Tumour Flashcards
Labs to order in multiple myeloma workup
Serum labs:
- Anemia
- increased Cr
- hypercalcemia
- ESR (increased)
- SPEP (M-spike)
Urine
- Proteinuria
- UPEP (Bence-JOnes protein)
What is a Bence-Jones protein?
Light chain immunoglobulin found in multiple myeloma
can be kappa or lambda light chain
UPEP will show monoclonal light chains
Lifetime risk of malignant transformation for solitary osteochondroma?
1%
Most common benign tumour of childhood?
NOF
Two important differences between Maffucis and Olliers?
Maffucis has hemangiomas
Maffucis has higher risk of secondary malignant transformation (100% vs. 30%)
Which type of liposarcoma does not require adjuvant radiotherapy?
Well differentiated liposarcoma
Can you do limb salvage in osteosarcoma in a patient with a pathologic fracture?
Yes
However increased rates of local recurrence and decreased survival overall in these patients
Adult Patient with osteochondrama has acute onset of pain at the location of lesion. What do you suspect?
Sarcomatous transformation
Treamtent for osteosclerotic myeloma
Chemo + radio+ plasmapheresis
Generally no surgery needed
(This is a form of MM associated with POEMS)
What is the multidrug resistance gene (MDR)
What percent of primaries is it found
hpow about METS
is it a poor or good prognostic indicator
Pumps chemo out of cancer cells
Present in 25% of primaries
50% of mets
Very poor prognostic indicator
What primary is very vascular, requiring embolization of lesions primary to ORIF?
RCC
Thyroid
What does GCT look like on MRI?
Dark on T1 and T2

List 4 types of surgical resection in terms of margins.
- intralesional (you cut into the tumor)
- marginal (you resect directly at the interface between tumor and normal tissue)
- wide (you resect the tumor with a cuff of normal tissue surrounding the tumor)
- radical (you resect the entire compartment from which the tumor arose)
Ddx for lytic lesion in greater than 40 year old
- Mets
- MM
- Lymphoma
- Metabolic (browns Tumor)
- Sarcoma
General treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma
En-bloc resection + adjuvant radiation
Diagnosis?

Melorheostosis
Periosteal formation of new bone
Looks like dripping candle wax
Benign but painful
Symptomatic treatment ± excision
Name these translocations!!
- t(2;13)
- t(11;22)
- t(X;18)
- t(12:16)
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma; t(2;13)
- Ewings Sarcoma; t(11;22)
- Synovial sarcoma; t(X;18)
- Myxoid liposarcoma; t(12:16)
Who gets Ewing’s sarcoma?
White males aged 10-20
What blood markers can be used to measure bone turnover?
ALP, LDH
What is stone man’s disease?
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Hallmarks:
- Progressive and EXTENSIVE heterotopic ossification (muscles, fascia, tendons, ligaments, joint capsules)
- Congenital malformation of the great toe
Mutation in ACVR1 gene (activin A type I receptor)

Enchondromatosis is characterized by:
A) multiple enchondromas, hemangiomas, lymphangiomas
B) multiple enchondromas in a unilateral distribution
C) auto-dominant transmission, multiple enchondromas and osteochondromas
C
Poor prognostic indicators in Multiple myeloma (9)
Renal failure (worst)
hypercalcemia
Stage
Type (plasmacytoma has best prognosis)
chromosome 13 deletion or translocation (t4;14), 4(14;16)
circulating plasma cells
increased beta 2 microgloblulin (indicates elevated tumor burden)
decreased serum albumin
increased marrow microvessels
Surveillance of soft-tissue & osteosarcoma?
(They are the same)
Physical exam, CXR, CT Chest
1-2 years: 3 months
3-5 years: 6 months
5-10 years: yearly
Common locations of ABC?
Femur > tibia > spine
What part of an osteochondroma is usually the site for secondary malignant transformation?
Cartilage cap
Name the tumours associated with NF1
Wilm’s tumour
Optic glioma - part of dx criteria
Neurofibroma
Neuofibrosarcoma
Astrocytoma
meningioma
melanoma
leukemia
rhabdoyosarcoma
pheochromocytoma
carcinoma
pancreatic endocrine tumors
Options for fixation of a met? (Be general)
- ORIF Plate with cement versus nail
- Arthroplasty
- Endoprosthesis
Describe FU for solitary enchondroma with no concerning features:
serial x-rays
q3-6 months for 1-2 years, then annually
What is the incidence of post radiation sarcoma in an area previously radiated to treat malignancy?
13%
(more common if also had chemo)
When do osteochondromas stop growing?
At skeletal maturity
Episyphyseal lesions?
Chondroblastoma, infection, GCT
Does thickness of cartilage cap have an associated with risk of sarcomatous change in osteochondroma?
If so, what is the limit?
Yes, but only in adults (skeletally mature)
In kids, it is an unreliable finding
>2cm is a risk for change to chondrosarcoma
What is the main dDx for intramuscular myxoma that you must rule out?
myxoid liposarcoma
True or false, lipomas can present with pain?
True
Angiolipoma often present as a painful mass
Name some negative prognostic characteristics of osteosarcoma.
- Poor response to Neo adjuvant chemo (% necrosis)
- Tumour size (> 8 cm is bad)
- Patient age (old is bad)
- Higher stage of Tumor
- Anatomical site (central is bad)
dDx for soft tissue sarcoma?
Soft-tissue sarcoma
hematoma
infection
±HO/MO if within a muscle
Chrondroblastomas are located where?
Epiphysis
Lifetime risk of malignant transformation for olliers?
30%
What are characteristics of a metastasis on X-ray?
Lytic
Permeative
Diaphysis/metadiaphysis
Proximal long bone or spine
Describe the Enneking system for classifying malignant tumours.
Three factors: Grade, site and metasteses
Grade is high or low
Site is intracompartmental (enclosed by natural barriers) or extracompartmental

Parosteal osteosarcoma with invasion into medullary cavity - what is the affect on prognosis?
No effect - still good prognosis
Name 2 scoring systems that may help you decide whether to operate on a pathologic spine tumour
Spinal instability neoplastic score
based on: location, pain, type of lesion, spinal alignment, vertebra body collapse, involvement of posterior elements
Score:
0-6: stable
7-12: impending instability
13-18: unstable
Modified Tokohashi Scoring system
based on: Karnofsky performance status, # of extraspinal bony mets, # of vertebral body mets, Mets to major organs, primary site of cancer, palsy
Score
0-8: <6 months life expecancy: conservative + palliative
9-11: life expectancy > 6 months: palliative surgery
12-15: life expectancy > 1 year. Excisional surgery
I think the principles of these scoring systems are imporant
JAAOS 2015
Dx & Treatment?

