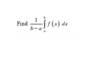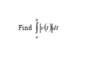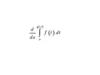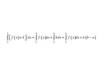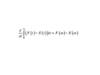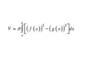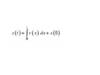When You See...Think Flashcards
(79 cards)
Find the zeros
Find roots. Set function = 0, factor or use quadratic
equation if quadratic, graph to find zeros on calculator
Show that f (x) is even
Show that f (−x) = f ( x )
symmetric to y-axis
Show that f (x) is odd
Show that f (−x) = − f (x) OR f (x) = − f (−x)
symmetric around the origin
Show that lim f (x) exists
x-> a
Show that lim f (x )= lim f (x ); exists and are equal
x->a- x->a+
Find lim f ( x ) , calculator allowed
x->a
Use TABLE [ASK], find y values for x-values close to a
from left and right
Find lim f ( x ) , no calculator
x->a
Substitute x = a
1) limit is value if b/c, incl. 0/c=0; c cannot equal 0.
2) DNE for b/0
3) 0/0 DO MORE WORK!
a) rationalize radicals
b) simplify complex fractions
c) factor/reduce
d) know trig limits
1. lim sinx/x= 1
x-\>0
2. lim 1-cosx/x= 0
x-\>0
e) piece-wise function: check if RH = LH at break
Find lim f ( x ) , calculator allowed
x →∞
Use TABLE [ASK], find y values for large values of x,
i.e. 999999999999
Find lim f ( x ) , no calculator
x →∞
Ratios of rates of changes
1) fast/slow= DNE
2) slow/fast= 0
3) same/same= ratio of coefficients
Find horizontal asymptotes of f (x)
Find lim f ( x ) and lim f ( x )
x →∞ x → −∞
Find vertical asymptotes of f (x)
Find where lim f ( x ) = ±∞
x-\>a±
1) Factor/reduce f (x ) and set denominator = 0
2) ln x has VA at x = 0
Find domain of f (x)
Assume domain is (−∞, ∞). Restrictable domains:
denominators ≠ 0, square roots of only non-negative
numbers, log or ln of only positive numbers, real-world
constraints
Show that f (x) is continuous
Show that…
1) lim f(x) exists (limf(x)=limf(x))
x-\>a x-\>a- x-\>a+
2) f (a) exists
3) lim f ( x ) = f (a )
x→a
Find the slope of the tangent line to f (x ) at
x = a.
Find derivative f ′(a ) = m
Find equation of the line tangent to f ( x ) at
( a, b )
f ′(a ) = m and use y − b = m ( x − a )
sometimes need to find b = f ( a )
Find equation of the line normal
(perpendicular) to f (x ) at ( a, b )
Same as above but m =
−1/f ′(a )
Find the average rate of change of f ( x ) on
[a, b]
Find (f (b ) − f (a ))/(b-a)
Show that there exists a c in [a, b] such that
f (c) = n
Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
Confirm that f ( x ) is continuous on [a, b] , then show that
f (a) ≤ n ≤ f (b) .
Find the interval where f ( x ) is increasing
Find f ′(x ) , set both numerator and denominator to zero
to find critical points, make sign chart of f ′( x ) and
determine where f ′( x ) is positive.
Find interval where the slope of f (x ) is
increasing
Find the derivative of f ′( x ) = f ′′( x ) , set both numerator
and denominator to zero to find critical points, make
sign chart of f ′′( x ) and determine where f ′′( x ) is
positive.
Find instantaneous rate of change of f (x ) at
a
Find f ′(a )
Given s (t ) (position function), find v(t )
Find v(t ) = s ′(t )
Find f ′( x ) by the limit definition
Frequently asked backwards
f ‘(x)= lim f ( x + h) − f ( x)/h or
h-\>0
f ‘(a)= lim f(x)-f(a)/x-a
x-\>a
Find the average velocity of a particle on
[a, b]

Given v(t ) , determine if a particle is speeding up at t = k
Find v ( k ) and a ( k ) . If signs match, the particle is
speeding up; if different signs, then the particle is
slowing down.