Week 1 Flashcards
3 types of muscle
How many and where are the nuclei?
Sk: multinucleated/periferal
C: One/center
Sm: One/center
What tissue give risue to all muscles?
What is an exception?
Mesoderm
Exception: iris (derives from ectoderm)
What contractile all muscles contain?
Actin and Myosin
Describe the three types of muscles
Skeletal muscle is composed of large, elongated, multinucleated fibers.
Cardiac muscle is composed of irregular branched cells bound together longitudinally by intercalated disks.
Smooth muscle is an agglomerate of fusiform cells. The density of the packing between the cells depends on the amount of extracellular connective tissue present.

What cells give rise to muscle cells?
What these cells form to produce muscle cells?
Mesenchymal cells -> Myoblasts -> Myotubes -> Mature muscle

Muscle fiber vs. myofibril
Muscle fiber = muscle cell
Myofibril = made up of the myofilaments actin and myosin

What is the purpose of the connective tissue in skeletal muscle?
Transmits the forces (muscle cells do not extend the length of the musscle)
Transmitting blood vessels
How muscle is organized (subcomponents)?

When is the number of muscle fibers steady?
14 years old (~puberty)
What might regenerate skeletal muscle cells in an adult?
Satellite cells
What is the molecule that regulates number of muscle cells (hormone)?
How does it regulate the number muscle fibers?
Myostatin
It suppresses skeletal muscle development.
What determines the strength of the muscle?
Total number of muscle fibers (not length)
What is the difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia?
Hypertrophy = Increase in muscle size
Hyperplasia = Increase in number of muscle cells
What is the functional unit of muscle cell?
Where does it extrends from?
What multiple sacromeres from?
Sacromere
Z to Z
Myofibrils
What skeletal muscle bands can we see?
Actin (7nm) makes up the thin I band (isotropic to polarized light)
Myosin (15nm) makes up the A band (anisotropic to polarized light)

Where are the T-tubules in skeletal muscle cells?
A-I band junction

What is triad (skeletal muscle) made of?
What is the function of triad?
T tubule + 2 SR (terminal cisterna of sarcoplasmic reticulum)
Calcium for uniform contraction

What are three bands in skeletal muscle?
A band made up of actin and myosin
I band made up of actin
H band made up of myosin

How contraction of muscle affects:
A band?
I band?
H band?
Two adjacent Z disks?
the A band stays the same length
the I bands and H bands shorten (sliding filament model)
The Z disks are moving closer to one another
What covers neuro-muscular junction?
Schwann cell

What is external lamina?
A structure similar to basal lamina that surrounds the sarcolemma of muscle cells. It is secreted by myocytes and consists primarily of Collagen type IV, laminin and perlecan (heparan sulfate proteoglycan). Nerve cells, including perineurial cells and Schwann cells also have an external lamina-like protective coating.
What is another name for neuromuscular junctions?
Motor end plates
What molecule plays crucial role in muscle contraction?
Calcium
Characteristics of cardiac muscle cells
Striations
Intercalated disks
1-2 centrally located nuclei per cell
Bifurcating & anastomosing cells
Highly vascular
Have atrial granules

What are atrial granules and where they are found?
The are found in cardiac muscle cells
They contain atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) that acts on kidney to regulate blood pressure through sodium and water reabsorption.
What are the three layers in heart?
Endocardium (homologous to tunica intima)
Myocardium (homologous to tunica medai)
Epicardium (homologous to tunica adventitia)

What is a difference between cardiac and skeletal muscle cells in terms of the T-tubules?
Skeletal muscle have and cardiac muscle lack cisternae
Skeletal muscle have T-tubule on A/I band border while cardiac muscle have t-tubule on Z-line
What is dyad (cardaiac muscle) made of?
T-tubule + sacroplasmic reticulum

What surrounds pericardial cavity?
Pericardium (visceral pericardium)
Parietal pericardium

What is an organelle that is excessively present in cardiac muscle?
Mitochondria

What are four types of muscle cells in heart?
Contractile cardicytes (myocardiocytes) = contraction
Purkinje fibers (modified myocardiocytes) = found deep to endocardium lining the interventricular septum; impulse conducting;
Myoendocrine cardiocytes = producing atrial natriuretic factor
Nodal cardiocytes = control the rhytmic contraction; found in SA and AV node; found deep to endocardium of the interatrial and interventricular septa

How Purkinje fibers can be distinguished from other muscle cells?
Location (deep to endocardium)
Size (larger)
Staining (lighter because of glycogen content)
Cardiac tamponade
Pericardial sac effusion
Unique cardiomyocytes that can be seen on microscope
Purkinje fibers
Myoendocribe cardiocytes

How cardiac muscle cells are connected?
Vertical (transverse): fascia (longer strip that goes between cells; wider) adherens and desmosomes
Horizontal (longitudinal): gap junctions.