Parosteal osteosarcoma
These are usually low grade
Treat with Wide-resection only (usually curative)
Chemo generally not indicated unless there is a high grade component
Presentation of glomus Tumour
Triad:
- cold sensitivity
- point tenderness
- intermittent severe pain
Also may have a bluish-reddish hue
Occur in subungal region
X-rays will show a scalloped, osteolytic defect
Name the 5 subtypes of liposarcoma.
Well differentiated liposarcoma
Myxoid liposarcoma
Pleomorphic liposarcoma
Dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Mixed-type liposarcoma
What is the most common sarcoma in the foot?
Synovial sarcoma
Soft tissue tumours that mets via LN & to places other than lungs
SCREAM
Synovial sarcoma
Clear cell sarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Epitheliod sarcoma
Angiosarcoma
Myxoid liposarcoma
Name 2 sarcomas for which excisional bx can be performed
Parosteal osteosarcoma
low grade chondrosarcoma
*not sure I would say this on an exam
It’s from AAOS CORE2
What is a defining feature on histo for extra-articular desmoid tumour?
100% positive for estrogen receptor-beta
4 Options for treating PVNS (think techniques)
Arthroscopic synovectomy: best for focal disease
arthroscopic + open synovectomy (ie arthroscopic + open posterior knee approach)
Total joint arthroplasty + synovectomy
Total synovectomy + arthrodesis
± radiation - addition of radiation combined with total synovetomy reduces recurrence to 10-20%
Risks for post-radiation fracture
Female
Anterior femoral compartment resection
Age
Periosteal stripping
Radiation dose
osteoporosis
2 negative prognostic indicators of CMF
children
lobulated with abundant myxoid material
Football player suffered injury after helmet to groin hit. Residual non-tender mass.
Diagnosis?
Treatment?

Myositis ossificans
Non-operative - most resolve in a year or so
If recalcitrant, excise, but not before it matures (> 6 months)
Note x-ray: it calcifies from outside in, vs. tumour, which goes inside out
Olliers is characterized by:
A) multiple enchondromas, hemangiomas, lymphangiomas
B) multiple enchondromas in a unilateral distribution
C) auto-dominant transmission, multiple enchondromas and osteochondromas
B
What colour is bone matrix on staining?
Pink
What findings differentiate chondrosarcoma from a benign lesion?
1) myxoid matrix - may still have chondroid matrix, but generally the more myxoid the higher the grade
2) cortical thinning or thickening
3) soft tissue mass
4) invasion of haversian system
5 tumors that can have an associated ABC?
- giant cell tumor
- chondroblastoma
- fibrous dysplasia
- chondromyxoid fibroma
- NOF
Fallen leaf sign
what is it
what is it pathognomonic for?
Cortical fragment in the bottom of an empty cyst
UBC

4 associated conditions of NOF
Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome
Neurofibromatosis
Familial multifocal NOF
ABC
What is the treamtnet of low-grade intramedullary osteosarcoma?
Surgial resection only
This is the exception of the usual rule of chemo-sx-chemo for sarcoma
Components of local staging?
MRI to characterize lesion (of entire bone)
Biopsy (can do soft tissue mass)
Send for pathology and cultures
Adequate hemostasis
Good lesional tissue
Use pathology to prognosticate
Physical exam for metastasis with unknown origin must include?
Thyroid exam
Lung exam
Abdomen exam
Breast/prostate exam
Describe the bones in enchondromatosis?
Dysplastic
They are not normal and can have deformities
Young, thirsty kid with these findings.
Diagnosis?

Hans-Schuller-Christian disease (disseminated eosinophilic granuloma)
Classic triad:
Exophthalmos
Diabetes insipidus
Lytic skull lesions
What malignant tumour can secondarily arise from a bone infarct, Paget’s disease or prior radiation?
Malignant fibrous histiocytoma
(aka Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma)
What do you do following unplanned excision of soft tissue sarcoma?
Work up as normal
Local staging to look for extent of tumour bed and contamination
Systemic staging to look for mets
Definitive is re-resection of tumour bed and all associated contaminated compartments
Radiotherapy (controversial whether pre or post-op)
Tumour association with poly-vinyl chloride
Angiosarcoma
very aggressive vascular tumour
Overall prognosis for multiple myeloma?
What confers the worst prognosis?
Poor
Median survival 3 years from diagnosis
5 year survival: 30%
10 years survival: 10%
Shortest survival in patients with renal failure
Name 3 syndromes assocaited with Fibrous Dysplasia
McCune Albright
Mazabraud
Osteofibrous dysplasia
What sarcoma has flat epithelial cells on pathology?
Synovial sarcoma
What is radiation dose for HO prophylaxis?
6Gy
(vs. 45-60 for soft tissue sarcoma)
Genetics for myxoid liposarcoma
t(12;16)
Creates CHOP-TLS fusion protein
What physeal zone does osteochondroma/MHE stem from?
Proliferative
What Tumor stains for MIC2 antigen?
Ewing’s sarcoma.
This is how you differentiate it from other small round blue cell tumors.
What is the most common malignant bone tumour of the hand?
Chondrosarcoma
THINK: common to have enchondromas in hand, so one of them must transform
3 non-neoplastic things to consider adding on to the end of a ddx for bone lesion?
EG
Infection
Hyperparathyroidism (if older)
What is the recurrence rate of osteoid osteoma treated with percutaneous radiogrequency ablation?
10-15%
Describe Harington’s Criteria
>50% destruction of diaphyseal cortices
>50-75% destruction of metaphysis (>2.5cm)
Permeative destruction of the subtrochanteric fermoal region
persistent pain following irradiation
Treatment of osteofibrous dysplasia?
nonoperative - observation
bracing if deformity interfering with walking
OR if you need correction of deformity (osteotomy)
Cause of Paget’s
Thought to be a slow viral infection by paramyxovirus or RSV as most are spontaneous
There is a small group of heritable Paget’s also
What kind of matrix does ewings usually have?
None
Poor prognostic indicators for EG
involvement at young age
rapid disease progression
organ involvement (eg pituitary, lung, hematopoietic, or liver involvement);
*organ dysfunction carries an especially poor prognosis
Older than 40 , blastic lesion DDx (4)?
Metastases (prostate)
Bone island
Bone infarct
Osteoblastoma
Infection
Name two enchondroma syndromes.
- Olliers
- Maffuccis
Classic findings of Hans-Christian-Schuller Disease
Disseminated form of EG
Triad:
Skull lesions
diabetes insipidus (thirst)
Exopthalmos (double vision)
Osteolysis in tumour is caused by the action of what cytokine on what cell?
RANKL on osteoclastic cells (not on tumour cells)

