Unit 1 Flashcards
What major element determines cardiac contractivity?
Calcium
Dimensions of an adult heart
- 5 in long
- 3 1/2 inches wide
- 2 1/2 inches thick
- 250-350 g= 11 oz= about the size of the fist
Endocardium
Smooth layer of cells that lines the inside of the heart; allows for smooth flow of blood

Myocardium
Muscular middle layer; thickest layer of the heart
Pericardium
Double layered membrane that covers outside of the heart
Septum
Muscular wall that separates the left and right sides

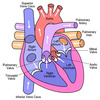
Right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body

Right ventricle
Receives blood from from right atrium and pumps blood into pulmonary artery

Left atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs

Left ventricle
Receives blood from left atrium and transports blood back to body through aorta

Tricuspid valve
Located between right atrium and ventricle; prevents blood from flowing back into right atrium
Possible causes of myocardial infarction
- smoking
- heavy meals
- CHF
- exercise
- anemia
- inadequate oxygen supply
- coronary artery narrowing (blockage)
- hypoxemia
Items needed to do an EKG
- Machine
- Electrodes
- Leads
- EKG paper
- patient gown
- alcohol wipes
- Shaving supplies
- patient’s chart
Sympathetic nervous system
Mobilizes fight or flight response
effects heart rate
Increases automaticity (ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit)
Parasympathetic
Has most influence on heart
sinus arrhythmia originates
inhibits automaticity
Location of the heart
Sits behind sternum and just above the diaphragm; lies mediastinum (space between the lungs) in the middle of the chest
2/3 of the heart lies left of midline of sternum
Precordium
Portion of the body over the heart and lower chest
Coronary Circulation
The system of circulation in which the heart gets its blood supply
Right coronary artery has a direct effect on what?
Heart rate; patients with right coronary artery occlusion (closure) and resulting inferior wall myocardial infarction may have bradycardia or various degree of heart block
Preload
Amount of muscle stretch at the beginning of a contraction
Afterload
The pressure against which it has to pump
Contractility
The force of the contraction
3 events that occur during cardiac cycle
Ventricular systole (contraction)
Ventricular diastole (relaxation)
Atrial systole (contraction)
SA node (Sino atrial node)

Acts as hearts natural pacemaker; located on right upper corner near anastamosis of superior and inferior vena cava
Frank Starling’s law
The greater the stretch of cardiac muscles, the stronger the contraction
Artifact
Disturbances in the EKG which can be caused by incorrect placement of lead or movements of patient
Systole
Contracting phase in which blood is expelled from the heart
Diastole
Relaxation phase is which the heart fills with blood


