Topic 3 (PP 9-10) - The Genetic Code and Protein Translation Flashcards
How many amino acid side R chains are there?
20
At what pH are both the amino acid and carboxyl groups ionized?
7
What is the bond between two amino acids?
peptide bonds

What molecule is lost in the reaction of a peptide bond?
H20

What are amino acid side chains called?
R-groups
Denature protein
a protein in its unfolded configuration
How can proteins be denatured with chemical exposure?
proteins exposed to high concentration of urea can denature the protein. Urea is a denaturing chemical that disrupts hydrogen bonds

How can denatured proteins recover their natural shapes?
remove urea
How can proteins be denatured with heat?
boiling proteins in solution
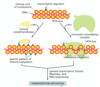
Protein structure is determined by which weak interactions?
non polar side chains, polar side chains, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals attraction, electrostatic interactions
What interactions affect protein structure in an aqueous environment?
nonpolar side chains packed into hydrophobic cores, polar side chains forming hydrogen bonds with water

What are three types of non-covalent bonds that help proteins fold?
electrostatic attractions, hydrogen bond, van der Waals attraction

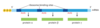
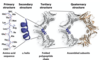
primary structure of a protein
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure of a protein
Presence of alpha-helices and beta-sheets

Tertiary structure of a protein
folding of individual proteins into a 3-D structure
Quaternary structure of a protein
assembled subunits
Prp
prion protein
PrPC
normal form of the prion protein, does not cause diseas
PrPSC
disease form of prion protein
What is the most common prion disease in the USA? Average cases per year? Average age onset?
Creuzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD), 350 cases per year, average onset of 60
What are the types of CJD onset in humans?
spontaneous, genetic, transmissible (kuru, new variant nvCJD)
How do prion diseases work?
- a single molecule of the normal form spontaneously converts to the diseased form (rare event)
- diseased form now acts like a catalyst to convert all normal form in the cell to diseased form
- diseased form aggregates, causing disease

What is the name of the prion disease in humans (shared by other mamals) that affects neurons?
spongiform encephalopathy
What is the Creuzfeldt-Jakob Disease?
a degenerative brain disorder that leads to dementia and death