Testing Flashcards
What does ‘create-react-app’ {filename} do?
It creates a react application with packages/dependencies that you need
After you set up your react application what is the ‘App.js’ file?
It is the Root component
How are you given testing functionality in create-react-app?
It comes with a testing functionality right out of the box, ready to go. It utilizes npm run test in the root directory and utilizes ‘App.test.js’
What dependencies did we get with create-react-app?
1) React . - The React Library
2) Webpack - Links together JS files
3) Babel - Turns ES6 and JSX into ES5 code
4) Jest - Automated test runner

What happens when we execute the NPM test command at the terminal?
1) We run ‘npm run test’ at the terminal
2) Jest test runner starts up
3) Jest finds all files ending in .test.js and executes tests inside of them
4) Jest prints out results of tests to the terminal
5) Jest waits for a file to change, then runs all tests again
What is the framework to follow to understand what tests you should write in your application?
Follow these three steps:
1) Look at each individual part of your application. Every reducer, every action creator, every component
2) Imagine telling a friend ‘heres what this piece of code does’
3) Write a test to verify each part does what you expect
In our ‘comments’ app, if we wanted to know all the tests in the app, what would they be?

What is the main construct of our testing suite?
it ( description of the test, function containing our test logic)
1) it is a global function - no need to import. It is used to organize all the different test that we write inside of a single file. So for each test we write we will call the IT function exactly one time
2) The first argument to the IT function is a string that is a description of the test that you are going to write. String description solely for ourselves
3) The second argument is the body, test logic that wants to execute. Runs what the 1st argument states
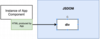
How can we trick React with JSDOM?
1) When we run JEST it’s being ran in our command line environment. From the terminal. Issue is that if we run React, it thinks it should be ran inside the browser. ONLY inside the browser does it work
2) So, Dependency is called JSDOM, code implementation of how the browser works. It fakes out the existence of a browser.
3) So then, React takes the App Component and creates the HTML produces by the App and sticks it in JSDOM’s div element
What is ‘expect’ when you test?
expect(value that we are inspecting).matcher statement(value that we expect to see);
1) Expect - Global function, the object property array etc. the thing we are looking at. Example, we want to inspect the HTML contained by that div element
2) Value that we are inspecting - The thing we want to verify
3) Matcher Statement - Designates how we want to inspect the ‘subject’.
4) Expected value 0 its what we want our ‘subject’ to be
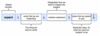
What’s a general rule about working with tests and internal workings of a component?
If we write a test for a component, then that test shouldn’t mess with the inner workings or the actual implementation details of any other component if possible
What is enzyme? npm install –save enzyme-adapter-react-16
Open source package created by Airbnb specifically made for testing re-act components a little bit easier
After you’ve dependency installed enzyme, what file do you need to create?
In SRC, you should create setupTests.js
So how does Enzyme really function?
Gives us three additional capabilities for writing our tests. Each of these render functions are going to take instance of components, take them or attempt to render them in a slightly different fashion and will return
1) Static Renderer - Render the given component and return plain HTML. A function that allows only HTML. Doesn’t allow us to do clicking etc.
2) Shallow Renderer- Render just the given component and none of its children. Really analyzing
3) Full DOM Renderer- Render the component and all of its children and let us modify it afterwards. Sends an object back that we can use to interact with the component. Like click events etc
Explain the ‘beforeEach’ helper function in jest
Extract out or pull out logic for each file. Before each test, we are going to do some setup of logic
Which package for the FullDOM rendered in enzyme?
You need to import mount from enzyme? Remember to do beforeEach and afterEach for each it function
How do you simulate an event for testing?
1) Find the textarea element
2) Simulate a ‘change’ event
3) Provide a fake event object
4) Force the component to update
5) Assert that the textareas value has changed
Using enzyme, what is the function that can simulate a change event?
simulate method. You can ‘simulate’ a given event
How do you pass a mock object for testing in enzyme?
You utilize the mock object: A mock event object that will be merged with the event object passed to the handlers
You want to trick the event handler with this kind of custom or fake or mock event object

Does react re-render the component instantly after ‘setstate’?
No, it queues and react gets to it whenever it can. In our test, we are going to need to use enzyme’s .update to force update the component
What is the ‘describe’ function in jest?
Is used to group together certain sets of test that have some common set up or tear down for each of them
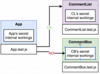
Describe the mechanics of how provider component works from react-redux?
It works with all the connects in the App to gain access to the redux store
What is a cherriowrapper?
It’s something similar to jQuery, it allows us to kind of crawl or run queries or essentially selectors over snippets of each HTML
What is redux promise?
Use it to handle asynchronous action creators or action creators that try to make network requests