What is syncytium?
What allows cardiac muscle to act as syncytium?
Syncytium is a multinucleated cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells, in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis.
Can because of : fascia adherens, desmosomes and gap junctions
Cardiac muscle cells exhibit spontaneous rhythmic contraction
What does this contraction depends on?
What regulates it?
Dependent upon gap junctions
autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulation
Smooth Muscle characteristics
elongated fusiform cell appearance (relaxed)
one nucleus / centrally located
no striations
Cytoplasmic dense bodies serve as Z lines
Possess caveolae and some SER but not T system
Gap junctions in single-unit smooth muscle
External basal lamina around each cell
Involuntary contraction initiated by several modalities one being the ANS

What is the function of caveolae?
Aid in Ca+2 uptake and release.

Different types of smooth muscle
Single unit (conntected by gap junction - syncytium; cannot contract independently of one another; found in the wall of hallow visceras)
Multi-Unit (has its own nerve supply and can contract independetly of one another; en passant)
Vascular (mix of single and muti unit)
Examples of single and mulit unit muscle cells
SU: intestine, uterus, ureters
MU: iris
En passant ??
(smooth muscle)
axonal swellings containing synaptic vesciles
Heart / Thorax 1

- Mediastinal part of parietal pleura
- Axillary vein
- Horizontal fissure
- Inferior lobe, right lung
- Diaphragmatic part of parietal pleura
- Fibrous pericardium
- Musculophrenic artery and vein
- Inferior lob, left lung
- Left oblique fissure
- Cardiac notch
- Costal part of parietal pleura
- Internal thoracic artery and vein

Two potential spaces around lungs
Costomediastinal recess
Costodiaphragmatic recess
Mediastinum
An undelineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. It contains the heart, the great vessels of the heart, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic nerve, the cardiac nerve, the** thoracic duct**, the thymus, and the lymph nodes of the central chest.
Heart / Thorax 2

- Esophagus
- T-9 Vertebra
- Thoracic aorta
- Mediastinal part of parietal pleura
- Left phrenic serve, left pericardiacophrenic artery and vein
- Pericardium
- Central tendom of diaphragm, middle leaflet covered by pericardium
- Right costomediastinal recess
- Inferior vena cava

Superior mediastinum components
Roots of great vessels
Esophagus
Trachea
Vagal, phrenic, and cardiac nerves

Inferior mediastinum
(anterior portion) branches of the interal thoracic artery and some thymus in children
(middle) heart and ascending aorta and SVC“everything in the pericardial sac”
(posterior) all other vessels, nerves and visceral structures anterior to vertebrae and between the parietal pleura of both lungs
Heart / Thorax 3

- Thymic remanant
- Internal thoracic artery
- Rib 1
- Left phernic nerve, left pericardiacophrenic artery
- Costal part of parietal pleura
- Fibrous pericardium
- Line of fusion of fibrous pericardium to diaphragm
- Superior epigastric artery
- Musculophrenic artery
- Line of fusion for fibrous pericardium with superior vena cava
- Right axillary artery and vein
- Right internal thoracic vein

Heart / Thorax 4

- Left Vagus
- Left subclavian
- Left axillary artery
- Left brachiocephalic vein
- Costal part of parietal pleura
- Left costocdiaphragmatic recess
- Fibrous pericardium
- Right and left phrenic nerves
- Right costodiaphragmatic recess
- Mediastinal part of parietal pleura
- Superior vena cava
- Arch of aorta
- Right brachiocephalic vein
- Right vagus nerve

Heart / Thorax 5

- Left brachiocephalic vein
- Ligamentum arteriosum and left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Left vagus nerve
- Mediastinal part of parietal pleura
- Transverse pericardial sinus
- Fibrous and parietal serous pericardium
- Left ventricle
- Auricle of left atrium
- Right ventricle
- Right atrium
- Auricle of right atrium
- Ascending aorta
- Pericardial reflections
- Superior vena cava
- Right brachiocephalic vein
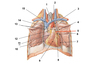
Heart / Thorax 6

- Ligamentum arteriousm
- Transverse pericardiac sinus
- Left superior and inferior pulmonary veins
- Oblique pericardial sinus
- Parietal layer of serous pericardium (fused to fibrous)
- Inferior vena cava
- Middle cardiac vein
- Coronary sinus
- Superior vena cava