Genetically, how does osteofibrous dysplasia differ than regular fibrous dysplasia?
It doesn’t have the Gs alpha activating mutation
Name the basic biopsy principles.
- Biopsy through (single) involved compartment
- Use extensile incision (usually longitudinal)
- Meticulous hemostasis
- Do not create multiple planes
- Bring out drains in line with incision (so the tunnel can be removed with definitive resection)
- should biopsy soft tissue component of bone tumour if possible
- round holes in bone, not square
- do not exanguinate before tourniquet
- avoid nv structures

Compare pre vs. post operative radiation for soft tissue sarcoma:
Pre/neoadjuvant RTx:
Lower dose
Lower field (b/c you haven’t contaminated it with surgery)
Lower rates of fibrosis
Also lower rates of edema and joint stiffness, but not statistically significant (Lower overall functional rates if they had fibrosis, edema and stiffness)
HOWEVER: higher risk of wound infection
Generally, neoadjuvant (pre) RTx is better, even tho wound complications are higher
SR2 study: know this data - it’s canadian
6 lesions on the posterior elements of spine
G: giant cell tumour (although most commonly in vertebral body)
O: osteoblastoma
T: tuberculosis
A: aneurysmal bone cyst (only one PURELY found posteriorly)
P: Paget disease
E: eosinophilic granuloma
GO TAPE
4 posterior element tumours
ABC
osteoid osteoma
osteoblastoma
osteochondroma
What systemic pathology (ie non ortho) do people with Paget’s disease get?
high output cardiac failure
due to increased turnover of bone
What percentage of vertebral body tumours are malignanet?
75%
What bone metasteses are not redio sensitive?
Which is the most readio-sensitive?
1) GI and Renal
2) Prostate
Classic spine finding in eosinophilic granuloma
Name 1 other classic finding
Vertebra plana aka platyspondia
Multiple punched out/lytic cranial lesions (ask for skull x-ray)

Which side of the spine in an osteoid osteoma normally found in?
Concavity of the spine
Histology of ewings sarcoma?
Small round blue cells
How do you classify UBC?
Active - in continuity with physis
Latent - bony bridge between UBC and physis
Most common location of mets in soft tissue sarcoma
Lungs
They can mets to LNs, but lungs are still most common
Survival rate of chondrosarcoma
Directly correlates with histological grade:
Grade 1: 90%
Grade 2: 60-70%
Grade 3: 30-50%
De-differentiated: 10%
What are the main steps in treatment of malignant bone tumour?
- Neo adjuvant chemotherapy
- Re-stage with imaging for response to therapy and operative planning
- Surgery - limb sparing vs. amputation
- Post-operative chemotherapy - use pathology to prognosticate
Treatment?

Chordoma
Wide resection is standard of care
± radiation if:
positive margins
inoperable tumour
What is the most common cause of painful scoliosis in the adolescent population?
osteoid osteoma
5 complications with treatment of UBC
recurrence
fracture
embolizatio of injected material
local reaction to injected material
growth disturbances
What kind of tumour results from malignant transformation of a chronic OM?
what is the treatment?
SCC
Treat with wide excision/amputation + adjuvant chemo/rads
Prognosis is poor with late diagnosis, good with early
Patient comes in post-MVC with a pathologic fracture through this. Dx as ABC. What is your plan?

Non-operative fracture management
Once healed, then proceed with intralesional curettage
Remember to treat path fractures non-op!
4 predisposing genetic factors for intramedullary osteosarcoma
Rb +
p53
Rothmund thomson syndrome
LiFraumeni syndrome
60 yo F with constitutional symptoms, pain palpable mass. (see picture)
Dx & treatment

Lymphoma
Treatment is surgical stabilization, chemo, radiation
*Lymphoma can have a soft tissue mass!
*lymphoma: small round blue cell
What do the terms onion skinning and sunburst refer to on radiographs? Which Tumors are each characteristic of?
Types of periosteal reaction
Onion skinning = ewings
Sunburst = osteosarcoma
Age range for GCT?
20-40
indications for excisional bx
superficial to fascia
Not overlying NV structure
excise AND LEAVE BEHIND FASCIA
“Pop corn densities” are useful in differentiating what secondary malignancy from its benign precursor?
Secondary chondrosarcoma from enchondroma.
What is the histo of periosteal osteosarcoma
osteoid + chondroblastic matrix
If no osteoid, will be classified as chondrosarcoma
What tumor shows predilection for the distribution shown in this figure?

