UE fractures- pictures Flashcards
The following shows which type of x-ray view in evaluation of which type of fx?
45 degree Cephalic tilt view
useful in evaluation of clavicle fx
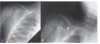
The following shows indication of what?

Surgical management of clavicular fx
(this shows tenting of the skin)
What is concerning about this x-ray image?

The fracture involves the distal 1/3, which is concerning. This fx requires surgical repair
What is the following X-ray showing?

This is a pathological fracture of the midshaft of the humerus.
The pic on the left shows a unicameral cyst (a weakened area of bone), which is how a midshaft fx is caused by FOOSH)

What type of fx is this and how would it be treated?

Midshaft humerus fracture
tx w/ surgery

What do the letters on the bottom pictures correspond to?

Letters= pediatric ossification centers
(#= age at which ossification center appears)
C- Capitellum (1)
R- Radial head (3)
I- Internal (medial) epicondyle (5)
T- Trochlea (7)
O- Olecranon (9)
E- External (lateral) epicondyle (11)- this is L in the picture
“CRITOE”
What does the following picture show?

Forearm compartment syndrome–> Volkmann’s Ischemia/contracture
(there will be pain w/ passive extension of the fingers)
What type of fracture? What is the Garland Classification of each?

Supracondylar fracture
A= Type I
B= Type II
C= Type III

What type of fracture and what is the Garland Classification

Supracondylar fracture
Type II
What type of fx and what is the Garland Classification?

Supracondylar fracture
Type I
What type of fx and what is the Garland Classification? What does this type of fracture mimic?

Supracondylar fracture
Type III
Mimics a posterior elbow dislocation

What type of fracture?
What is the management?

Supracondylar fracture

Non-surgical- Type I, Type II w/ reduction
Surgical- Type III, (Type II when reduction fails)
What type of fracture?
What “sign” is seen on this x-ray?
Other than AP and Lateral X-ray views, what other view should be obtained?

- Radial head fracture
- may be occult on initial x-rays–> look for fat pad sign
- Should also obtain oblique view

What type of fracture?

Radial head fracture
What type of fracture?
Stable or unstable?

Nightstick fracture (mid to distal ulnar shaft fracture)
Stable forearm fracture
What type of fracture?
Stable or unstable?

Both bone forearm fracture (radial and ulnar shaft fracture)
Unstable forearm fracture
What fracture? Stable or unstable? Management?

Monteggia fracture (ulna fx, radial head dislocation)
Unstable forearm fracture
Management- sx
What fracture? Stable or unstable? Management?

Galeazzi fracture (radius fx + carpoulnar dislocation)
Unstable forearm fracture
Management- Surgical
The following picture shows 2 different MOIs. Which fractures are associated w/ each?
What classic deformity is seen w/ each?

Left= Colle’s fracture (FOOSH w/ extension)–> dinner fork deformity
Right= Smith’s fracture (FOOSH w/ flexion)–> garden spade deformity

Which type of fracture is associated with the following deformity?

Colle’s fracture–> dinner fork deformity
Which type of fracture is associated with the following deformity?

Smith’s fracture–> Garden spade deformity
What type of fracture?
What other x-ray view should be obtained (other than AP and lateral)?

Colle’s fracture- dinner fork deformity
Should also obtain oblique view

What type of fracture?
What other x-ray view should be obtained (other than AP and lateral)?

Smith’s fracture (soft tissue swelling is unique to this)
Should obtain oblique view

What type of fracture? What population is this MC in?

Pediatric distal radial fracture–>
Radial torus (“Buckle”) fracture
MC in children <10
What type of fx? What is the MOI?

Radial Torus “Buckle” Fracture
MOI: FOOSH

What type of fx?

Radial Torus “Buckle” Fracture
What type of fx?

Greenstick fracture
What type of fx?

Radial Greenstick fracture

What type of fx?

Scaphoid fracture
What type of fracture?

Scaphoid fracture
(FYI: top right picture is called the “scaphoid view”)
What type of fracture?

Scaphoid fracture
The following x-ray depicts what type of complication for which fracture?

Scaphoid fracture- Avascular necrosis
List the type of fractures from left to right

a: transverse shaft fracture
b: oblique shaft fx
c: spiral shaft fx
d: metacarpal base fx
e: metacarpal head fx
f: comminuted fx
What type of fx? MOI?

5th metacarpal “Boxers” fracture
MOI: closed fist striking an object
What type of fx? What other x-ray views should also be obtained in addition to AP

5th Metacarpal “Boxers” Fracture
Should also obtain lateral and oblique view

What type of fx?

5th Metacarpal “Boxer’s” Fracture
What type of fx?

Boxer’s fracture
(right pic shows the head of 5th metacarpal displaced)
What type of fx?

Extension tendon avulsion fracture (“Mallet finger”)
What type of fx has the following MOI?

Flexor tendon avulsion fx–> “Jersey Finger”

What type of fx

Flexor Tendon Avulsion Fracture–> “Jersey Finger”
If a patient presents to your clinic w/ a subungual hematoma (shown in pic), why should you obtain an x-ray before drilling a hole in the nail to relase the blood?

to check for distal phalanx fx
The following picture shows the MOI of which fx?

Clavicular fx
MOI- direct fall on the shoulder w/ arm at side (MC)
direct blow
The following shows the MOI of which fracture?

Proximal humerus fx
MOI: fall onto an outstretched hand (MC)
75% occur in >60y/o w/ a simple fall (decreased bone density)
What type of fracture?

Midshaft humerus fracture