Heart / Thorax 7

- Left vagus nerve
- Pulmonary trunk
- Transverse pericardial sinus
- Left phernic nerve and pericardiacophrenic artery and vein
- Left inferior pulmonary vein
- Parietal layer of serous pericardium
- Fibrous pericardium
- Inferior vena cava
- Right superior pulmonary vein
- Superior vena cava
- Ascending aorta
- Ligamentum arteriosum
- Left recurrent laryngeal nerve

Heart 1

- Brachiocephalic artery (trunk)
- Right atrium
- Inferior vena cava
- Coronary sinus
- Pulmonary veins
- Auricle of left atrium
- Right and left pulmonary arteries
- Left subclavian
- Left common caroitd

Heart 2

- Left coronary artery
- Cricumflex artery
- Left marginal artery (obtuse)
- Great cardiac vein
- Anterior interventricular artery (Left anterior descending, LAD)
- Right marginal artery (acute)
- Small cardiac vein
- Right coronary artery
- Atrial branch of right coronary artery
- SA artery

Heart 3

- Sinuatrial node artery
- SA Node
- Small cardiac vein
- Right coronary artery
- Middle cardiac vein
- Right marginal artery
- Posterior interventricular artery (posterior descrnding)
- Left marginal artery
- Coronary sinus
- Great cardiac vein
- Circumflex artery

Heart 4

- Ascending aorta
- Auricle of right atrium
- Crista terminalis
- Pectinate muscles
- Septal cuscp of tricuspid valve
- Ostium and valve of coronary sinus
- Inferior vena cava
- Fossa ovalis
- Limbus of fossa ovalis
- Interatrial septum
- Superior and inferior right pulmonary veins
- Right pulmonary artery
- Superior vena cava

Heart 5

- Pumonary trunk
- Auricle of left atrium
- Pulmonary valve
- Conus arteriosus
- Supraventricular crest
- Papillary muscles (septal)
- Papillary muscles (anterior)
- Papillary muscles (posterior)
- Septomarginal trabecula
- Trabeculae carneae
- Chordae tendineae
- Tricuspid valve (posterior cusp)
- Tricuspid valve (septal cusp)
- Tricuspid valve (anterior)
- Ascending aorta

Heart 6

- Ligamentum arteriosum
- Coronary sinus
- Inferior vena cava
- Cordinae tendineae
- Trabeculae carneae
- Papillary muscles (anterior/posterior)
- Epicardium
- Endocardium
- Myocardium
- Bicuspid valve (anterior)
- Bicuspid valve (posterior)
- Pulmonary trunk
- Auricle of left atrium
- Arhc of aorta

Heart 7

- Aortic valve (left, right, and posterior cusp)
- Right coronary artery
- Tricuspid valve (anteior, septal, and posterior cusp)
- Atrioventricular nodal artery
- Posterior intraventricular artery
- Middle cardiac vein
- Left and right fibrous trigones
- Bicuspid valve (anterior and posterior cusp)
- Circumflex artery
- Left coronary artery
- Pulmonary valve (left,right, and anterior?)

Heart 8 Aortic Valve

- Ostium of left coronary artery
- Mitral valve anterior cusp
- Interventricular septum muscular part
- Interventricular septum membranous part
- Nodule
- Ostium of right coronary artery
- Sinuses of aortic valve

Heart 9 Tricuspid

- Tricuspid valve (septal, anterior, and posterior)
- Chordae tendineae
- Papillary muscle (posteior)
- Papillary muscle (posteior, septal, and anterior)
- Interventricular septum membranous part
- Ostium of coronary sinus
- Ostium of inferior vena cava

Heart 10
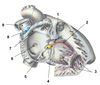
- Left bundle
- Right bundle
- Subendocrinal (Purkinje) fibers
- Atrioventricular bundle (of His)
- Atrioventricular node
- Fossa ovalis
- Crista terminalis
- Sinu-atrial (SA) node
- Superior vena cava

Heart / Thorax 8

- Cervical cardiac vagal branches
- Left vagus nerve
- Thoracic cardiac vagal branches
- Left recurrent largyngeal nerve
- Cardiac plexus
- Thoracic sympathetic cardiac branches
- Sympathetic chain ganglion
- Cervical symapthetic cardiac branches

