Water Properties Flashcards
What are the 3 states of water?

Water is unique in that it is the only natural substance that is found in all three states at the temperatures normally found on earth.
Examples: Liquid, Solid, Gas

Why is the water molecule called polar?

A water molecule is made up of 2 hydrogens and 1 oxygen molecule. This molecule is neutral It is consedered “polar” due to the uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms
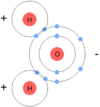
What are two different types of water “bonds”?

Water molecules tend to attrach each other making water kind of “sticky” or cohesive. The oxygen side of the molecule is slightly negative and the hydrogen side of the molecule is slightly postive.
Covalent bonds: Oxygen and hydrogen - very strong bonds
Hydrogen bonds: Water molecule to water molecule - weak bonds that allow water molecules to stick together or break apart.
Example: Surface tension

Why is water called the “Universal Solvent”?

- It is called the universal solvent because it dissolves more substances than any other liquid.
Example:
Salt and nutrients dissolve in water
Minerals dissolve in your blood.

What is cohesion?

Cohesion is when water molecules stick to “each other”.
Example: water molecules stick together to form a water drop

What is adhesion?

Adhesion is when water is attracted to another surface?
Example: A water drop attached to a plant leaf.
Water drops attached to mirror in your bathroom after a shower.

What is a mixture?

A mixture a material composed of two or more elements or compound that physically mix together but do not chemically combine.
Example:
A. Sediment will “mix” with water but will settle out and fall to the bottom - heaviest particles first
Sediment that stays suspended in the water can cause increased turbidity.
B. A salad is a mixture: tomatoes, cheese, lettuce and dressing. You can ‘mix” them together but they don’t change chemically.

What is a solution?

In a solution all components are evenly distrubuted thoughout
Example:
Sugar dissolved in water
Salt dissolved in water

What is a solute?

When mixing salt and water the “salt” is the solute.

What is a solvent?

When mixing water and salt the “water” is the solvent.
HINT: Water is the UNIVERSAL SOLVENT because it can dissolve more substances than anything else.

What is a suspension

A suspension occurs when the materials mixed to not dissolve but separate into pieces so small that they do not settle out. The movement of the water keeps the small particles suspended.
Example: Silt is a very fine partlcle that will stay suspeneded in water for a very long time. Large amounts of silt in the water will cause increased turbidity.

What is difference between an acid and a base?

The water molecule is made up of hdyrogen and oxgyen. The molecule can react to for “ions”.
H20 ————–> forms H+ and 0H - (hydroxide) ions
The more H+ ions in the water the more acidic it is
The more 0H- ions in the water the more basic it is

What is pH and why is it important?

pH is a measure of the hydrogen or hydroxide ions in a mixture. It tells you how acidic or basic a substance it.
The pH scale range is from 0 - 14
0 - 6 Acidic
8 - 14 Basic
7 - Neutral
IMPORTANCE:
Adult fish die at a pH of 3
Fish reproduction is affected at a pH of 4
Local waters have a pH of between 7 - 8. Our water tends to be slightly basic because of our geology (lots of limestone rock)

At what temperature does water freeze and boil?

Freezing
Fahrenheit: 32 degrees
Celsius: 0 degrees
Boiling
Fahrenheit: 212 degrees
Celsius: 100 degrees
Adjustments are made based on elevation
IMPORTANCE: Water is the one substance that can float in itself when it is a solid. This means that ICE floats in water. It floats because it is LESS dense. Ice floating on the surface of a the ocean or a lake acts like a thermal blanket and keeps water from freezing solid all the way to the bottom. This means water on the bottom of the ocean does not freeze and allows animals to survive.

What is specific heat?

Water had a high specific heat. That means it can absorb a lot of heat BEFORE it gets hot. It also means that once hot it cools down very slowing.
IMPORTANCE: This means it helps regulate the rate at which air temperature changes. This is why the temperature change between seasons is gradual rather than sudden near the oceans.
Over winter the ocean water temperature cools down so that in the late spring and early summer the water temperature is cooler even as the air temperature warms.
In the early fall, the air temperture starts to cool but the water temperature is still warm so the coastal areas stay warmer a little longer as the air temperature cool.
Image: The ballon is full of water. The water absorbs the heat which keeps the balloon from poping.

What is surface tension?

Water has a high surface tension because of cohesion. It is “sticky” and elastic and tends to clump together.
IMPORTANCE:
It allows aquatic insects to walk on the surface of the water.









