The Orbit Flashcards
(23 cards)
What bones make up the bony structure of the orbital cavity?
- Palatine bone
- Ethmoid bone
- Lacrimal bone
- Maxilla
- Zygomatic Bone
- Frontal bone
- Sphenoid bone (greater wing)

What are the layers of the eyelid?
- Skin
- Subcutaneous tissue
- Orbicularis oculi muscle
- oribital septum
- Conjunctiva
- Tarus

What do we need to remember about the skin and subcutaneous tissue?
These are a thin layer, and the subcutaneous tissue acts as a potential space. With a skull fracture → raccoon eyes

What do we need to remember about the Oribicularis Oculi muscle

This is a two-part voluntary muscle, that extends outside the orbital cavity
- Palpebral Part: of the eyelids
- Orbital: Around the eye
Seals the orbital cavity, and is innervated by the facial nerve

What is the orbital septum
A continuation of the periosteal dural layer, running within the upper and lower eyelid
What are the muscles that control the tarsus raise of the eyelid and what innervates them? What happens if you get a loss of function?
The Levator palpebral superioris muscle (LPS) and the superior tarsal muscle (ST) ((a smooth muscle)).
LPS ⇔ occulamotor nerve
ST ⇔ postganglionic sympathetic fibres from the superior cervical ganglion
- *Loss of function → ptosis (drooping)**
- complete (LPS) or partial (ST)*

What do the tarsus glands secrete
They sit in the tarsus and secrete an oily substance, for protective lubrication

**a septum runs through the tarsus to stabilise it.
If the septum clogs → ‘chalazion’ bump on the eyelid (usually painless)
Don’t confuse with a painful sty which is an infected sweat gland!
What is the conjuctiva and what can go wrong?
The thin conjuctiva membrane covers the eyelid, avoids damage and scratching on eye.
Conjuctivitis is just an infection of this
What’s the innervation of the eyelid?
First division of the trigeminal = Upper lid
Second division of the trigeminal (maxillary) = lower lid
What’s the contents of the orbital cavity?
- Eyeball
- Extrinsic muscles of the eyeball
- Lacrimal apparatus
- Neurovascular structures
What are the extrinsic muscles of the eye?
Superior rectus
Inferior rectus
Medial rectus
Lateral rectus
Superior oblique
Medial oblique
Although in the orbit theres only one periosteal dura kayer the ‘periorbita’, where the cranial nerve enters the orbit there is ____
A seal made of both the periosteal and meningeal layer

The seal around the cranial Nerve is called the ________
Common tendinous ring (thickening of the periosteum).
Point of origin for all 4 rectus muscles, and many nerves run within this structire.
What runs in the oribital canal?
- Cranial Nerve II (Optic nerve)
- Ophthalmic artery

What runs in the superior orbital fissure?
- Superior ophthalmic vein
Whats in the lacrimal apparatus
- Lacrimal gland: on lateral side of orbit, hugging LPS, drains tears back to the eye
- Lacrimal canaliculi
- Lacrimal sac
- Nasolacrimal duct
Puncta: a pump that drains tears from lacrimal canaliculi → lacrimal sac → nasolacrimal duct → nose (*why you get a runny nose when you cry!!)

Whats the main arterial supply of the orbit
The Ophthalmic artery through the optic canal, has lots of branches that go to different areas.
If you lose these arteries you will go blind
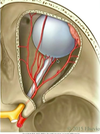
Whats the main venous supply of the orbit?
Ophthalmic Vein, which communicates with the cavernous sinus and the facial nerves. THis is therefore where infection may drain to the brain, the ‘danger triangle’

Although nearly everything is innervated by the occulomotor nerve CN III, what extrinsic muscles aren’t?
- Lateral Rectus: CN 6
- Superior Oblique: CN 4
So what parts of the oculomotor nerve supply what?
Superior branch: Levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus
Inferior Branch: Medial rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, ciliary ganglion
You can figure out where the fracture is dependent on what symptoms?

Superior Oblique origin, innervation
Innerevate by CN IV (trochlear), Doesn’t attach to the common tendonous ring, and its two bellies strangely comes medially, and then has a ‘pulley’ which allows it to pull the eye in/down.
Therefore a fracture on the medial side may damage the pulley attachment.

What does the Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1) innervate?
Branches:
Lacrimal Nerve → lacrimal gland
Frontal Nerve → sensory supply to frontal face
Nasociliary Nerve → Lacrimal duct/sac and nasal cavity

The dogma of the dangerous triangle is that it is devoid of valves, hence can cause the spread infection. What is the truth?
in 75% specimens, valves were found in the superior veins, and non in the inferior.
Therefore superior ophthalmic, angular and supraoribital veins are NOT devoid of veins!
The Real Issue: there is a direct connection between veins, and the cavernous sinus.