Giant Cell Tumor
Desribe AJCC classification system
Soft soft tissue tumours:
See picture

Name 5 signs/symptoms that are concerning for chondrosarcoma, you know, that may be in a stem of a question
Deep Endosteal scalloping (>2/3)
Pain/progressive pain
Night symptoms/constitutional symptoms
Periosteal reaction
Soft tissue extension
Lysis of prior chondroid mineralization
Ddx for multiple giant cell containing lesions?
Multifocal GCT
Browns Tumor
Management of hypercalcemia
Fluids (200-300mL/hr initially, then maintaining u/o 100-150mL/hr)
Calcitonin
Bisphosphonates
Can use denosumab if refractory to bisphosphonates
LOOP DIURETICS ARE NOW NOT RECOMMENDED
dDx for Benign Latent Lesion (3)
Osteochondroma
NOF
Enchondroma
Treatment for suspected low-grade chondrosarcoma (instead of enchondroma)
intralesional curettage
Histopathology of GCT?
Multinucleated giant cells.
May see bone.
Mononuclear stromal cells
Where is the most common place for sarcomas to metastasize?
- Lungs
- Another bone
What is Denosumab?
RankL inhibitor.
This is a ligand for the Rank receptor and acts as a signal for bone removal.
Denosumab is an analogue and used in GCT tumours to prevent bone turnover.
General treatment approach for bone sarcoma?
- Neo adjuvant chemotherapy, multi-agent
- Re-stage with imaging to assess for interim progression/metastases and pre-op planning
- Wide resection
- Chemotherapy - use response to pre-op chemo to prognosticate (% necrosis of surgical pathology) and target therapy
Name & decribe the possible life threatening complication of hemangioma
Kasabach-Merrit syndrome
entrapped platelets in the hemangioma leading to a possible fatal coaguloapthy
Phases of Paget’s disease
Lytic: osteoclastic resorption
Mixed: resorption & compensatory bone formation
Sclerotic: bone formation predominates
All 3 may exist at same time so Paget’s can look lytic, mixed or sclerotic (like OM its a mimicker)
Differential for small round blue cells on histology?
Ewing’s sarcoma
Lymphoma
Osteomyelitis
Multiple myeloma
Histiocytosis
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Neuroblastoma
(LERN’M)
What tumor shows predilection for the distribution shown in this figure?

Osteoid Osteoma
What happens to NOF as the patient grown and reaches skeletal maturity
Migrate to diaphysis as patient grows AND GET LARGER
Will then usually self-resolve (become sclerotic and then go away) as the patient reaches skeletal maturity
Local Recurrence rate for well differentiated vs. high grade?
Well differentiated: 10%
High grade: 20%
Benign tumours that can metastasize to lungs (2)
GCT
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyseal Lesion with this biopsy.
Diagnosis?
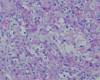
Clear cell chondrosarcoma
7yo M severe pain after ice skating.
How do you treat?

UBC (fallen leaf sign)
Weight bearing area
Treat with bone grafting and internal fixation
What is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in kids?
Rhabdomyosarcoma
On an exam, what tumour has codman’s, what has onionskinning?
Codman’s: osteosarc
Onion-skinning; Ewings
2 risk factors for malignant transformation of osteochondroma
Cartilage cap >2cm in adults (some say >0.9cm is a risk factor)
Sessile lesions
What primary cancer diagnosis is associated with the shortest life expectancy after pathologic fracture?
Lung cancer
Medical managmeent for fibrous dysplasia?
bisphosphonate
decreases pain and bone turnover
How do you differentiate between ABC/GCT vs. UBC on x-ray
UBC is not as expansile
It generally doesn’t go past the width of the physis
Which chondrosarcoma variant is typically epiphyseal?
Clear cell chondrosarcoma
Osteosarcoma: poor prognostic indicators:
Advanced stage of disease (most prognostic of survival)
Mets on presentation
Axial location/mets
Skip lesions
Poor response to chemotherapy (>98% necrosis is a GOOD sign)
Increased LDH and/or ALP
Tumour site & size
Expression of P-glycoprotein
Vascular involvement
Margins
Site & size of tumour
Type of sarcoma (parosteal better than intramedullar/conventional)
Imaging for metastasis with unknown origin?
Chest X-ray
X-ray of involved bone
Any painful extremities
Bone scan
If suspect myeloma, skeletal survey
Consider MRI of bone lesion
Ct chest/abdo/pelvis
What is a unique treatment option of neuroblastoma?
In young kids, nonoperatiave as they may spontaneously regress
4 extraosseous findings in fibrous dysplasia
cafe-au-lait spots
precocious puberty
intramuscular myxoma
Chereubism
Define the stages and survival for AJCC
IA
IVB
IA:
low grade
<8cm
No LN
No mets
5 year survival 98%
IVB:
Any tumour with mets to site other than lungs
5 year survival 30%
What tumor shows predilection for the distribution shown in this figure?

Ewings Sarcoma
What is the primary difference between sarcomas and carcinomas? (In terms of lineage)
Carcinomas = epithelial Sarcomas = mesemchymal
What is the most important factor for 5 year disease free survival in soft tissue sarcoma?
What happens if this is not achieved?
Size of operative margin
larger margin = better b/c it avoids microscopic contamination
If you have + margins, must take back for re-resection of tumour bed
What is the most common malignancy of bone?
What is the most common primary malignancy of bone?
What is the most common malignancy of bone?
Mets
What is the most common primary malignancy of bone?
myeloma
Describe Mirel’s score

What mutation is characteristic of fibrous dysphasia?
G-Protein mutation
Treamtent of leiomyosarcoma?
Surgical resection and CHEMO
Although effet is variable, some studies show better outcomes with surgical resection + chemo. No role for radiation except if you can’t get margins
This is one of the exceptions of regular ST sarcoma treamtent of surgery and radiation
Recall: synovial sarcoma may be respnsive to chemo also, but in that one you use RTx
Knee pain and this picture. Previous aspiration showed hematoma.
Diagnosis & management?

PVNS
clue: affects both sides of the joint and causes OA like destruction (cysts)
Debridement ± radiation
What % of plexiform neurifibroma’s transform into neurifibrosarcoma?
10%
Post-op radiation after prophylactic surgery for impending pathologic fracture has what 3 goals
Decrease pain
slow progression
treat remaining tumour burden not removed at surgery
Recurrence for PVNS?
30-50% - high
Therfore for treatment, may start with minimally invasive (arthorscopi) but make patient aware you may have to open later on
Diagnosis & treatment?

