Thorax 2 (Cardiovascular System) - part 1 Flashcards
Vaugly, what does the mediastinum contain?
Contents of the thorax other than the lungs and their covering pleurae
What are the sections of the mediastinum?
Superior
Inferior (further divided)
What is the inferior mediastinum further divided into?
Anterior
Middle
Posterior
What is A?

Pericardial cavity
What is B?

Pleural cavity
What is C?

Pleura
What is D?

Spinal cord
What is E?

Right lung
What is F?

Mediastinum
What is G?

Heart
What is H?

Left lung
What is A?

Superior mediastinum
What is B?

Inferior mediastinum
What is C?

Sternal angle
What bone forms the anterior border of the mediastinum?
Manubrium
What vertebrae form the posterior border of the superior mediastinum?
T1 - T4
What plane seperates the superior from the inferior mediastinum?
Transverse
What are some structures found in the superior mediastinum?
Arteries (aortic arch, brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery)
Veins (brachiocephalic vein, superior vena cava)
Nerves (vagus nerve, phrenic nerve)
Trachea
Oesophagus
Picture is the inferior mediastinum, what is A?

Middle mediastinum
Picture is the inferior mediastinum, what is B?

Posterior mediastinum
Picture is the inferior mediastinum, what is C?

Anterior mediastinum
Where in the mediastinum is the thymus found?
Anterior
Where in the mediastinum is the heart, pericardium and great vessels found?
Middle
Where in the mediastinum is the descending aorta found?
Posterior
Where in the mediastinum is the oesophagus found?
Posterior
Where in the mediastinum is the thoracic duct found?
Posterior
Where in the mediasinum is the azygos vein found?
Posterior
Where in the mediastinum is the sympathetic chain found?
Posterior
What is the difference between the pericardium, and the pleura and the peritoneum?
Pericardium has an outermost dense fibrous connective tissue layer - the fibrous pericardium
The picture shows the pericardium, what is A?
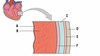
Endocardium
The picture shows the pericardium, what is B?

Myocardium
The picture shows the pericardium, what is C?

Pericardial cavity
The picture shows the pericardium, what is D?

Fibrous pericardium
The picture shows the pericardium, what is E?

Parietal layer of serous pericardium
What is F?

Epicardium (visceral layer of serous pericardium)
What is the epicardium also known as?
Visceral layer of serous pericardium
What are the 3 layers of the pericardium from superficial to deep?
Fibrious pericardium
Parietal pericardium
Visceral pericardium (epicardium)
Between what 2 layers of the pericardium does the pericardial cavity lie?
Parietal layer and visceral layer
What is the endocardium composed of?
Simple square endothelium
What is the myocardium composed of?
Cardiac muscle
What is the epicardium composed of?
Simple square epithelium
What layer belongs both to the heart wall and the serous pericardium?
Epicardium
Which layer of the serous pericardium is inseperably attached to the inner aspect of the fibrous pericardium?
Parietal layer
What protective role is furfilled by the fibrous pericardium?
Prevents overfilling
Explain the innervation of the pericardium?
Visceral pericardium - autonomic from T-T4 and vagus nerve via the cardiac plexus
Parietal and fibrous pericardium - phrenic nerve
What part of the pericardium does the vagus nerve and T1-T4 nerves innervate?
Visceral pericardium
What part of the pericardium does the phrenic nerve innervate?
Parietal and fibrous pericardium
Which layer of the pericardium is innervated by pain fibres?
Fibrous and parietal pericardium
What role do the auricles have in a heart?
Direct blood to the atrial ventricular gap
What is A?

Left atrium
What is B?

Right atrium
What is C?

Left ventricle
What is D?

Right ventricle
What organ is the left atrium anterior to?
Oesophagus

What is the shape of the heart?
Pyramidal
What chamber of the heart forms the apex?
Left ventricle
What chamber of the heart forms the base?
Left atrium
What is A?

Opening for superior vena cava
What is B?

Interatrial septum
What is C?

Fossa ovalis
What is D?

Opening for coronary sinus
What is E?

Opening for inferior vena cava
What is F?

Tricuspid valve
What is G?

Crista terminalis
What is H?

Musculi pectinati
What is I?

Left auricle
What is the fossa ovalis a remnant of?
Foramen ovale in the foetus
The fossa ovalis is a remnant of the foramen ovale in the foetus, what function did this have?
Shunt the blood from the right atrium to the left to pass the lungs
What is A?

What is B?

What is C?

What is D?

What is E?

What is F?

What is G?

