Template Directed Synthesis of Unnatural Products Flashcards
(23 cards)
In template directed synthesis, are the reactions tyipically entropically favorable?

No, requires a lot of particles to react together at once which is very unlikely
Considering the change in entropy of most tempate directed synthesis, what allows these reactions to happen at all?
Consider dG=dH-TdS
If dS is -ve then dH must compensate for it by being even more negative
Where dH represents noncovalent interactions
Describe ion-ion interactions
Strong interaction non-directional opposite coulombic charges
Describe ion-dipole interactions
Similar to ion-ion interactions except an ion interacts with a dipole
Describe cation-pi interactions
An electrostatic interaction between a cation and a π-electron system
Describe pi-pi interactions
The weak electrostatic interactions that occur between aromatic rings, often where one is relatively rich and the other electron poor
In general there are two types: face-to-face and edge-to-face
Describe Hydrogen Bonding
A hydrogen bond is an example of a disproportionately large dipole-dipole interaction.
It is the attraction of a hydrogen atom which is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (or electron withdrawing group) to a neighbouring dipole or electron rich functional group.
Explain the Hydrophobic Effect
Makes it possible to bind non-polar molecules to polar ones in order to dissolve them in aqueous medium.
Explain the Chelate Effect
Metal complexes with multidentate are considerably more stable than a complex with similar monodentate ligands
Easier to overcome repulsions with a multidentate ligand (dH lower)
Bodning at multiple sites (dS higher)
lower free energy -> Stabilizes
Explain the Macrocyclic Effect
Related to the chelate effect
Macrocyclic complexes are more thermodynamically stable
Very similar thermodynamic Reasons to the chelate effect
What is an interesting property of crown ethers and spherands?
Macrocyclic compounds which can coordinate to cations allowing them to be dissolved in aqueous solution via hydrophobic effect
Note that cations of ideal size work better (for spherands only Li or Na are often used due to small size of cavity.)
What are the properties of a template directed synthesis?
Organizes the assembly of atoms and molecules
favors the formation of product
promoted bond formations
Explain the differences between kinetic and thermodynamic TDS
Kinetic - Bond formations are covalent and irreversible, the template instead lowers the energy of the transition state
Thermodynamic - Covalet bond formations are reversible. Without the template, the product will decompose into its initial reactants or otherwise
How are template effects quantified?
Quantified by creating a ratio with the rate constants of reactions shown below
The larger Euntemp the larger cyclic product is formed as opposed to polymeric
The larger Etemp the larger cyclic product is formed as opposed to polymeric with the template

As chain becomes longer, is does cyclization become more or less likely
How does this effect the effective molarity?
Cyclization becomes less likely as oligomeric products are formed
Em decreases
When considering the mechanism of a template directed synthesis, what’s important to keep in mind?
Only 2 (max 3) molecules will react together, 4+ molecules reacting together is very unlikely
What is the Curtin-Hammett principle?
For a reaction that has a pair of reactive intermediates or reactants that interconvert rapidly (as is the case for [2] and [3]pre-catenanes), each going irreversibly to a different product, the product ratio will depend only on the difference in the free energy of the transition state going to each product, and not on the equilibrium constant between the intermediates
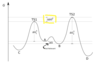
What is Effective Molarity
Ratio of rate of formation of cyclization over polymerization
represents concentration at which constants are equal

What are the mechanisms for the reversible thiol exchange?

What are the mechanisms for olefin metathesis?
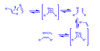
What is the Gauche Effect?
The term “gauche” refers to conformational isomers (conformers) where two vicinal groups are separated by a 60° torsion angle.
In the hyperconjugation model, the donation of electron density from the C–H σ bonding orbital to the C–F σ* antibonding orbital is considered the source of stabilization in the gauche isomer. Due to the greater electronegativity of fluorine, the C–H σ orbital is a better electron donor than the C–F σ orbital, while the C–F σ* orbital is a better electron acceptor than the C–H σ* orbital.

Explain why interlocked architectures are often thermodynamically preferred in comparison to non-interlocked by-products and hence the benefits of synthesising these molecules using reversible covalent bond-forming reactions.
Interlocked products are often thermodynamically favoured over other products as they can maximise energetically favourable intercomponent interaction
However, “mistakes” such as oligomerisation reactions, lead to a decrease in the yields of interlocked products if covalent bond formation is irreversible
When a reaction is carried out under thermodynamic control, the use of reversible covalent bond forming reactions allows for “error checking” whereby side-products of higher energy are recycled to give lower energy products
The downside of interlocked molecules prepared in this manner is that they are intrinsically “unstable”, unless the reversibility of the covalent bond-forming reaction can be halted.