Synovial chondromatosis
(calcified stippling affecting both sides of joint)
Treatment:
Arthroscopic debridement (symptomatic treatment)
Why do you take out a retroperitoneal lipoma?
It has a higher chance of being a liposarcoma
Dosing side effects of wound healing post external beam radiation
<45 Gray: usually leads to uncompliated tissue healing
45-55 Gray: tissue heals but with problems
>60 Gray: tissue will likely not heal
Jaffe-Companacci syndrome
Congenital syndrome of:
multiple NOFs
cafe-au-lait pigmentation
mental retardation
heart, eyes, gonads involved
What tumour is associated with Dupuytrens, Ledderhose and Garrods?
What other inherited condition is it associated with?
Extra-abdominal desmoid tumour
familial adenomtaous polypsis (FAP)
Indications for non-excisional bx
>5cm
deep to fascia
surrounds NV structure and NOT a lipoma
overlies bone
Hx of “treated” carcinoma
unclear diagnosis
What are Birbeck granules diagnostic of?
Eosinophilic granuloma
You should embolize mets from which lesions?
RCC
Thyroid
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Local recurrence rate of chordoma?
50% (very high)
Proton-photon beams may help decrease this
Inheritance pattern of enchonromatosis (Ollier’s/Maffuci)?
No inheritance pattern
MHE is AD though
What primary bone malignancies are more likely in patients over 40?
Plasmocytoma (solitary myeloma)
Primary lymphoma of bone
Chondrosarcoma
MFH
Genearlly, what do soft tissue sarcomas look like on MRI?
Dark on T1
Bright on T2
Management of pathologic fracture through enchondroma?
Cast with delayed curettage until after healing
dDx for Benign Active lesion (6)
Fibrous dysplasia
UBC
EG
Osteoid osteoma
Chondroblastoma
Painful enchondroma
GCT location mainly?
Prox tibia, distal femur, proximal humerus, distal radius
I.e. Where a lot of growth occurs
Poor prognostic indicators for Ewing’s (5)
spine and pelvic tumors
tumors greater than 100cm3
< 90% necrosis with chemotherapy
elevated lactic dehydrogenase levels
p53 mutation in addition to t(11:22) translocation
Diagnosis & Treatment?

Schwannoma
Classic “String Sign” (Soap on a rope)
Marginal excision
Try not to damage nerve to preserve function
Best cure rate of SCC?
Moh’s microsurery
t(12;16)(q13;p11.2) (CHOP transcripton factor)
Myxoid liposarcoma
Treatment for solitary plasmacytoma
External beam irradiation alone
± surgical stabilization
What is the approach to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for pre-operative malignant bone tumour?
Multiagent chemotherapy:
- Methotrexate
- cisplatin
- Doxorubicin
- Ifosfamide
Most common complication of TKA & THA in Paget’s popuation?
TKA: malalignment
THA: excessive bleeding
Therefore, treat medically before elective hip/knee surgery to decrease bleeding risk
What is the most common subungla malignancy?
SCC
GNAS mutation is associate with what condition?
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
Mcune Albright syndrome
What percentage response to chemo is a good prognostic indicator?
>98%
Where do neurofibrosarcoma’s arise?
From a peripheral nerve or from a neurofibroma (malignant transformation)
What must you do to gain adequate margins when resecting a chordoma?
Sacrifice the nerve roots
You suspect soft tissue sarcoma but MRI is indeterminant.
Your core biopsy comes back as hematoma only
Next step?
Open biopsy
CANNOT resect this tumour if you suspect soft tissue sarcoma as many of the core’s come back as hematoma
Recurrence of chondrosarcoma is directly related to what?
Increased telomerase activity
In synovial chondromatsis, is the cartilage normal?
No - metaplastic
Benign bone lesion in spine is usually what?
Osteoblastoma
Does radiation have a role in treatment of Ewing’s sarcoma?
Yes, if wide resection is technically difficult or if a Tumor was inadequatly resected based on pathology
Synovial sarcoma is a misnomer. What percentage of these tumours actually arise is a major joint?
10%
At what age does metastases become more common than primary bone malignancy?
40
Diagnosis?

Chondroblastoma
classic:
chondroid matrix
epiphyseal crossing into metaphysis
lots of surrounding edema
dDx: clear cell chondrosarc
How can you differentiate schwannoma from neurofibroma on MRI?
Schwannoma is eccentric and separate from nerve.
Neurofibroma is central with the nerve runnign through it.
What is the most important factor in preventing local recurrence of a tumour?
adequacy of surgical margin
Treatmet for symptomatic, large NOFs
curettage & bone graft
This patient is having leg pain unresponsive to conservative mangaement.
Diagnosis?
Treatment?

