Upper limb COPY Flashcards
1
Q

A
Biceps brachii
2
Q

A
Brachialis
3
Q

A
Triceps brachii
4
Q

A
Anconeus
5
Q

A
Teres major
6
Q

A
Subscapularis
7
Q

A
Deltoid
8
Q

A
Coracobrachialis
9
Q

A
Supraspinatus
10
Q

A
Infraspinatus
11
Q

A
Teres minor
12
Q

A
Proximal phalanges
13
Q

A
Middle phalanges
14
Q

A
Distal phalanges
15
Q

A
Palmaris brevis
16
Q

A
Adductor pollicis
17
Q

A
Dorsal interossei
Abduction at the MCP joint
18
Q

A
Palmar interossei
Adduction at the MCP joint
19
Q

A
Lumbrical muscles
Flex at MCP joint and extend at IP joint

20
Q

A
Flexor retinaculum
21
Q

A
Pisiform
22
Q

A
Hook of hamate
23
Q

A
Metacarpal bones
24
Q

A
Trapezium
25

Trapezoid
26

Capitate
27

Lunate
28

Scaphoid
29

Hamate
30

Triquetral
31

Flexor digitorum profundus
32

Pronator quadratus
33

Pronator teres
34

Flexor carpi radialis
35

Palmaris longus
Absent in 15% of the population
Does not travel through the carpal tunnel so can see the tendon at the wrist when the thumb and pinky touch

36

Flexor digitorum superficialis
(there is a flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus. Profundus means deeper. The profundus flexes the distal interphalangeal joints)

37

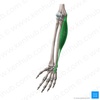
Flexor carpi ulnaris
38

Flexor pollicis longus

39

Brachioradialis
40

Extensor digiti minimi
41

Extensor indicis
42

Supinator
43

Extensor carpi ulnaris
44

Extensor digitorum
45

Extensor pollicis longus
46

Extensor pollicis brevis
47

Abductor pollicis longus
48

Extensor carpi radialis brevis
49

Extensor carpi radialis longus
50
What are the muscles in the superficial compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Palmaris longus
Flexor carpi radialis
Pronator teres

51
What are the muscles in the intermediate compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor digitorum superficialis

52
What are the muscles in the deep compartment of the anterior forearm?
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexor pollicis longus
Pronator quadratus
Allow you to clench your fist then pronate it like you're ready to punch someone.
Flexor digitorum profundus + flexor pollicis longus = clenching
Pronator quadratus = pronation

53
Which nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the upper arm?
**Musculocutaneous**
## Footnote
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Coracobrachialis
54
Which nerve innervates the posterior arm?
**Radial nerve**
## Footnote
(posterior extensors of the forearm and triceps)
55
What are the superficial muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm?

56
What are the deep muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm?

57
Which forearm muscles are innervated by the ulnar nerve?
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexor digitorum profundus (1/2 of it)
The ulnar nerve is sandwiched between these muscles
The rest of the anterior forearm is innervated by the medial nerve
58
Which hand muscles are innervated by the median nerve?
1/2 loaf
L - lateral **lumbricals** (1st and 2nd digit)
*+ the thenar muscles*
O - **opponens** **pollicis**
A - **adductor pollicis** **brevis**
F - **flexor pollicis** **brevis**

59
Which hand muscles are innervated by the median nerve?
Thenar muscles
Lateral two lumbricals
(the rest are innervated by the ulnar nerve)
60
What are the thenar muscles?
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
61
Which structures pass through the axilla?
Axillary artery
Axillary vein
Axillary lymph nodes
Brachial plexus
Biceps and coracobrachialis
62
What are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
Superior: imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus
Lateral: medial border of the brachioradialis
Medial: lateral border of the pronator teres
63
What are the contents of the cubital fossa? Medial to lateral
Median nerve
Brachial artery
Biceps tendon
Radial nerve (not always considered part of the cubital fossa)
(My Bulging Biceps Rock)

64
Label this diagram

(radial and ulnar are mixed up in this diagram)

65
Label this diagram
| (deep veins of the upper limb)


66
Label this diagram
| (superficial veins of the upper limb)


67
What does an upper brachial plexus injury look like and what nerve roots are affected?
C5/6
The affected limb hangs limply, medially rotated by the unopposed action of pectoralis major. The forearm is pronated due to the loss of biceps brachii. This is position is known as ‘waiter’s tip’, and is characteristic of Erb’s palsy.

68
Which nerve roots form the musculocutaneous nerve?
C5-7
69
Which nerve roots form the axillary nerve?
C5-6
70
Which nerve roots form the radial nerve?
C5-8
71
Which nerve roots form the median nerve?
C6-T1
72
Which nerve roots form the ulnar nerve?
C8-T1
73
Which nerve innervates the posterior arm?
Radial nerve


