Tree Terminology Flashcards
(24 cards)
Root
In a tree data structure, the first node is called as Root Node. Every tree must have a root node. We can say that the root node is the origin of the tree data structure. In any tree, there must be only one root node. We never have multiple root nodes in a tree.

Edge
In a tree data structure, the connecting link between any two nodes is called as EDGE. In a tree with ‘N’ number of nodes there will be a maximum of ‘N-1’ number of edges.
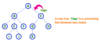
Parent
In a tree data structure, the node which is a predecessor of any node is called as PARENT NODE. In simple words, the node which has a branch from it to any other node is called a parent node. Parent node can also be defined as “The node which has child / children”.
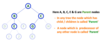
Child
In a tree data structure, the node which is descendant of any node is called as CHILD Node. In simple words, the node which has a link from its parent node is called as child node. In a tree, any parent node can have any number of child nodes. In a tree, all the nodes except root are child nodes.
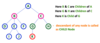
Siblings
In a tree data structure, nodes which belong to same Parent are called as SIBLINGS. In simple words, the nodes with the same parent are called Sibling nodes.
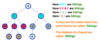
Leaf
In a tree data structure, the node which does not have a child is called as LEAF Node. In simple words, a leaf is a node with no child.
In a tree data structure, the leaf nodes are also called as External Nodes. External node is also a node with no child. In a tree, leaf node is also called as ‘Terminal’ node.
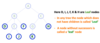
Internal Nodes
In a tree data structure, the node which has atleast one child is called as INTERNAL Node. In simple words, an internal node is a node with atleast one child.
In a tree data structure, nodes other than leaf nodes are called as Internal Nodes. The root node is also said to be Internal Node if the tree has more than one node. Internal nodes are also called as ‘Non-Terminal’ nodes.
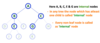
Degree
In a tree data structure, the total number of children of a node is called as DEGREE of that Node. In simple words, the Degree of a node is total number of children it has. The highest degree of a node among all the nodes in a tree is called as ‘Degree of Tree’
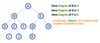
Level
In a tree data structure, the root node is said to be at Level 0 and the children of root node are at Level 1 and the children of the nodes which are at Level 1 will be at Level 2 and so on… In simple words, in a tree each step from top to bottom is called as a Level and the Level count starts with ‘0’ and incremented by one at each level (Step).
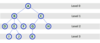
Height
In a tree data structure, the total number of edges from leaf node to a particular node in the longest path is called as HEIGHT of that Node. In a tree, height of the root node is said to be height of the tree. In a tree, height of all leaf nodes is ‘0’.
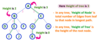
Depth
In a tree data structure, the total number of egdes from root node to a particular node is called as DEPTH of that Node. In a tree, the total number of edges from root node to a leaf node in the longest path is said to be Depth of the tree. In simple words, the highest depth of any leaf node in a tree is said to be depth of that tree. In a tree, depth of the root node is ‘0’.
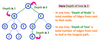
Path
In a tree data structure, the sequence of Nodes and Edges from one node to another node is called as PATH between that two Nodes. Length of a Path is total number of nodes in that path. In below example the path A - B - E - J has length 4.
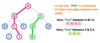
Sub Tree
In a tree data structure, each child from a node forms a subtree recursively. Every child node will form a subtree on its parent node.

Types of Binary Tree Traversals
Generally, Trees can be traversed in two ways:
- Breadth First Search traversal (BFS or Level Order Traversal)
- Depth First Traversals (Of which there are three types)
- In - Order Traversal (Left-Root-Right)
- Pre - Order Traversal (Root-Left-Right)
- Post - Order Traversal (Left-Right-Root)
In-Order Traversal
A DFS Traversal:
Algorithm: leftChild - root - rightChild
In In-Order traversal, the root node is visited between the left child and right child. In this traversal, the left child node is visited first, then the root node is visited and later we go for visiting the right child node. This in-order traversal is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree. This is performed recursively for all nodes in the tree.
That means here we have visited in the order of I - D - J - B - F - A - G - K - C - H using In-Order Traversal.
Pre-Order Traversal
A DFS Traversal:
Algorithm: root - leftChild - rightChild
In Pre-Order traversal, the root node is visited before the left child and right child nodes. In this traversal, the root node is visited first, then its left child and later its right child. This pre-order traversal is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree.
That means here we have visited in the order of A-B-D-I-J-F-C-G-K-H using Pre-Order Traversal.
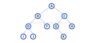
Post-Order Traversal
A DFS Traversal:
Algorithm: leftChild - rightChild - root
In Post-Order traversal, the root node is visited after left child and right child. In this traversal, left child node is visited first, then its right child and then its root node. This is recursively performed until the right most node is visited.
Here we have visited in the order of I - J - D - F - B - K - G - H - C - A using Post-Order Traversal.
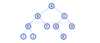
BFS vs DFS Tree traversal
Two of the most popular tree traversal algorithms are breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS). Both methods visit all vertices and edges of a graph; however, they are different in the way in which they perform the traversal. This difference determines which of the two algorithms is better suited for a specific purpose.
BFS:
- BFS starts traversal from the root node and visits nodes in a level by level manner (i.e., visiting the ones closest to the root first).DFS starts the traversal from the root node and visits nodes as far as possible from the root node (i.e., depth wise).
- Usually implemented iterativley using a queue. (FIFO)
- list
- collections.deque
- queue.Queue
- Same time complexity but generally requires more memory than DFS.
- Optimal for finding the shortest distance.
- Used for finding the shortest path between two nodes, finding how many levels away, testing if a graph is bipartite, finding all connected components in a graph, etc.
DFS:
- DFS starts the traversal from the root node and visits nodes as far as possible from the root node (i.e., depth wise).
- Usually implemented using a stack (LIFO)
- list
- Collections.deque
- queue.LifoQueue
- Same time complexity but generally requires less memory than BFS.
- Not optimal for finding the shortest distance.
- Used for topological sorting, solving problems that require graph backtracking, detecting cycles in a graph, finding paths between two nodes, etc.
How to Pick One?
- DFS: When using Backtracking, complete search, exhausting possible paths
- BFS: To check if a path exists between nodes, finding “hops” or distance out or “levels” away.
- Extra Space can be one factor (BFS uses more than DFS)
- Depth First Traversals are typically recursive and recursive code requires function call overheads.
- The most important points is, BFS starts visiting nodes from root while DFS starts visiting nodes from leaves. So if our problem is to search something that is more likely to closer to root, we would prefer BFS. And if the target node is close to a leaf, we would prefer DFS.
Full Binary Tree
A Binary Tree is a full binary tree if every node has 0 or 2 children. We can also say a full binary tree is a binary tree in which all nodes except leaf nodes have two children.
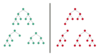
Complete Binary Tree
Complete Binary Tree has all levels completely filled with nodes except the last level and in the last level, all the nodes are as left side as possible.
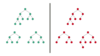
Perfect Binary Tree
A Binary Tree in which all internal nodes have 2 children and all the leaf nodes are at the same depth or same level.
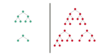
Balanced Binary Tree
Balanced Binary Tree is a Binary tree in which height of the left and the right sub-trees of every node may differ by at most 1.
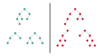
Degenerate Binary Tree
A Degenerate (or Pathological) Binary Tree is a Binary Tree where every parent node has only one child node.

Simple Tree BFS Pseudocode
- Initialise the queue by enqueuing the root node of the tree to traverse
- While the queue is not empty:
- Dequeue a node from the queue,
- Output the value of this node,
- Enqueue the left and right node of this node to the queue.


