Vascular Pathology I Flashcards
Ischaemia
deficiency of O2’d blood in a tissue causing impaired aerobic respiration and cell death
Hypoxia
deficiency of oxygen in tissues
Hypoxemia
deficiency of oxygen in blood
Infarct
area of necrosis caused by acute ischemia
Thrombus
clotted blood within the cardiovascular system
Embolus
intravascular solid, liquid, or gaseous mass carried in blood stream to some site remote from its origin (e.g. detached thrombus, CO2 poisoning in diving)
Atherosclerosis
- underlying disease of most CVD
- accumulation of lipid and fbirous CT = plaque
- intima of MEDIUM and LARGE ARTERIES
- caused by endothelial dysfunction and chronic inflammation
Risk factors for artherosclerosis include
- High blood lipids
- high BP
- smoking
- age
- sex
- genetics
- diabetes (diabetic dyslipidaemia: altered balance of HDL & LDL; smaller denser LDL)
- lipoproteins (genetics, diet) e.g. elevated LDL, VLDL
- obesity, metabolic syndrome
- proteinuria
What does dysfunctional endothelium lead to?
Increased permeability to LDL in blood
decreased production of NO (vasodilation) and prostacyclin (PGI2, inhibiton of platelet aggregation)
What are the 5 main classes of lipoproteins?
- chylomicrons
- very low density L
- LDL
- intermediate DL
- high DL
What happens when LDL enters the intima?
oxidized by ROS
trapped
inflammatory response
IL-8 –> macrophages
phagocytosed –> foam cells
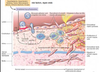


What is the consequence of media smooth muscle cells migrating to the intima?
(due to PDGF, TGF-b, cytokines from macrophages, etc.)
generates ECM inside the intima
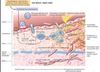
Where does lipid accumulate from in the plaque?
breakdown of foam cells
cholesterol from cell membranes (form cyrstals)

What contributes to increased disease risk (e.g. atherosclerosis, type II diabetes, hypertension, fatty liver disease) in metabolic syndrome?
cytokines and growth factors released from adipose tissue interfere with insulin signalling and BP regulation


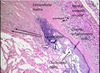

What cell type is this?

Foam cells: macrophages with foamy cytoplasm from phagocytosed LDL
What are 3 major complications of atherosclerosis?
Ischaemia
Infafction
Aneurysm
What is the mechanism by which atherosclerotic plaque leads to aneurysm?
- placque buildup in intima puts pressure on media, imparing O2 saturation (usually by lumen)
- media atrophies and weakens and dilates
- leads to aneurysm
- possible thrombus, thrombo-embolis formation, rupture
What atheroscleortic complication is this?

Fixed vessel narrowing (coronary artery)
Red circle denotes normal lumen size
H&E: fibrous placque (not as much lipid as L)
What are important sites of atherosclerosis?
- abdo aorta (AAAs most common)
- corontary arteries (lead to CVAs, infarcts)
- femoral arteries, popliteal
- kidnes (renal arteries)
- mesenteric arteries (small bowel)
What is the character of a true/fusiform anuerysm?
entire circumference of vessel wall is dilated
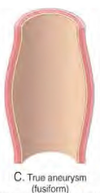
What type of aneurysm is this?
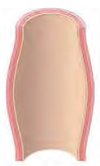
True/fusiform
complete circumferential dilation
What type of aneurysm is this?

True: saccular
unilateral/focal dilation
What is the character of a true/saccular aneurysm?
Focal/unilateral dilation

What type of aneurysm is this?

False
Occur when local bleeding from a vessel is contained intissues surrounding it; appears as dilation from exterior
What is the character of a false aneurysm?
appears dilated from exteriour
local vessel bleeding contained in pouch within surrounding tissue, not from within the vessel


- Dissection
- NOT aneurysms
- no ballooning/dilation
- blood bleeds into wall (intima into media)
- dissects along the wall, pushing them apart
- shredding of vessel walls
- usually aortic

Where are the primary sites for aneurysm?
vessels w/weakened media (arteries)
sometimes in the LV
What are the causes of aneurysms?
- atherosclerosis
- congenital media weakness (esp. berry/saccular in circle of Willis
- systemic hypertension causeing microaneurysms in cerebral arterioles
- infection of arterial wall (mycotic)
What is the most common region of the aortia affected by dissection?
Proximal ascending aorta
also can arise in descending
What is Marfan’s Syndrome?
Genetic abnormality of fibrillin, which is important in the formation of elastic tissue (e.g. in the aorta, tf predisposed to aneurysms)
What is the main risk factor for aneurysm?
Hypertension
Aneurysm
Weakened media due to thickened intima dilates and ruptures, causing an aneurysm
thrombus may form, which may embolise
Dissection
Blood bleeding into the vessel wall, from the intima bleeding into and along the media
Arteriosclerosis
- Thickening of the arteries
- +ECM deposition
- media elastic tissue degenerates
- fibrosis, loss of elasticity and dilation
- intimal fibrosis
- includes atherosclerosis and age related arterial changes
- arteriosclerosis can be in larger arteries (athero) or arterioles
What are age related arterial changes?
- arteriosclerosis of large arteries (atherosclerosis)
- intimal thickening of small arteries
- arteriosclerosis (arterioles)
- may cause slight +BP w/age
- changes to smaller vessels exacerbated by systemic hypertension
What is hyaline arteriosclerosis?
- age-related change
- occurs in arterioles
- normally, wall is 1-2 layers of SM
- wall is replaced with hyaline
- amorphous, proteinaceous, eosiniphilic staining on H&E

What is the mechanism of hyaline arteriosclerosis?
- endothelial stress over time leads to leaky enodothelium
- plasma proteins (albumin, fibrinogen) deposit into wall, some collagen by smooth muscle
- seen as amorphous pink material (protein, tf eosinophilic)
- narrows lumen (far right)
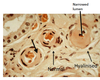
What are the risk factors and outcomes of hyaline arteriosclerosis?
- hypertension (as with atherosclerosis)
- in hypertension, greater risk of rupture
- stroke in brain
- retinal ischaemia or infarction, exudates –> vision problems
- chronic ischaemia in kidney, glomerular atrophy, kidney atrophy
What is the mechanism of arteriosclerosis?
- elastic media tissue of aorta and other elastic arteries degenerate with age
- fibrous deposition, collagen deposition in media
- -elasticity, -dilation
- +systolic pressure
- intimal fibrosis
- occurs in aorta and ateries, not arterioles
- does not narrow aorta
- -distensibility
What age related change is seen here?
What is each arrow?
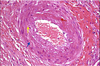
Intimal thickening
- blue arrow: media/smooth muscle cells w/long nuclei
- yellow arrow: internal elastic lamina, wavy band around intima
- red arrow: thickened intima with ECM
occurs in small, medium, large arteries and the aorta


