What Is Strategy? Flashcards
(19 cards)
Purpose of strategy is to…
Enable a company to gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
- No competition = no need to strategize
- Optimization ≠ Strategy
Definition of Strategy:
“Strategy is the integrated set of choices that positions the business in its industry so as to generate superior financial returns over the long run”
(Ghemawat, 2010)
The creation of a unique and valuable position, involving a different set of activities.
Operational Effectiveness (OE) =
Performing similar activities better than rivals perform them
- A company that better utilize its inputs by e.g. developing better products faster
While operational effectiveness is important and even a mandatory requirement of doing business, being operationally effective is not a strategy.
Porter’s Central Argument:
Various management tools (total quality management, benchmarking, time-based competition, outsourcing, partnering, etc.), that are used today, do enhance and dramatically improve the operational effectiveness of a company but fail to provide the company with sustainable profitability
Porter argues the problem is the failure of management to distinguish between operational effectiveness and strategy
Flaws with OE:
- Imitation and homogeneity:
- Competitors can quickly imitate management techniques, new technologies etc.
- Competitive Convergence: strategies tend to converge along the same basic dimensions of competition (i.e. price)
OE is necessary but not sufficient
“Once a company establishes a new best practice, its rivals tend to copy it quickly. Best practice competition eventually leads to competitive convergence, with many companies doing the same things in the same ways. Customers end up making decisions based on price, undermining industry profitability.”
Difference between operational effectiveness (OE) and Strategic positioning :
Differentiation arises from both the choice of activities and how they are performed.
Strategic positioning =
Performing different activities from rivals’ or performing similar activities in different ways.
Strategic positioning attempts to achieve sustainable competitive advantage by preserving what is distinctive about a company.
Competition based on operational effectiveness (OE) (schema):

Southwest Airlines’ Activity System (schema):

What are the three different strategic positions:
- Serving few needs of many customers (e.g. Screw Manufacturers)
- Serving broad needs of few customers (e.g. Private Wealth Management Firms)
- Serving broad needs of many customers in a narrow market (targeting rural instead of urban- based customers) (e.g. local cinema chain)
Strategic Positioning & Fit :
Strategy involves creating “fit” among a company’s activities:
- the ways a company’s activities interact and reinforce one another
- Fit drives both competitive advantage and sustainability: when activities mutually reinforce each other, competitors can’t easily imitate them.
Southwest’s strategy involves a whole system of activities, not a collection of parts. Its competitive advantage comes from the way its activities fit and reinforce one another
Strategy as Positioning:
(Competing for the present)
Where are we competing?
- Product market
- Segment
- Geography
- Vertical scope
How are we competing?
- What is the basis of our competitive advantage (what to do differently with respect to competitors)
Strategy as a direction:
(Preparing for the future)
What do we want to become?
- Vision
What do we want to achieve
- Mission
- Performance goals
How will we get there?
- Guidelines for development
- Priorities for capital expenditure, R&D
- Growth mode : organic growth, alliances, M&A
The pay-off of a strategy depends on the alignment of:
- Strategic choices
- Internal resources
- Structural forces
- Competitive dynamics
A Hierarchy of Company Statements:

The 3 Basic Elements of a Strategy Statement:
-
Objective: precise objective of what will drive the business
- should include end point + time frame for reaching it
-
Scope: the part of the landscape in which the firm will operate
- Customer, Geography, Vertical Integration
- Advantage: What your business will do differently from or better than others.
Most critical aspect of a strategy statement, defines the all-important means by which the company will achieve its stated objective
That advantage has complementary external and internal components:
- a value proposition that explains why the targeted customer should buy the company’s product above all the alternatives
- a description of how internal activities must be aligned so that only the company can deliver that value proposition
(Porter’s activity-system map)
Trade-offs:
- Defining the objective, scope, and advantage requires trade-offs. They are fundamental to strategy
Examples of Trade-Offs:
- If growth or size, then profitability will suffer.
- If institutional clients, then may ignore retail customers.
- If lower prices, then low quality
Madonna’s successful strategy:
- Madonna’s success cannot solely be attributed to superior resources:
While possessing energy, intelligence, and an impressive capacity for work, she lacks outstanding talents as a vocalist, musician, actress etc.
- Madonna’s success cannot solely be attributed to luck
Occasional failures (particularly in acting)
BUT
- Obsession with stardom and career building
- Continually changing look and evolving musical styles
- Willingness to surround herself with talented people
- Growth and importance of her production companies
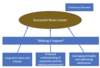
Elements of successful strategy:
- Long term mission and vision (clear goals)
- Profound understanding of consumers and the industry environment
- Leveraging strengths and addressing weaknesses (resource appraisal)
- Consistent Implementation
- Continuous Renewal
Superiority in initial endowments of skills and resources is usually not the determining factor