Paget’s disease
Treatment with metaphyseal osteotomy with plate fixation
(Metaphyseal > diaphyseal, plate > IMN - Parvizi)
3 Manifestations of fibrous dysplasia
McCune Albright
Mazabraud
Osteofibrous dysplasia
Treatment of lymphoma
Multiagent chemotherapy ± local radiation
± surgical fixation for instability/pathologic fractures
Accuracy of core biopsy done in the office?
80%
What is the classification system for GCT?
Campanacci:
I: Intramedullary lesion confined to bone
II: Thinned, expanded lesion
III: Cortical breach
Name 3 reasons why prophylactic fixation is better than fixing an actual pathologic fracture
Shorter OR time
Less morbidity
Quicker recovery
You diagnose myxoid liposarcoma. How do you stage?
CT chest, abdo, pelvis
(not just CT chest)
Myxoid liposarcoma specifically has the tendency to spread to areas other than lungs
2 differentiating factors from myositis ossificans and tumour
Calcifies from outside - in (vs. tumour - inside out)
Intramuscular origin
What Tumor has characteristic fluid levels on MRI?
ABC
Most common site for bony mets
Most common site for pathologic fracture secondary to mets to bone
Most common site: thoracic spine
Most common site of pathologic fracture due to mets: proximal femur
Treatment algorithm for soft tissue sarcoma
Radiation + wide excision
Whether you do pre-vs. post op radiation is controversial with pros and cons
Risk of metasteses with Liposarcoma by grade?
- Low grade (well differentiated) =
- High (undifferentiated) = 50%
Cell type of synovial sarcoma
Usually biphasic with spindle cells (fibrous) & epithelial cells
NOT SYNOVIAL CELLS
Lifetime risk of malignant transformation for multiple hereditory exostosis?
10%
Name the radio-resistant tumours
(TUMOR)
Thyroid
Undifferentiated soft tissue tumour & chondrosarcoma (Except mesenchymal and dedifferentiated??)
Melanoma
Osteosarcoma
RCC
What is the most common solid tumour of childhood?
Is it malignant or benign?
Neuroblastoma
Malignant
Patient with RTC symptoms and solitary enchondroma found on imaging. Plan?
Treat mechanical symptoms of RTCT.
No need to treat incidentally found enchondromas as they normally have nothing to do with adjacent joint mechnical symptoms
If enchondroma is truly symptomatic, then intralesional curettage
Distal radius lytic lesion DDH? (4)
GCT
Abc
Chondrosarcoma
Telientatic osteosarcoma
Poor prognostic indicators in osteosarcoma (11)
advanced stage of disease (most predictive of survival)
response to chemotherapy (as judged by percent tumor necrosis of resected specimen)
- >98% is a good prognostic indicator, but doesn’t say what’s bad
tumor site and size
expression of P-glycoprotein
tumor cells can pump chemotherapy out of cell with MDR expression
present in 25% of primary lesions and 50% of metastatic lesions
high serum alkaline phosphatase
high lactic dehydrogenase
vascular involvement
surgical margins
type of chemotherapy regimen
Genetic translocation association with osteosarcoma?
None
no translocation
However it has associted mutations: p53, Rb
dDx for path with giant cells
GCT
ABC
telangiectatic osteosarcoma
conventional osteosarcoma
Metastatic Tumor that is blastic?
Prostate
A translocation of chromosome 11 and 22 resulting in a chimeric protein is characteristic of what Tumor?
Ewing’s sarcoma
Translocation results in EWS gene
You are working up a malignant looking tumor. It is bright on T2 with liquid, purulent looking gross pathology and no osteointegration matrix. what is it?
Ewing’s sarcoma
Synovial sarcoma treatment
Same as any other soft tissue sarcoma:
wide resection + radiation
Radiation can be pre or post op (controversial)
UNLIKE other ST sarcomas, chemo may help in synovial sarcoma in both local control and overall survival
What colour is chondroid matrix on staining?
Blue
You’re suspicious of multiple myeloma. How do you stage it?
Skeletal survey
NOT bone scan, b/c they will be cold in 30% (b/c it lacks osteoblastic activity)
What is the diagnostic criteria for MM?
requires one major and one minor (or three minor) criteria for diagnosis
major criteria
biopsy confirmation of plasmacytoma
>10% plasma cells on bone marrow biopsy
serum IgG > 3.5g/dL, IgA > 2g/dL
urine IgA > 1g/24hr or presence of Bence Jones proteins
minor criteria
10-30% plasma cells on bone marrow biopsy
serum or urine protein levels below those listed for major criteria
presence of multiple lytic bone lesions (“punched out” lesions without evidence of surrounding sclerosis)
decreased serum IgG levels
Recurrence rate of UBC
depends on treatment modality but generally up to 25-30% is reasonable
With steroids, some have reported recurrence up to 88%
(JAAOS 2014)
What benign tumour is characterized by fatty infiltration of sub synovial connective tissue?
Lipoma aborecens
What primaries metastasize to bone?
Lymphoma
Melanoma
Visceral carcinomas: Breast Prostate Lung Kidney Thyroid
Driving cell behind Paget’s?
ostoclasts
What primaries are most likely to present as metastasis with unknown origin?
Lung and kidney (because they are more likely to be occult)
How do you differentiate between ABC and telangiectatic osteosarcoma on MRI?
It’s hard - you can’t really
orthobullets says you need bx to truly differentiate
top: TO
Bottom: ABC

What part of bone does ewings usually occur?
Diaphysis
Most common tumour of hand?
enchondroma
What on histo is pathognomonic for Schwannoma?
Verocay bodies
Composed of 2 rows of aligned nuclei in a palisading formation

