Unit 2: Who Am I? Flashcards
Four Aspects of Being
- Physical
- Mental
- Emotional
- Spiritual

Influence of biology on thoughts, feelings and behavior?
Why and how we behave and think is a function of how the brain and body work.
Motivation
The internal state of an organism that drives it to behave in a certain way.
Emotions
Responses to an interaction between subjective feelings and an objective experience.
Social Perception
Process where someone infers other people’s motives/intentions from observing their behavior; deciding whether causes of behavior are internal or situational.
Attitudes
Long lasting patterns of feelings and beliefs about other people, ideas, or objects based in people’s experiences and shape future behavior.
Social Cognition
The thought process of making sense of events, people, oneself, and the world in general through analyzing and interpreting them.
Learning
An adaptive process where the tendency to perform a particular behavior is changed by experience.
Memories
Information encoded when stored, in forms dictated by people’s assumptions, attention, and schema.
Intelligence
The overall capacity of an individual to:
- Act purposefully
- To think rationally
- To deal effectively with the environment
Phineas Gage’s impact on psychology?

1) We learned that the frontal lobes of the brain enable us to control our emotions.
2) Damage to the frontal lobe part of the brain alters the way people express their emotions.
3) We learned that thoughts and emotions are closely related due to physical connections between the limbic system and other brain structures.
Developmental Psychology:
Continuous Change
Developmental change is gradual with achievements at one level building on the level coming before.
Developmental Psychology:
Discontinuous Change
Occurs in distinct stages or steps bringing about behavior assumed to be different from earlier stages.
Developmental Psychology:
Critical Period
A specific time during development when a particular event has its greatest consequences.
Developmental Psychology:
Life Span Approach vs Particular Period Focus
Focusing on the entire life span when studying an individual is important because developmental growth and change continues during every part of life. We need to understand the people who are largely providing those influences.
Developmental Psychology:
Nature
Genetic Influences
Developmental Psychology:
Nurture
Influences of the physical and social environment.
Sensory Organs
Sensory Organs Do All Of The Following:
- Detect stimuli
- Encode them into an electical impulse
- Transmit impulses to the brain via a nerve(s).
Aristotle’s 5 Senses
- Hearing
- Sight
- Smell
- Taste
- Touch
Senses Gather/Detect Information About?
Forms of Energy such as:
- Sound
- Light
- Heat
- Physical Pressure
Proprioceptors
Sense organs buried deep in the tissues of muscles, tendons and joints that give rise to sensations of weight, body position, and angle of joints.
Outside of Aristotle’s 5, Other Senses Include:
Balance
Hunger
Thirst
Fatigue
Pain
How do we hear?

How do we see?

How do we taste?

How do we sense touch?
Sensations
Messages from our sense organs
Perception
The process of using information and your understanding of the world.
Sensations vs Perceptions
Before something can be perceived it must be sensed.
Perception allows sensations to become meaningful experiences.
Perceptions influence thoughts, feelings and actions.
Subliminal Perception
Non-conscious processing
E.S.P.
Extra-Sensory Perception
Four Types:
Telepathy
Clairvoyance
Precognition
Psychokinesis
Telepathy
The transfer of thought from one person to another.
Clairvoyance
The ability to recognize objects or events that are not present to normal sensory receptors.
Example: Reading a message in a sealed envelope
Precognition
Unexplained knowledge about future events.
Psychokinesis
The ability to move objects using one’s mental powers.
Neuron
Nerve Cells
a.k.a. the conducting elements of the nervous system

Nerve Impulse
The electrical signal traveling between neurons.
4 Parts of A Neuron

- Cell Body - contains nucleus and other organelles
- Dendrites - short, highly branched fibers that receive impulses
- Axon - long, thin fiber carrying impulses away from the cell body towards other neurons
- Myelin Sheath - insulating protective covering of the axon that prevents shorting of impulses

How do neurons conduct nerve impulses?
The transmission of nerve impulses is a chemical process. The end of an axon is called the synaptic knob. Within the synaptic knob there are many small sacs called synaptic vesicles that contain special chemicals called neurotransmitters.
When the electrical impulse reaches the synaptic knob neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic gap. The diffusion of these chemicals across the gap allows the electrical impulse to be carried to the neighboring nerve cell by changing the permeability of its membrane. Usually, only the ends of axons release neurotransmitters. Therefore, impulses only travel in one direction across the synapse…from axons towards dendrites!

Neurotransmitter
A chemical designed to carry the electrical impulse across the synaptic gap while changing the permeability of the neighboring neuron’s cell membrane.
This allows the dendrites of the next neuron to receive the electrical impulse.
Adrenaline
A type of neurotransmitter affecting fight-or-flight stress response
Noradrenaline
A type of neurotransmitter affecting concentration
Seratonin
A type of neurotransmitter affecting mood control
Dopamine
A type of neurotransmitter affecting reward or pleasure
Endorphins
A type of neurotransmitter affecting our natural painkillers or euphoria
Gaba
A type of neurotransmitter affecting calming
Acetylcholine
A type of neurotransmitter affecting learning
Glutamate
A type of neurotransmitter affecting memory
Oxytocin
A type of neurotransmitter affecting bonding
Cerebrum

Responsible for intelligence and reasoning
Thalamus

Acts as a relay station for sensory information; conduct electrical impulses to and from the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus

- Plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis
- Regulates body temperature, blood sugar levels, and endocrine system
- Affects behaviours such as eating, drinking and sexual arousal
Limbic System

Interconnected structures responsible for emotions, memory, social behaviours and common brain disorders such as epilepsy
Corpus Callosum
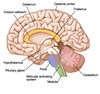
A thick band (200 million nerve fibres) that physically connects and conveys messages between cerebral hemispheres; damage to it results in 2 separate brains within one skull
Cortex

The exterior covering of the brain intricately involved in thought and reason; divided into areas or lobes with characteristic structures and functions
Midbrain

Interprets signals and relays information to forebrain and hindbrain areas; causes the body to act at once
Hindbrain/Reptilian Brain

The oldest part of the brain controls the body’s vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, body temperature and balance. Our reptilian brain includes the brainstem and the cerebellum.
Receives sensory information from the body, via the spinal cord, and other areas of the brain before causing the body to act in response. Responsible for all survival mechanisms - fight, flight, freeze, and reproduction.
Medulla

Dense, elongated bundle of fibres that maintain involuntary functions such as controlling heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing
Reticular Formation

Controls awareness of sensory information, muscle tone, cardiac and circulatory reflexes, and attention.
Pons

Affects sleep, dreaming, and respiration
Cerebellum

A large structure attached to the back of the brain stem responsible for balance, posture, coordination, movement, and single-joint actions; also involved in thinking operations including learning.


