Unit 2: Forelimb 1&2 Flashcards
in most species, the _____ cartilage increases the surface area for attachment of the rhomboideus m. and part of serratus ventralis m.
in most species, the scapular cartilage increases the surface area for attachment of the rhomboideus m. and part of serratus ventralis m.
in the horse, the _________ lies within the intertubercular groove of the humerus and stabilizes the biceps brachii m.
in the horse, the intermediate tubercle lies within the intertubercular groove of the humerus and stabilizes the biceps brachii m.
two heads of the deltoideus m. in the ox
- acromion head
- spinous head
in the horse, the thoracolumbar fascia continues cranially in the serratus ventralis m. as the ______
in the horse, the thoracolumbar fascia continues cranially in the serratus ventralis m. as the dorsoscapular ligament
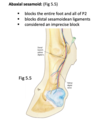
the ____ bursa is located over the caudal part of the greater tubercle of the humerus and doesnt communicate with the shoulder joint capsule
the infraspinatus bursa is located over the caudal part of the greater tubercle of the humerus and doesnt communicate with the shoulder joint capsule
the _____/_____ bursa protects the proximal tendon of the biceps brachii m. and is separate from the joint capsule of the shoulder.
the intertubercular/bicipital bursa protects the proximal tendon of the biceps brachii m. and is separate from the joint capsule of the shoulder.
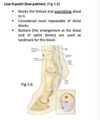
list the three attachments of the biceps brachii m. in the horse (1 proximal and 2 distal)
- supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
- radial tuberosity (on proximal, medial aspect of the radius)
- metacarpal tuberosity (on cranial, proximal surface of 3rd metacarpal bone)
______ is the long tendon of the biceps brachii m. and connects the fibrous core of the muscle to the CT of the extensor carpi radialis m.
lacertus fibrosus is the long tendon of the biceps brachii m. and connects the fibrous core of the muscle to the CT of the extensor carpi radialis m.
in the horse, the _____ is entirely fibrous and also called “the long part of the medial collateral ligament”
pronator teres
the ______ is the thick fibrous CT at the palmar aspect of the carpus that the carpal bones are embedded in. it prevents hyperexension.
palmar carpal ligament
____ are remnants of carpal and tarsal pads in the horse
chestnuts
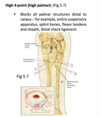
distal attachements of the superficial digital flexor m.
ox:
horse:
distal attachements of the superficial digital flexor m.
ox: P2 only
horse: distal P1 and proximal P2
attachements of the deep digital flexor m. in both ox and horse
P3
the ____ of the metacarpophalangeal (fetlock) joint acts as a bursa for the common digital extensor
dorsal pouch
____ is the remnant of the metacarpal pad in the horse
ergot