Preferred treatment of EG. Name 5 modalities
Salvage procedures
Nonop with treatment of mechanical symptoms preferred
- Obervation alone
- bracing (if amenable)
- Low dose radiation (for spinal lesions that cause neuro symptoms)
- Chemo (diffuse HSC)
- Corticosteroid injections
- Bisphosphonates
Operative if fails:
- Curettage and bone grafting for lesions endangering articular surface
- Spinal deformity correction
Dose for adjuvant radiation in soft-tissue sarcoma?
What are complications of 45 Gy vs 60Gy?
45-65Gy
45Gy: woudn has delayed healing
60Gy: wound not expected to heal
CD99
Ewing’s sarcoma
8 lesiosn that can be found in vertebral body
multiple myeloma (most common primary tumor of spine)
- chordoma
- osteosarcoma
- hemangioma
- giant cell tumor of bone: sacrum;
- eosinophilic granuloma
- osteosarcoma of the spine
- osteoid-osteoma and osteoblastoma of the spine
dDx for Benign aggressive lesion
Osteoblastoma
GCT
ABC
CMF
Chondroblastoma
±UBC
Long term survival of parosteal osteosarcoma when local contrl has been achieved
95%
What subtype of lipoma is painful?
AngioLipoma
Poor prognostic indicators in Ewing’s
male age >14
fever
anemia
high LDH
axial location
use of radiotherapy without surgery
poor histologic response to chemo
Transcription Type II (Survival benefit with transcription type I EWS/FLI1 mutation)
Poor response to chemo
No effect of pathologic fracture
Local recurrence not as poor prognostic factor as in osteosarcoma (“death sentence” if local recurrence in osteosarcoma)
Most common site of mets of osteosarcoma
Lung: most common
Another bone: second most common
Tumours that mets to bone
breast
lung
thyroid
renal
prostate
*all the paired organs
What are the three treatment facets of a MM bone lesion?
With a confirmed diagnosis, the treatment of multiple myeloma involves radiotherapy, bisphosphonates +/- surgical stabilization.
Surgical stabilization is utilized when there is a complete or impending fracture.
CD31 & polyvinyl chloride exposure is a risk for what?
ANgiosarcoma
rare
What is the local recurrence rate with ABC?
Name 1 adjunct that may help decrease local recurrence?
25% local recurrence
High speed burr
Phenol
Less common in older kids
Bloodwork for metastasis with unknown origin?
Spep/upep
CBC
Esr
Lytes
Liver enzymes
Psa
Alp
LDH
Survival of Chordoma?
60% 5 year survival
25% long term survival
local extension may be fatal
What kind of biopsy is contraindicated in chordoma?
transrectal
Maffuccis is characterized by:
A) multiple enchondromas, hemangiomas, lymphangiomas
B) multiple enchondromas in a unilateral distribution
C) auto-dominant transmission, multiple enchondromas and osteochondromas
A
What does it mean if a Tumor is biphasic?
It contains both epithelial and mesemchymal neoplastic cells
For ewings sarcoma, what blood markers should be added to the typical malignant work up and why?
CBC, esr and crp to differentiate it from osteomyelitis
In ewings esr will be up (but not crp?)
Indications for marginal resection of lipoma (4)
Symptomatic lesions
Rapidly growing mass
Deep to fascia or in retroperitoneum
Spindle cell & pleomorphic variants
What term is typically used to describe the following genes: p53 and RB-1
Tumor suppressor genes.
In terms of tumour location, what are apophyses treated like?
Epiphysis
THINK: locations for chondroblastoma (GT apophysis, calcaneal apophysis etc…)
3 dDx for anterior tibial liesion
osteofibrous dysplasia
adamantinoma
malignant fibrous histiocytoma
What tumor am I?
Estrogen Beta Positive
Locally invasive but benign
Can treat with Tamoxifen
Associated with FAP and Dupuytrens
Extra-Abdominal Desmoid Tumor
Lifetime risk of malignant transformation for solitary enchondroma?
1%
What is special about biphasic sarcomas in terms of metasteses?
They can go to lymph nodes, which is unusual for sarcomas.
Also they metastasize to locations other than the lungs.
Name 2 types of benign periepheral nerve sheath tumours
What’s the difference
Scwannoma: only made up of Schwan cells
Neurofibroma: Arises from Schwann cells but also has other cells (fibroblasts etc)
PVNS typically contains which pigment?
Hemosiderin deposits
Gene associated with primary ABC?
Tre2
3 Predictors of UNSUCCESSFUL treatment of UBC with steroids
active lesion
large size
multiloculated
Long standing chronic draining wounds or burn scar are at risk of what?
Transformation into SCC (Marjolin’s ulcer)
What Tumor is usually epiphyseal in skeletally immature with chicken wire calcifications?
Chondroblastoma
Also has mononuclear chondroblasts
Name 3 soft tissue tumours that chemo can help with:
Synovial sarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (only in paediatric population, not adults)
Common presentations in Chordoma?
bladder & bowel changes are common!
palpable on rectal exam
What staging investigation must you include in epitheliod sarcoma (and certain other soft tissue sacomas)
Sentinel LN biopsy
Li-Fraumeni syndrome:
what germ line mutation & tumour is it associated with
p53
osteosarcoma
also: breast, colon Ca
Name 4 vertebral body tumours
hemangioma
GCT
chordoma
multiple myeloma
Lymphoma
What is the most common benign radiation induced tumour of bone?
osteochondroma
Indications for bone marrow biopsy?
(i.e. what tumors necessitate this)
- Ewings
- Multiple Myeloma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
Patient is complaining of on and off pain, tenderness to palpation and cold intoleratnce. This is the clinical picture. Diagnosis & Management?

Glomus tumour
Classic triad
- paroxysmal pain
- exquisite tenderness to palpation
- Cold intolerance
Treatment: marginal resection is curative
Tretment of fibrous dysplasia?
Observation ± bisphosphonates: asymptomatic lesions
Operative with internal fixation and autologous bone graft (symptomatic)
What is unique in Ewing’s as part of staging?
Bone marrow biopsy
looks for BM mets that would change prognosis
Which primary has worst prognosis once mets are present in bone?
Lung
How do you differentiate between ABC and telangiectatic osteosarcoma?
Biopsy
Telengiectatic osteosarcoma is Slayers Sarcoma because it is Lakes of Blood

A 75-year-old man presents with a displaced femoral neck fracture. During your surgical exposure for a hemiarthroplasty, the femoral neck has fractured through a pathologic lesion which is diagnosed as a lymphoma on frozen section. The lesion is located in the center of the femoral neck and the calcar femorale is not involved. Your treatment should include
Hemiarthroplasty & postoperative staging and chemo-radiotherapy as needed
Lymphoma can be treated with chemo-rads for local and distant disease
If it was osteosarc: close and regular sarcoma protocol
SYT-SSX1, SYT-SSX2, or SYT-SSX4 translocation (t(X;18)(p11;q11))
Synovial sarcoma
Classic spine finding in EG?
vertebra plana
Couldn’t find a good picture but can be subtle - remember the SPORC case??
What is the risk of malignante transformation of fibrous dysplasia?
1%
into osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma or MFH
What is the usual indication for radiation therapy at the following doses?
a) 6 Gy
b) 30 Gy
c) 60 Gy
a) HO prophylaxis
b) Treatment of a boney Met
c) Adjuvant therapy for soft tissue sarcoma
Poor prognostic sign in neuroblastoma?
bony mets
Name 2 tumours affecting multiple vertebra
metastatic disease
multiple myeloma (remember may be cold on bone scan)
Benign aggressive looking lesion. Must rule out what malignancy?
Telangiectatic osteosarcoma
Enchondromas always central metaphyseal t/f?
True
Which sarcoma is radio/chemo resistant?
A) liposarcoma
B) osteosarcoma
C) chondrosarcoma
D) Ewing’s sarcoma
C) chondrosarcoma
What are the three biphasic sarcomas?
- Synovial sarcoma
- Angiosarcoma
- Mixed liposarcoma
UBC on MRI?
very Dark on T1
Very bright on T2

