Viral classification Flashcards
What are the seven families of double stranded DNA viruses?
- Poxviridae
- Asfaviridae
- Iridoviridae
- Herpesviridae
- Adenoviridae
- Papillomaviridae
- Polyomaviridae
What are the two families of single stranded DNA viruses?
- Parvoviridae
- Circoviridae
What DS DNA viral family is complex-shaped (no symmetry), enveloped, and has linear DNA? Where do these replicate?
Poxviridae
Replicate in cytoplasm (“viroplasm”) and are released by budding
What are the two subfamilies of poxviridae? To which do vaccina virus (human/animal) and Orf virus (sheep/goats) belong?
-
Chodropoxvirinae
- Vaccina and Orf virus belong to this subfamily
-
Entomopoxvirinae
- infect insects
What virus family has members with DS linear DNA and an enveloped spherical structure with icosohedral symmetry?
What is the only genus within this family and what disease is the family named after?
Where does it replicate?
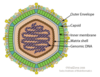
Family: Asfaviridae
Genus: Asfavirus
African Swine Fever virus (pigs)
Replication in cytoplasm and nucleus
What viral family, named after iridescence, has members with linear DS DNA, icosahedral symmetry and an envelope?

Iridoviridae

What are the three genera in the family Iridoviridae?
- Ranavirus (frogs)
- Lymphocystivirus
- Goldfish virus 1
What order contains three families, has DS, linear DNA, is enveloped, and has an icosahedrally symmetry nucleocapsid surrounded by tegument?

Herpesvirales

What are the three viral families in order Herpesvirales and what organisms does each family infect?
- Herpesviridae
- Herpesviruses of mammals, birds, and reptiles
- Alloherpesviridae
- Herpesviruses of fish and frogs
- Malacoherpesviridae
- Herpesviruses of oysters and Abalonies
What viral family has linear, DS DNA, is non-enveloped, and has icosahedral symmetry? What diseases is it responsible and what animals do they infect?

Adenoviridae
Human, equine & canine, avian, ovine, frog adenovirus
(Chicken) egg drop syndrome

What two families share the properties of having circular DS DNA, icosahedral symmetry, and being non-enveloped?
What common STD is in one of these families?

Papillomaviridae and Polyomaviridae
HPV - human papillomavirus

What viral family has members with linear negative or negative/positive sense SS DNA, that are non-enveloped, have icosahedral symmetry, and replicate in nucleus of cells in S phase of cell cycle?

Parvoviridae
What are the two subfamilies within family Parvoviridae and which infects mammalian hosts?
- Parvovirinae
- infects mammals, e.g. Feline & canine parvovirus
- Densovirinae
- no mammalian hosts, mainly insects

Which group of parvoviruses need co-infection with the other viruses like Adenoviruses for their replication?
Adeno-associate viruses (AAV)
What viral family has members with circular negative or negative/positive sense SS DNA, that are non-enveloped, have icosahedral symmetry, replicate in nucleus of cells in S phase of cell cycle, and are the smallest of all viruses?

Circoviridae



