TutorialsPoint.com Java Interview Questions Flashcards
(199 cards)
Five features of Java?
- Object Oriented
- Platform independent
- Robust
- Interpreted
- Multi-threaded
Why architectural neutral?
Compiler generates byte code which then can be interpreted by Java runtime
What do you know about Java?
- High level programming language originally developed by Sun Microsystems.
- Runs on many platforms such as Windows, Mac OS, Unix various OS
Supported platforms?
- Windows
- Mac OS
- Unix/Linux various versions
How Java enabled high performance?
Uses just-in-time compiler which is a program that turns Java byte code which is interpreted into instructions that can be sent directly to the processor.
Why Java is considered dynamic?
Designed to adapt to an evolving environment
What is Java Virtual Machine (JVM)?
- Java is compiled into platform independent byte code.
- The byte code is distributed over the web and interpreted by the Java Virtual Machine on the platform it is being run.
List two or three Java IDEs?
- Eclipse
- Netbeans
- IntelliJ
List some Java keywords unlike C, C++?
- Import
- Super
- Finally
Describe Object?
- A runtime entity in which it’s state is stored in fields and behavior is shown via methods.
- Methods operate on object’s internal state and serve as the primary mechanism for object-to-object communication.
Define class?
- A blue print from which individual objects are created.
- Contains fields and methods to describe the behavior of an object.
What kind of variables a class can consist of?
- Local variable
- Instance variables
- Class variables
What is a local variable?
- Variables defined inside methods, constructors, or blocks.
- Declared and initialized within method and destroyed when method completes.
What is an instance variable?
- Variable within a class but outside any method.
- Instantiated when class is loaded.
What is a class variable?
Declared within a class, outside any method, with the static keyword.
What is Singleton class?
Ensures that only one instance of a class is created.
Define Constructor?
- A special method which is invoked when a new object is created.
- Every class has a constructor.
- Java compiler builds default constructor when none explicitly found.
List three steps for creating an Object for a class?
- Declared
- Instantiated
- Initialized
Default value of byte data type?
0
Default value of float and double data type?
- 0.0f
- 0.0d
When byte data type is used?
Save space in large arrays, in place of integers, since 4 times smaller than int.
What is a static variable?
Class variable which is declared with static keyword in class, but outside a method, constructor, or block
Define Access Modifier?
Used to set access levels for classes, variables, methods, and constructors. Defaults to package access level.
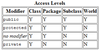
What is protected access modifier?
Variables, methods, and constructors declared protected in a superclass can be accessed only by:
- subclasses in other package
- any class within the package of the protected members’ class.





