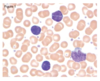
White Blood Cells Flashcards
What are granulocytes
Neutrophils Basophils Eosinophils All contain granules
What are some myeloid growth factors
Granulocyte colony stimulating factor Macrophage colony stimulating factor Granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor
Granulocyte maturation

Facts about the neutrophil
Nucleus is segmented
Survives 7-10 hr in blood
It phagocytoses
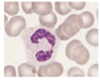
What is chemotaxis
Migration to tissues
Adhere to vessel lumen
How do neutrophils phagocytose
Superoxide dependent
Oxygen independent - antimicrobial enzymes released
Facts about eosinophil
Defence against parasitic infection
Less time in circualtion
Phagocytosis
Facts about basophil
Granules that contain histamine and heparin
Involved in a variety of immune and inflammatory reponse
Modulates inflammatory responses by releasing heparin and proteases
Facts about monocytes
Spend several days in circulation
Phagocytosis
Antigen presentation
Travel to the tissue where they develop into macrophages/histiocytes
Facts about macrophages
Phagocytic and scavenging function
Store and release iron
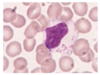
Photo of B lymphocytes
Also known as plasma cell
Nucleus towards edge of cell

What are NK cells
Can kill tumour cells and virus infected cells
Can T and B cells be distinguished
No
How to distinguish lymphocytes
Cell markers
Immunoglobins
T cell receptors
What is the definition of leukcytosis
Too many white blood cells