Aortic valve stenosis
What happens during it?
Would be treated immediately?
What this might result in?
Opening of the aortic valve is narrowed
Heart hypertrophy to compensate
No because heart is getting stroned
Heart failure
What are the components of innate immunity?
Epithelia (physical barrier)
Phagocytic cells (macrophages and neutrophils)
Natrual killer cells
Blood proteins: complement system
What are the components of adaptive immunity?
B cells and plasma cells – humoral immunity (antibody mediated)
T cells - cell-mediated immunity (cellular immunity)
3 types of Lymphocytes and their function
B cells - respond to cell free and plasma membrane bound antigens
T cells - respond to cell-bound antigens
Natural killer cells - non-specific production of perforins and granzymes
What is a difference between T cells and NK cells?
NK cells:
lack T cell recepotr (TCR)
lack CD4 and CD8
do not enter thymus to become immunocompetent
What are accessory cells of immune system?
Their function?
Macrophages (APC or phagocytic)
Dendritic cells (fibroblast-like cells forming the stroma of lymphatic tissue)
Epithelial reticular cells - found exclusively in the thymus
APCs (express MHCI & MHCII; present antigen; produce cytokines)
* many APCs belong to mononuclear phagocytic system
T cells
Where do they originate?
Where do they become immunocompetent?
Where they can be easily found?
What “test” do they need to pass?
Bone marrow
Thymus
Paracortical regions of the lymph nodes & Periarterial sheaths of the spleen (vasculature)
Ability to differentiate between self and antigen
What is Naive T cell?
Immunocompetent T cell that must be activated
2 types of mature T cells
Memory T cells
Effector T cells
Three types of effector T cells
T helper cells (recognition of foreign antigens)
Cytotoxic T Cells (responsible for killing foreign cells, tumor cells, and and virus infected cells)
Suppressor T cells (suppresses the immune response of other T lymphocytes)
B cells
General function?
Origin?
In order to become plasma cells what cell they need to interact?
When do B cells proliferate and differentiate?
Are they found in all lymphoid tissue?
Humoral immunity
Bone marrow
T-helper
When they encouter antigen
In all except thymus (very little)
B cells
Types?
Function?
Where B memory cells are found?
Plasma cells (clock face): synthesize / secrete Ab; responsible for primaryresponse
B Memory cells: responsible for secondary response
Mante layer of lymph node
What is important about IgG and IgA?
IgG is most abundant in serum, fetal aquired immunity
IgA most abundant in glandular secretions (digestive, respiratory, and integument)
What is the name of the protein that is attached to IgA and prevents them from degradation in mucosal linings?
J protein
Stroma vs. Parenchyma
Stroma
supportive tissue = connective tissue fiber e.g. reticular fibers in lymph node; could be also dendritic cells; epithelial-reticular cell, but all have tight junctions
Parenchyma
functional unit = sits in the stroma = T, B, Ma, hepatocyte (liver)
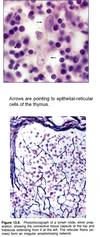
Lymphocytes undergo ____ differentiation in the primary lymphatic organs
Lymphocytes undergo ____ activation in the secondary lymphatic organs
antigen-independent
antigen-dependent
Lymphatic System
Concentrate and eliminate antigens
Production and maturation of lymphocytes
Addition of antibodies
Provides a means for returning tissue fluid
Absorption of chylomicrons from the small intestine
Lymphoid Organs
Primary?
Secondary?
PRIMARY
Bone marrow
Fetal liver
Thymus
SECONDARY
Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue
Tonsils
Lymph nodes
Spleen
What cells/componets (4) are usually found in lymphoid organs?
Reticular fibers
Dendritic cells (APC)
Macrophages (APC/phagocytic)
Lymphatic vessels
What captures antigens in intestinal walls?
What are these cells are adjacent to?
What layer are lymphocytes located in?
M cells (mucosa/microfold)
Peyer’s patches
Lamina propia
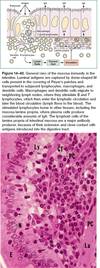
What is lymphatic nodule
Examples?
Primary composition?
Is it pernament?
Connective tissue (capsule)?
basic structural unit of diffuse lymphatic tissue
tonsils, lymph nodes, spleen ,GALT (gut associated lymphatic tissue), B (bronchus) ALT and M (mucosa) ALT
B cells, lymphoblasts, plasma cells, memory cells
Not always pernament; can be transitory

Types of lymphatic nodules (differentiation stage)
Color?
primary nodule = one that has not seen antigen
secondary = one with a germinal center in response to antigen
(light cells inside that undergo mitosis – lymphoblasts)

Are there germline centers in fetus?
No, there are none because fetus has not seen any antigen.
Waldeyer’s Ring
Anatomical term collectively describing the annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx





































