waves Flashcards
(38 cards)
what do waves have?
1) Wavelength (lambda sign) is the distance from one peak to the next.
2) frequency(f) is how many complete waves there are per second(passing a certain point) it is measured in hertz(Hz). 1Hz is 1 wave per second.
3) Amplitude is the height of the wave (from rest /equilibrium to crest)
4) the speed (v, for velocity)is , well , how fast the wave goes.
5) The period (T) is the time it takes (in seconds) for one complete wave to pass a point.

Equation for wave frequency?
Frequency (f) = 1 .
time period
Equation for wave speed?
Wave speed = frequency x wavelength
(m/s) (Hz) (m)
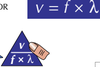
What is a transverse wave?
Most waves are transverse waves.
In transverse waves the vibrations are at 90 degree to the direction energy is transferred by the wave
1) light and all other EM waves
2) a slinky wiggled up and down
3) waves on strings
4) ripples on water

What is a longitudinal wave?
A wave where vibrations occur parallel to the direction the wave is travelling

example of longitudinal waves?
1) sounds waves
2) ultra sound
3) shock waves e.g sesmic waves
4) a slinky spring, when you push the waves
what do you waves tranfer?
energy and information but not matter
give an example of wave transfering energy?
all waves carry and transfer energy in the direction they are traveling.
eg microwaves in the oven that makes things warm up - their energy is transferred to food you’re cooking.
sound waves can things vibrate or move, e.g loud bangs can start avalanches
give an example of wave transfering information?
Waves can also be used as signals to transfer information from one place to another — e.g. light in optical fibres, or radio waves travelling through the air.
What is Wavefronts?
Two or more waves moving together in same direction have wavefronts
A horizontal line drawn linking all the peaks in a set of waves
Wavefronts are imaginary planes that cut across all the waves, connecting the points on adjacent waves which are vibrating together.
The distance between each wavefront is equal to one wavelength, i.e. each wavefront is at the same point in the cycle.

What is the Doppler effect?
The change in frequency and wavelength caused by relative movement of the source of
wave or observer
Give an example of the Doppler effect in sound waves?
- When an ambulance goes past you the siren decreases in pitch
- This is because the wavelength of the sound waves increases
1) If a wave source is moving towards an observer, the frequency of the wave they observe will be higher and the wavelength will be shorter than the original wave emitted by the source.
2) If a wave source is moving away from an observer, the frequency of the wave they observe will be lower and the wavelength will be longer than the original wave emitted by the source.
3) This is because the wave’s speed is constant — if the source is moving, it ‘catches up’ to the waves in front of it. This causes the wavefronts to bunch up in front of the moving source and spread out behind it.

How many Electromagnetic(EM) wave are there?
there are 7 types of EM waves
name the 7 types of electromagnetics (EM) waves, from longest to shortest waveslenghts?
radio waves
microwaves
infra-red waves
visible light
ultra - violet
x-ray
gamma rays

what type of waves are EM
they are transverse waves
Do EM waves transfer energy?
yes they do
can EM waves be reflected and refracted?
yes they can
Do EM waves travel at the same speed?
they travel at the same speed through free space(a vacuum).
do the different colours of visible light have the same wave lenght?
no, red has the longest wave lenght and lowest frequency and violet has the shortest wave lenght and highest frequency.
what are radio waves mainly used for?
Radio waves are mainly used for communications
are radio waves shorter than 10 cm?
no, they are longer than 10cm
how long are long radio waves and how are they transmitted?
they are 1- 10km,
long radio waves can be transmitted a long way because long wave lengths are bent around the curved surface of the earth

how short are short radio waves and how are they transmitted?
about 10m - 100m.
short radio waves can transmitted long distance via a transmitter. Thats because they are reflected from the ionosphere(a layer of the earths atmosphere)







