Wk 6 GI Flashcards
(113 cards)
Except for chewing, swallowing, and defecation, how are the movements of the digestive system (GI motility) controlled?
Autonomic nervous system (sympathetic & parasympathetic) & hormones
What are the 4 layers of the GI tract? (inside to outside, include the sublayers)
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, & serosa
Mucosa (epithelium, lamina, muscularis mucosae)
Submucosa
Muscularis (Circular muscle layer, longitudinal muscle layer)
Serosa (connective tissue layer, peritoneum)

What are the 3 enteric nerve plexuses and their locations?
Submucosal plexus, myenteric plexus, & subserosal plexus
Submucosal plexus (Meissner plexus) - in the muscularis mucosae
Myenteric plexus (Auerbach plexus) - in btwn circular & longitudinal muscle layers
Subserosal plexus - beneath the serosa

How many permanent adult teeth in the mouth?
32
What are the 3 salivary glands?
Parotid, submandibular, & sublingual

How much saliva is secreted per day?
1 L
What is saliva made up of?
Mucus
Electrolytes (sodium, bicarbonate, chloride, potassium)
Ptyalin (salivary alpha-amylase)
What is ptyalin?
Salivary amylase - an enzyme that digests carbohydrates in mouth and stomach
What stimulates and inihibits salivary glands?
ANS controls salivation.
Cholinergic parasympathetic fibers & beta-adrenergic sympathetic fibers stimulate
Atropine (anticholinergic agent) inhibits salivation & makes it dry
Are salivary glands regulated by hormones?
No
How does saliva prevent tooth decay?
Bicarbonate has pH of 7.4 = neutralizes bacterial acids
IgA (immunoglobulin A) prevents infection (also found in saliva)
Exogenous fluoride (fluoride in drinking water) absorbed & excreted in saliva
How does swallowed food move from the mouth to the stomach?
Esophageal peristalsis
What is peristalsis?
Coordinated sequential contraction & relaxation of the outer longitudinal & inner circular layers of muscles.
Describe the muscles and nerves in the esophagus.
Upper = striated muscle innervated by motor neurons
Middle = mix of striated & smooth muscle
Lower = smooth muscle innervated by preganglionic cholinergic fibers frm the vagus nerve

How is peristalsis in the esophagus stimulated?
As food passes & causes stretching of the walls, afferent fibers sense changes in the wall tension.
The greater the tension, the greater the esophageal contraction.
Name & descibe the function of the esophageal sphincters.
Upper esophageal sphincter (cricopharyngeal muscle) & lower esophageal sphincter (cardiac sphincter)
Upper esophageal sphincter (Cricopharyngeal muscle) - prevents entry of air into the esophagus during respiration.
Lower esophageal sphincter (Cardiac sphincter) - prevents regurgitation frm the stomach.
How is swallowing controlled?
Swallowing center in the brainstem
Name & describe the 2 phases of swallowing.
Oropharyngeal & esophageal
Oropharyngeal (voluntary) phase - food bolus forced posteriorly by the tongue toward the pharynx. Superior constrictor muscle of the pharynx contracts, preventing movement of food into the nasopharynx. As respiration is inhibited, the epiglottis slides downard to prevent the bolus frm entering larynx & trachea.
Esophageal (involuntary) phase - food bolus enters the esophagus. Primary peristalsis occurs. If bolus of food b/comes stuck, 2ndary peristalsis occurs. Peristalsis = wave of relaxation (allows food to pass & reduces resistance), then wave of contraction (pushes food along).
What is partially digested food called?
Chyme
Describe the anatomic structure of the stomach.
Boundaries of the stomach: lower esophageal sphincter (cardiac sphincter), greater & lesser curvatures, pyloric sphincter
Functional areas of the stomach: fundus (upper portion), body (middle portion), & antrum (lower portion)

Name the 3 smooth muscle layers of the stomach (inside to outside)
Oblique layer
Circular layer
Longitudinal layer

Which parts of the stomach does the muscle layers become progressively thicker?
Body & antrum b/c ths is where food is mixed, churned, & pushed out to tthe duodenum

What artery supplies blood to the stomach?
Celiac artery
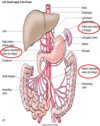
Describe the veins of the stomach
Splenic vein drains R side of stomach
Gastric vein drains L side of stomach








































