Week 1 Flashcards
Efficacy
The maximal amount of effect
Ionisation of weak acids/bases -How does pH effect drug uptake -What is “ion trapping”
Henderson Hasselbalch equation describes pH as a measure of acidity - Ionisation of a drug markedly reduces its lipid permeability and thus ability to penetrate membranes Weak acid gives H+ -More soluble at acidic pH Weak base take H+ -More soluble at alkaline pH In the kidney weak acids are excreted faster if urine is alkaline and vice versa -“Ion trapping” alters urine pH to inhibit reabsorbtion of toxins across to renal tubular membranes

Potency
Amount of effect for a given concentration -Reflected by EC50
Antagonist
A molecule that binds to a receptor and inhibits it in some way
Volume of distribution
VD -The apparent space in the body required to contain the drug if the drug is spread evenly at the concentration in blood -High in lipophilic drugs as they have high concentrations extravascularly
First-Pass elimination
Drug metabolism in the gut wall, portal blood and (primarily) hepatic clearance from portal circulation
Phase 1 and 2 reaction
Phase 1 -Modification so a polar and reactive group is added to the drug -Can be via oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis or cyclization Phase 2 -Conjugation -Drug is combined with charged molecules such as glucuronidation, acetly, sulfate or glycine -Aims to detoxify and produce more polar molecule, thus more water soluble and easier to renally excrete
Partial agonist
An agonist that activates but to a sub-maximal level
Drug
An agent that brings about change in biological function through its chemical actions
Clearance
Body’s ability to eliminate a drug -Rate of elimination divided by plasma concentration -May be from different organs (kidney, lungs, liver), need to add these together
TD 50
Median toxic dose -Dose required to produce a particular toxic effect in 50% of animals
Pharmacokinetics
Action of the body on the drug -e.g absorption, distribution, elimination
First order elimination vs zero order kinetics
First order -Elimination cannot be saturated, elimination directly proportional to concentration Zero Order -Rate of elimination is constant Mixed Order -Once concentration of drug is too high, saturates elimination and becomes zero order (alcohol, phenytoin)
Rate of elimination
(Vmax x C)/(Km + C) -Vmax= max elimination capacity -Km= Drug concentration at which rate of elimination is 50% of max -C= Concentration
LD 50
Median lethal dose -Dose required to produce death in 50% of animals
Flow dependent elimination
Drugs that are cleared so well most is eliminated on first pass through organ -Elimination solely depends of rate of delivery (ie blood flow) -E.g propanolol, verapamil
EC50
Concentration required to reach 50% of maximal effect
Pharmacodynamics
Actions of the drug on the body
Agonst
A molecule that binds to a receptor and activates it in some way to brin about an action, either indirectrly or directly
Therapeutic Index
Dose required to produce desired effect vs the dose required to produce undesired effect (ie TD/effective dose)
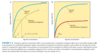
Dose-Response curves -Draw with EC50 and E max -How do competitive and irreversible antagonists effect this
Competitive antagonist -Increases EC50 but Emax is the same Non-competitive (Irreversible) antagonist/Partial agonist -EC 50 is the same but Emax is reduced
Receptor
Site where a ligand binds to effect a change or inhibit the usual action
Half life
Time requied to halve the amount of drug in the body -T1.2=O.7xVd/Clearance
Extraction ratio
Effect of first pass metabolism on bioavailabilty -ER= Liver clearance/hepatic blood flow
Bioavailability
Percentage of unchanged drug reaction systemic circulation -Ie pills affected by absorption and first pass metabolism
Second Messengers
A way of transducing messages from surface to intracellular level Ligand binds to receptor -Activation of G protein -Activation of enzyme/ion channel etc -Increase intracellular concentration of second messenger(eg Ca2+, cAMP, phosphoinositides) -Causes the biological effect of the ligand -eg B adrenoceptors, thyrotropin receptors, glucagon


