Test #2 prep Flashcards
Quantum Mechanical
Model of an atom to Explain the way in which electrons exist and behave.
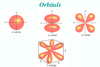
Orbitals
Volume in space with high probability of finding the electron

Quantum Numbers
To describe the orbitals each electron is described by a unique set of quantum numbers.

Angular Quantum Number (L)
(principle 2)
Sublevel (subshell)
Specific type of orbital
Value given by L is given by numvers that go from
- 0 to N-1
Each possible value of L represents a sublevel
(a specific type of orbital)
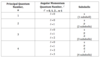
Value Of L Type of orbital
0 S
1 P
2 D
3 F
Quantum Number (N)
(Principle 1)
Represents the Energy level (or shell)
Values 1-7
It is given by the peroids on the perodic table

Magnetic Number (ML)
(Principle 3)
How many orbital of each type
Ex. if there are three possible values of Ml. There are 3 orbitals of that specific type of orbital.
- Value of ML
- L to +L
Ex, if L=3
-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3
7 possible values of ML (7 orbitals)

Spin Quantum Numbers (MS)
(Principle 4)
electron configuration
+1/2 up or -1/2 down
Ionic Bonds
(compound)
transfer of electrons
M X
M= metal always +
X= Negative
example, NaCl

Covalent or Molecular Bond
(compound)
Sharing of electrons
Example, CO2
NON METALS!!!

Valence electron e-
Electrons in the highest energy level
Elements losing e-
Positive e- is cations
Elements gaining e-
Negative ions are anions
Electron configuration for Cr Chromium
and Cu Copper

Acetate
Formula and Charge
C2H3O2-
Carbonate
Formula
CO32-


