UE2 Flashcards

- bicipital groove
- lateral epicondyle
- medial epicondyle
- radial (spiral) groove

- radial fossa
- capitulum
- trochlea
- coronoid fossa

olecranon fossa

trochlear notch

- proximal radual ulna joint (PRUJ)
- distal radial ulna joint (DRUJ)

- trohelar notch
- coronoid process
- tuberosity

radial notch of the ulna

- head of ulna
- styloid process of ulna

- radial head
- neck of radius
- radial tuberosity
- body
- interosseus membrane
- ulna

- radial head
- radial neck

- radial styloid
- dorsal tubercule of radius

Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle
- scaphoid
- lunate
- triquetrum
- pisiform
- trapezium
- trapezoid
- capitate
- hamate

- radiocarpal joint
- midcarpal joint
- carpalmetacarpal joint (CMC)

- base of MC
- metacarpal (MC)
- head of MC

- proximal phalanx of thumb
- distal phalanx of thumb
- proximal phalanx
- middle phalanx
- distal phalanx

- thumb CMC
- thumb MCP
- IP
- CMC
- MCP
- PIP
- DIP

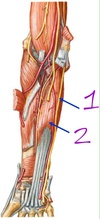
- olecranon fossa
- medial epicondyle
- olecranon
- radial head
- lateral epicondyle

- radial head
- radius
- ulna
- olecranon
- trochelar notch

cubital fossa
Define the cubital fossa
triangular hollow area - anterior elbow
What are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
- superior: imaginary line between med and lat epicondyles
- medial: pronator teres
- lateral: brachioradialis
What is the floor of the cubital fossa?
- brachialis
- supinator muscles
What is the roof of the cubital fossa?
fascia reinforced by bicipital aponeurosis
What can be palpated in the cubital fossa?
- brachial a.
- distal biceps tendon
- bicipital aponeurosis
- pronator teres
- brachioradialis
- median cubital v.
What forms the cubital tunnel?
- medial epicondyle
- tendinous arch of FCU
What is the content of the cubital tunnel?
- ulnar n.
- post. recurrent ulnar a.
What is cubital tunnel syndrome?
entrapment of cubital tunnel
**What is the only n. in the posterior elbow?**
(TEST QUESTION)
ulnar n.
What are the two compartments of the forearm?
- anteriomedial
- posteriolateral
What is contained in the anteriomedial compartment of the forearm?
flexors & pronators
What is the innervation of most muscles in the anteromedial forearm?
median n.
What is the innervation of 1 1/2 muscles in the anteromedial forearm?
ulnar n.
What does the posterolateral compartment contain?
extensors & supinators
What innervates ALL muscles of the posterolateral compartment of the forearm?
radial n.
What are the divisions of the forearm compartments?
- interosseus membrane
- subq border of ulna (posterior)
- radial a. (anterior)
What are the groups of muscles in the anteromedial forearm?
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
What muscles make up the superficial group?
- pronator teres
- flexor carpi radialis (FCR)
- palmaris longus
- flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU)
In general, what is the action of the anteromedial muscles?
- flex wrist
- pronate forearm
What muscles make up the intermediate layer of the anteriomedial compartment?
flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS)
What muscles make up the deep group of the anteriomedial compartment of the forearm?
- flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
- flexor pollicis longus (FPL)
- pronator quadratus
pronator teres
O/I
- O: med epicondyle & coronoid process
- I: mid lat radius
pronator teres
N
median n.
(passes b/t two heads of the muscle)
pronator teres
A
A: pronates & flexes forearm
FCR
O/I
O: med epicondyle
I: base of 2nd MC
FCR
N
N: median n.
FCR
A
A: flexes & radial deviates wrist
What lies immediatly lateral and medial to the FCR at the wrist?
- lateral: radial a.
- medial: median n.
palmaris longus
O/I
O: med epicondyle
I: palmar aponeurosis & distal 1/2 of flexor retinaculum
palmaris longus
N
N: median n.
palmaris longus
A
A: flexes wrist & tightens palmar aponeurosis
What is located lateral to palmaris longus at the wrist?
median n.
FCU
O/I
O: humeral head - medial epicondyle; ulnar head - olecranon process & posterior ulna
I: pisiform, hook of the hamate, & base of the 5th MC
FCU
N
ulnar n.
(passes between two heads)
FCU
A
A: flexes & ulnarly deviates wrist
What is immediatly lateral to FCU at the wrist?
ulnar n. & a.

- pronator teres
- FCR
- FCU
- palmaris longus
- FDS
FDS
O/I
O: humeroulnar head - medial epicondyle & coronoid process; radial head - superior 1/2 of ant. radius
I: middle phalnges of digits 2-4 (splits to let FDP pass to distal phalanx)
FDS
N
N: median n.
FDS
A
A: flexes PIP of digits 2-5; some wrist & MCP flexion
What structures pass through the two heads of FDS?
- median n.
- ulnar a.

- median n.
- FDS
FDP
O/I
O: proximal anterior ulna
I: base of distal phalanges on digits 2-5
FDP
N
N: lateral portion - AIN of median n.; medial portion - ulnar n.
FDP
A
A: DIP flexion of digits 2-5; also some wrist flexion

- AIN
- FDP
- ulnar n.
FPL
O/I
O: anterior radius
I: base of distal phalanx of thumb
FPL
N
N: AIN of median n.
FPL
A
A: IP flexion

FPL
pronator quadratus
O/I
O/I: distal 1/4 radius & ulna
pronator quadratus
N
N: AIN of median n.
pronator quadratus
A
A: pronates forearm

- AIN
- pronator quadratus

- pronator teres
- supinator
- pronator quadratus
In general, what do the muscles of the posterolateral compartment do?
- extend wrist/digits
- supinate forearm
- brachioradialis flexes elbow
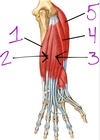
- extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
- extensor digiti minimi
- extensor digitorum
- extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB)
- extensor carpi radialis longus ( ECRL)

- EDS
- ECU
- extensor indicies
- extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
- extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
- abductor pollicis longus (APL)
- ECRB
- ECRL

brachioradialis

- brachioradialis
- ECRL
- ECRB

extensor indicies

- EPL
- extensor indicies
- EPB
- APL
What are the muscles that extend & deviate (both ulnar & radial) the wrist?
- ECRB
- ECRL
- ECU
What are the muscles that extend digits 2-5?
- extensor digitorum
- extensor indicies
- extensor digiti minimi
What are the muscles that either extend or abduct the thumb?
- APL
- EPB
- EPL
brachioradialis
O/I
O: lateral supracodylar ridge
I: lateral distal ulna
brachioradialis
N
N: radial n.