Test Review Flashcards
Lymph follicle
Not enclosed w/i a capsule. Occur singly or in aggregates. Sites of B cell locatlization and proliferation. Transient
Primary Lymph follicle
Spherical, tightly packed accumulations of virgin B cells and dendritic reticular cells that have not been exposed to antigens
Secondary follices
Derived from primary follicles that have been exposed to non self antigens - not present at birth.
Structure of secondary lymph follicle
Cortex: darker peripheral region composed of densely packed B lymphocytes. Germinal center - central, lighter stained region. Composed of B lymphocytes, memory B cells, plasma cells, dendritic reticular cells which function as antigen-presenting cells.
CD4+ T cells
Recognize antigens bound to MHC class II molecules. Helper cells - assist CD8+ cells differentiation and B cell differentiation
CD8+ T cells
recognize peptide fragments of foreign proteins bound to MHC class I on the surface of cells. Cytolytic t cells - release perforins and fas
CD16+ Tcells
Natural killers. Activated by tumor cell antigens to release cytokines (interleukins, MAF, chemotactic and TNF)
What is the most important opsonin?
c3b
HEVs
In the deep (inner) cortex of the lymph node - port of entry for circulating differentiated lyphocytes to seed lymph node.
Double negative T cells
Lack cell surface molecules typical of mature T cells. Enter corex from blood vessels. Proliferate in subcapsular area.
Double positive T cells
Move to the outer cortex. Confronted w/ epi cells w/ curface MHC classes I and II for clonal selection. Express both CD4 and CD8 coreceptors and TCR receptors
Single positive T cells
Move to inner cortex. Express TCR receptors and either CD4 and CD8 co receptors.
Where is clonal deletion of T cells completed?
in the medulla of the thymus
Hassall’s corpuscles
Thymus medulla - whorls of highly keratinized medullary epithelial cells. Produce cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoeitin.
Cords of billroth
Form the red pulp parenchyma (spleen). Contain various blood cells, plasma cells, and antigen presenting cells. Terminal capillaries open directly into substance of cords (open circulation)
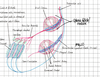
Lymph node
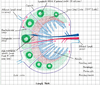
Space of Disse
Separates hepatic cells from endothelial cells. Active transfer between blood and parenchyma.
Classic lobule
Central venule in the center with portal triads at the angles. Sinusoids receive blood from hepatic vein and artery.
The anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3 of the tongue is separated by?
sulcus terminalis