What percentage of UBCs heal after fracture?
10-15%
(JAAOS 2014 says
Which soft tissue tumour is relatively insensitive to both radiation and chemo?
Angiosarcoma
Man has radicular buttock pain
MRI shows large nerve lesion in sciatic
What is it likely?
Neurofibrosarcoma (malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour)
They affect large nerves
Must resect entire affected nerve
What type of nerve cells is responsible for the neurofibromas in NF1?
non-myelinating Schwann cells
(vs. myelinating in solitary neurofibromas)
What type of resection are you performing with PVNS
Marginal resection is what you’re aiming for
(with arthroscopic, probably doing intralesional)
Host lamellar bone entrapment is characteristic of what malignancy?
Chondrosarcoma
Best UBC lesions to pursue steroid injections
Predictors of success following UBC treated with steroids
approaching skeletal maturity
Not loculated
smaller size
Fracture of inner wall
(radiograhpically active - Can’t find a reference - probabyl a POOR sign though. This contrasts “approaching skeletal maturity”)
Most common presentation of chondroBLASTOMA
pain
Treatment for multiple myeloma
multiagent chemotherapy (mainstay)
bisphosphonates (helps reduce number of skeletal events)
Surgical stabilization
Orthopaedic Tumours that Spread to LN’s
Synovial Sarcoma
epitheliod sarcoma
angiosarcoma
rhabdomyosarcoma
clear cell sarcoma
Diagnosis & Treatment?

Adamantinoma
(NOT OFD b/c not confined to cortex - much more malignant. ALso associated with bowing)
Treatment: wide resection + reconstruction (intercalary graft)
Histologically, how do you differentiate ABC from telangiectatic osteosarcoma?
TO: lakes of blood filled mixed with neoplastic cells (top)
ABC: Cavernous blood filled spaces with no endothelial lining (bottom)

Describe Mazabraud syndrome
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
intramuscular myxoma
What is a Bence Jones Protein?
Light chain immonuglobulin found in multiple myeloma.
What kind of chondrosarc does enchondrama change into?
low grade chondrosarcoma
Lifetime risk of malignant transformation for Maffucis?
100%
Name the 3 manifestations of eosinophilic granuloma and their characteristics
Eosinophilic granuloma
- Single self-limited lesion in younger patients
Hand-Schuller-Christian disease (HSC)
- chronic, disseminated form with bone and visceral lesions
Letterer-Siwe Disease
- Fatal form that occurs in young kids
Can be Monoostotic or Polyostotic
What tumor shows predilection for the distribution shown in this figure?

Lymphoma
Recurrence rate of GCT of tendon sheath after marginal excision?
5-50%
Treatment for neurofibrosarcoma (malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour)?
What must you specifically do?
Wide resection
Must resect the entire affected nerve
Name the syndromes associted with the spectrum of Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Eosinophilic Granuloma
- Self-limited in younger patients
Hand-Schuller-Christian Disease
- Chronic, disseminated form
Lettere-Siwe Disease
- Fatal for in young kids
Do osteochondroma transform into high or low grade chondrosarcoma?
Low grade
Which primary can have mets distal to knee and elbow?
Lung
Name 1 poor prognostic factor for parosteal osteosarcoma
de-differentiation
Indicatios for surgical resection in osteoid osteoma
painful scoliosis
Too close to vital strucures for radiofrequency ablation (neural elements, skin)
NOF can be associated with what other tumour
ABC
In operative management of fibrous dysplasia, what should you never use
Autograft
It will rapidly be turned into fibrous dysplastic woven bone
Benign aggressive lesions? (3)
GCT, ABC, osteoblastoma
Seven questions for evaluating bone lesion on x-ray?
(as per Toronto group)
- where is it?
- how big is it?
- What is it doing to bone? (destructive? geographic? permeative?etc.)
- what is bone doing to it? (sclerosis? periosteal rxn?)
- matrix?
- cortex? (eroded? preserved? neocortex? endosteum?)
- soft tissue mass?
Which soft tissue sarcomas need chemo?
RSSD
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Synovial sarcoma
Soft-tissue Ewings
de-differentiated chondrosarc
HOWEVER THIS IS CONTROVERSIAL
SAFE ANSWER FOR TREATMENT OF SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA IS WIDE RESECTIO + RADIATION
Treatment of this pathologic fracture?

Sling for comfort
Nonop of pathologic fractures through UBC, unless they are in a weight bearing zone (proximal femur)
Which way do pedunculated osteochondraom lesions point?
Away from the joint
3 poor prognostic indicators for soft tissue sarcoma?
High grade
size >5cm
tumour location below deep fascia
how often is ABC associated with another tumour?
30% of the time
Synovial sarcoma genetics
t(X;18)
Forms SYT/SSX1 & SYT/SSX2 fusion transcripts
Medical treatment options in UBC
Bone graft (poor success with high recurrence rates)
Steroid
autologous bone marrow (controversial - may be better than steroids)
JAAOS 2014
Why must you follow chordoma patients long term post resection?
- High recurrence rate
- Mets occurs late in disease
Occurs in 30-50% to lung, rarely bone
Nonoperative mangement of Paget’s
When is it indicated
Bisphosphonates
Calcitonin
Indicated in sympomatic cases
asymptomatic you just treat supportively
What tumor shows predilection for the distribution shown in this figure?

Chondroblastoma
What extra-articular tumor has pathology similar to PVNS?
Giant cell tumor of tendon
What are the basic types of soft tissue sarcoma (think histo)
Synovial (sarcoma)
Lipo(sarcoma)
Rhabdomyo(sarcoma)
Fibro(sarcoma)
GCT histology?
Mononuclear cells with Uniformly distributed multinucleated giant cells


