Females - Vestigial Round ligament of the uterus
Also (in both sexes) contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels & the ilioinguinal nerve