Test 1 Flashcards
(155 cards)
What are the classifications and characteristics of A fibers?
alpha, beta, gamma, delta; fast, sharp, well-localized sensation
Name whether or not A, B, C fibers are myelinated or non-myelinated.
A and B are myelinated and C is non-myelinated.
What are the characteristics of C fibers?
slow, prolonged, poorly-localized; non-myelinated
What is the innervation, function, conduction velocity, and diameter of A-alpha fibers?
muscle spindle motor to skeletal; proprioception, motor; 15um; 100 m/s
What is the innervation, function, conduction velocity, and diameter of A-beta fibers?
touch and pressure afferents; touch, pressure; 10um; 50 m/s
What is the innervation; function, conduction velocity, and diameter of A-gamma fibers?
motor to muscle spindles; muscle spindles; 5um; 25 m/s
What is the innervation, function, conduction velocity, and diameter of A-delta fibers?
mechanoreceptors, nociceptors; pain (sharp), temperature; <5um; 25 m/s
What is the innervation/function, conduction velocity, and diameter of Type B fibers?
sympathetic pre-ganglionic, autonomic; <3um; 10 m/s
What is the function, conduction velocity, and diameter of Type C-dorsal root fibers?
pain (dull), temperature; 1um; 1 m/s
What is the function, conduction velocity, and diameter of Type C-sympathetic fibers?
post-ganglionic; 1um; >1 m/s
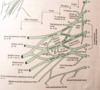
Review the image for interscalene block.
The targets of anesthesia for this block are the roots and proximal trunks of the brachial plexus where they are sandwiched between the anterior and middle scalene muscles at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra (C6).

The trunks are contained within the interscalene fascial sheath at this level. This block is indicated mostly for surgical anesthesia to the shoulder, upper arm, and forearm, but is often insufficient for the hand. A continuous block via interscalene catheter provides excellent analgesia after shoulder arthroplasty.
Identify the landmarks for the interscalene block.
The main surface landmark (sternocleidomastoid muscle) used for this block can be accentuated by asking the patient to reach for the ipsilateral knee and by rotating the head approximately 45º to the non-operative side. The head should also be slightly elevated, and the patient should be instructed to take a deep breath (contraction of the scalenus muscles accentuates the interscalene groove).
The interscalene groove lies immediately behind the lateral border of the clavicular head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level of the cricoid cartilage (C6) and is located approximately 1 cm above the separation of the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.

Define Transduction:
Noxious stimuli translated into electrical activity at the sensory nerve endings
Define Transmission:
Propagation of impulses throughout the sensory nervous system.
Define Modulation:
Efferent control of pain.; Modulation is telling the body “its not going to be so bad”.
Label the following structures of the Myelinated Nerve Fiber:

Ultrastructural features of myelinated (A) and unmyelinated (B) nerve fibers. (1) Nucleus and cytoplasm of a Schwann cell; (2) axon; (3) microtubule; (4) neurofilament; (5) myelin sheath; (6) mesaxon; (7) node of Ranvier; (8) interdigitating processes of Schwann cells at the node of Ranvier; (9) side view of an unmyelinated axon; (10) basal lamina.
Picture of anatomy of peripheral nerve:

Picture of the Unmyelinated Nerve Fiber:

________ or _______ pathways transmit pain, temperature, pressure, touch, vibratory sense, and proprioceptive information to the CNS.
Sensory or Afferent
Receptors for pain and temperature are located in the ________ and _______; those for pressure, touch, vibratory sense, and proprioception are located in the ________.
epidermis; dermis; dermis
Receptors can be classified as _______, which are located near the surface of the skin and oral mucosa, and _________, which are located in deeper skin layers, joint capsules, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and periosteum.
exteroceptors; proprioceptors
______ order neurons in the ganglia reach the spinal cord and synapse with the ______ order neuron.
first; second
What is a the primary site of opioid spinal analgesia?
substantia gelatinosa; apex of the posterior horn of the gray matter of spinal cord is capped by a V-shaped mass of translucent, gelatinous neuroglia called S.G.; Many mu and k opioid receptors, presynaptic and postsynaptic are found on these nerve cells; it is gelatinous due to low concentration of myelinated fibers.

How many cervical vetebrae exist in the human spinal cord?
7