What is the function of the moderator band?
Strengthen and prevent overballooning
Carries primary conductor band with right bundle of his (goes across chamber to cut conduction time)
Is the right ventricle wall or left thicker?
The left is thicker by 3x
Why is the left ventricle wall 3x thicker than the right?
It has to pump blood to the systemic circulation, not just the pulmonary
How many cusps make up the tricuspid valve?
3
How many papillary muscles are found in the right ventricle?
3
What is A?

Superior pulmonary vein
What is B?

Inferior pulmonary vein
What is C?

Left atrium
What valve guards entry from the left atrium into the left ventricle?
Mitral valve
How many cusps are present in the mitral valve?
2
How many papillary muscles are found in the left ventricle?
2
What is the function of the papillary muscles?
Stop valve failure
Produce tension
What is the function of the chordae tendineae?
Stop valve failure
What supplies the heart wall with blood?
Left and right coronary arteries and their anastomosing branches
How is blood drained from the heart wall?
Cardiac veins almost entirely to the coronary sinus
What is the coronary sinus?
Wide venous channel on the posterior surface of the heart
Where does the coronary sinus drain into?
Right atrium
Where do the coronary arteries and cardiac veins lie?
Together in both the atrioventricular sulcus adn the interventricular sulci of the heart wall
What is A?

Atrioventricular sulcus
What is B?

Interventricular sulcus
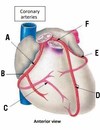
What is 1?

Aortic arch
What is 2?

Right coronary artery
What is 3?

Left anterior descending artery
What is 4?

Circumflex artery
What is 5?

Left coronary artery
What is 6?

Posterior interventricular artery
What does the left coronary artery branch into?
Left anterior descending artery
Circumflex artery
From which part of the aorta do the coronary arteries arise?
Ascending aorta
What pair of coronary arteries anastomose in the coronary sulcus?
Right and left coronary arteries
What pair of coronary arteries anastomose in the interventricular sulcus?
Left anterior descending and posterior interventricular artery
What does the right coronary artery branch into?
Right marginal artery
Right posterior descending artery
What does the circumflex artery branch into?
Left marginal artery
Circumflex artery (continues)
Where are the coronary arteries initially distributed?
Embedded within the epicardium, then piercing the myocardium and giving off branches that surround each cardiac muscle cell
What are the origins in the ascending aorta for the coronary arteries called?
Right and left aortic sinuses
What is A?

Opening for right coronary artery
What is B?

Aortic sinus
What is C?

Nodule
What is D?

Lunule
What is E?

Left coronary artery
What is F?

Left semilunar cusp
What is G?

Posterior semilunar cusp
What is H?

Right semilunar cusp
What is I?

Right coronary artery
What is A?

Anterior cardiac veins
What is B?

Coronary sinus
What is C?

Small cardiac vein
What is D?

Middle cardiac vein
What is E?

Oblique vein of left atrium
What is F?

Great cardiac vein
What is A?

Right coronary artery
What is B?

Posterior interventricular artery
What is C?

Right marginal artery
What is D?

Anterior interventricular artery
What is E?

Circumflex artery
What is F?
Left coronary artery
What does the anterior interventricular artery supply blood to?
Interventricular septum and anterior walls of both ventricles
What does the circumflex artery supply blood to?
Left atrium and posterior walls of the left ventricle
What does the right marginal artery supply blood to?
Lateral right side of heart (including right atrium)
What does the posterior interventricular artery supply blood to?
Posterior right ventricle walls
Where does the great cardiac vein lie?
Alongside the left anterior descending artery in the anterior interventricular groove
here does the middle cardiac vein lie?
Alongside the posterior descending artery in the posterior interventricular groove
Where does the small cardiac vein lie?
Alongside the right marginal artery near the righ inferior margin of the heart
Where does the coronary sinus lie?
Alongside the circumflex artery in the coronary sulcus on the posterior surface of the heart
Where does the coronary sinus drain directly into?
Right atrium
What are venae cordis minimae?
Small veins which drain the heart wall directly into each chamber of the heart
What are small veins which drain the heart wall directly into each chamber of the heart called?
Venae cordis minimae
What is A?

Aortic arch
What is B?

Ascending aorta
What is C?

Common iliac arteries
What is D?

Abdominal aorta
What is E?

Descending aorta
What is F?

Thoracic aorta
What vertebrae level does the beginning and termination of the aortic arch occur?
T4
What vertebrae level does the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta occur?
L4
What vertebrae level does the bifurcation of the common iliac arteries occur?
L5
What branches occur from the ascending aorta?
Right coronary artery
Left coronary artery
What branches occur from the aortic arch?
Brachiocephalic trunk
Left common carotid artery
Left subclavian artery
What is A?

