Week 6 - RNA Splicing and Processing Flashcards
(113 cards)
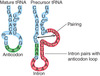
Pre-mRNA
the nuclear transcript that is processed by modification and splicing to give an mRNA
RNA splicing
the process of excising the introns from RNA and connecting the exons into an continuous mRNA
RNA is modified
in the nucleus by
- additions to the 5’ and 4’ ends
- by splicing to remove the introns
RNA splicing and modification
The 5 end of eukaryotic mRNA is
capped
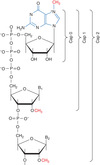
The 5’ end of eukaryotic mRNA is capped
- a 5’ cap is formed by adding a G to the terminal base of the trancript via a 5’-5’ link
- 5’ 7-methylguanosine cap
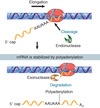
- the cap structure is recognized by protein factors to influence mRNA stability, splicing, export, and translation
- major function is to protect the mRNA from degradation
- cap is recognized by cap binding protein heterodimer (CBP20/80) to facilitate export from the nucleus
5’ cap
7-methylguanosine
- add CH3 at C7 (methylated guanine)
- 5’ to 5’ phosphotriester linkage
- protects unstable RNA (stops degradation)
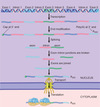
The 5’ capping process takes place
during trancription
• may be important for release from pausing of transcription
3 forms of (5’) capping
- all contain cap 0
- the 5’ cap of most mRNA is monomethylated, but some small noncoding RNAs are trimethylated
- 50% of mRNA is capped at 20 nucleotides
- at 30 nucleotides almost all mRNA is capped
3 forms of capping
… enzymes work together to add the cap
- 3 enzymes work together to add the cap
- RNA triphosphatatse and guanylytransferase activities are present in the same protein and called the capping enzyme
Capping enzyme
RNA triphosphatase and guanylytransferase activities are present in the same protein
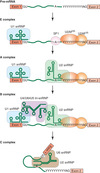
Addition of the 5’ cap
PICTURE

Addition of the 5’ cap
basic steps
- remove 1 P (from the 3 at the 5’ end)
- transfers guanosne to 5’ of RNA, 5’-5’ phosphodiester link
(^both in capping enzyme)
- add methyl to guanosine
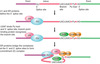
Capping enzyme is recruited by
the CTD of RNA polymerase II
Capping enzyme is recruited by the CTD of RNA polymerase II
- RNA pol II CTD must be phosphorylated on Ser-5 to target a transcript for capping
- CE interacts with Ser-5 phosphorylated pol II
- capping must happen in transcription
Capping enzyme is recruited by the CTD of RNA polymerase II
PICTURE
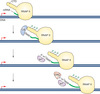
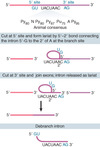
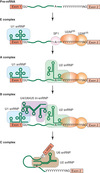
RNA splicing occurs
during and/or after transcription
Splicing makes
transcript diversity
diversity in protein function in splicing the transcript
Nuclear splice sites are
short sequences
Nuclear splice sites are short sequences
- splice sites - sequences immediately surrounding the exon-_intron_ boundaries
- the 5’ splice site at the 5’ (left) end of the intron includes the consensus sequence GU
- the 3’ splice site at the 3’ (right) end of the intron includes the consensus sequence AG
- GU-AG or U2 type introns (98% of human introns)
Splice sites
sequences immediately surrounding the exon-intron boundaries
sequence motifs, consensus in intron that allows splicing
U2-type introns (98% of human introns)
The 5’ splice site at the 5’ (left) end of the intron includes the consensus sequence
GU
U2-type introns (98% of human introns)
The 3’ splice site at the 3’ (right) end of the intron includes the consensus sequence
AG