Oesophagus
What is B?

Trachea
What is C?

Aorta
What is D?

Brachiocephalic trunk
What is E?

Left common carotid artery
What is F?

Left subclavian artery
What branches from the descending thoracic aorta?
Posterior intercostal arteries (only identifiable ones on wet specimen)
Bronchial arteries
Oesophageal arteries
Pericardial arteries
What is A?

Right bronchial artery
What is B?

Posterior intercostal arteries
What is D?

Oesophageal arteries
What is E?

Mediastinal branches
What is F?

Left bronchial artery
How do the arteries, veins and nerves supplying the chest wall occur?
Segmentally for each intercostal space being supplied in the form of a neurovascular bundle running anteriorly along the space
Where do the vessels of the neurovascular bundle arise from, or drain to?
Larger vessels that run vertically along the anterior and posterior chest wall
What chest wall arteries arise from the descending thoracic aorta?
Posterior intercostal arteries
What chest wall arteries arise from internal thoracic (mammary) artery?
Anterior intercostal arteries
What artery gives origin to the internal thoracic artery?
Subclavian arteries
Where does the internal thoracic artery lie?
Parasternally, being accompanied by the internal thoracic veins

Where do the anterior intercostal veins drain to?
Internal thoracic veins
What do the branches of the internal thoracic arteries supply?
Anterior intercostal arteries
Fibrous pericardium
Parietal pleura
Diaphragm
What is A?

Perforating branches
What is B?

Superior epigastric artery
What is C?

Musculophrenic artery
What is D?

Anterior intercostal arteries
What is E?

Pericardiacphrenic artery
What is F?

Subclavian artery
What do the arteries that arise from the abdominal aorta supply?
Diaphragm
Adrenals
Kidneys
Gonads
Gut tube
At what vertebral level do the common iliac arteries arise?
L4
At what vertebral levels do the external iliac arteries arise?
L5
At what vertebral level do the internal iliac arteries arise?
L5
What do the iliac arteries lie in?
Iliac fossae
What does the external iliac arteries go onto become?
Femoral artery
What are the common iliac arteries the terminal branches of?
Descending aorta
What are the external iliac arteries the terminal branches of?
Common iliac arteries
What does the internal iliac arteries supply?
Pelvic viscera
What are the internal iliac arteries the terminal branch of?
Common iliac arteries
What is A?

Right common iliac artery
What is B?

Right external iliac artery
What is C?

Right femoral artery
What is D?

Right internal iliac artery
Arteries have branches, what do veins have?
Tributaries
What are the great arteries leaving the heart?
Aorta
Pulmonary trunk
What are the great veins entering the heart?
Superior and inferior vena cava
Where does the superior vena cava (SVC) drain blood from?
Hear
Neck
Upper limbs
Where does the inferior vena cava (IVC) drain blood from?
Abdominal and pelvic cavities
Lower limbs
What drains the intercostal veins to the left and right brachiocephalic veins?
Internal thoracic (mammary) vein
Where does the internal thoracic (mammary) vein drain from and to?
Drains the anterior intercostal veins to the left and right brachiocephalic veins
What is A?

Superior vena cava
What is B?

Phrenic nerve
What is C?

Phrenic nerve
What is D?

Pulmonary trunk
What is E?

Aorta
What are the tributaries of the superior vena cava?
Left and right brachiocephalic veins
Azygos vein
What are tributaries of the inferior vena cava?
Left and right common iliac veins
What is A?

Right brachiocephalic vein
What is B?

Superior vena cava
What is C?
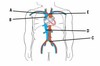
Left and right common iliac veins
What is D?

Inferior vena cava
What is E?

Lef brachiocephalic vein
What drains blood from the posterior intercostal veins to the superior vena cava?
Azygos venous system
Where does the azygos venous system drain blood from and to?
Drains blood from the posterior intercostal veins to the superior vena cava
What does drainage of the posterior chest wall consist of?
Azygos veinous system on the right side
Hemiazygos veinous system on the left side
Where does the hemoazygos vein drain into?
Azygos vein by crossing from left to right at T8/T9
Where does the hemiazygos vein cross the median line from left to right?
T8/T9
Into which vein does the azygos vein drain into?
Superior vena cava
Which chest wall veins are drained by the azygos and hemiazygos venous systems?
Posterior intercostal veins
Where does the azygos vein drain into?
Right subclavian vein
What is A?

Azygos vein
What is B?

Hemiazygos vein


