Systemic Perio Disease Flashcards
from a historical perspective, there is a long-standing awareness of certain links between oral health and ___, and of systemic effects on ___
- systemic health
- oral tissues
special considerations are needed for patients with ____
systemic conditions
during disease (periodontitis), there is a high level of what 5 pro-inflammatory molecules?
- IL-1beta
- TNF-alpha
- INF-gamma
- PGE2
- MMPs
during disease (periodontitis), there is a low level of what 5 pro-inflammatory molecules?
- IL-4
- IL-10
- TGF-beta
- IL-1ra
- TIMPs
during health (no periodontitis), there is a low level of what pro-inflammatory molecules?
- IL-1beta
- TNF-alpha
- INF-gamma
- PGE2
- MMPs
during health (no periodontitis), there is a high level of what pro-inflammatory molecules?
- IL-4
- IL-10
- TGF-beta
- IL-1ra
- TIMPs
compelling evidence suggests periodontitis may be related to the risk for what 4 diseases?
- cardiovascular disease
- preterm low-birth weight infants
- diabetes
- respiratory disease
possibly others
name 5 conditions that can have risk factors associated with periodontitis
- osteoporosis
- menopause
- pregnancy
- smoking/ethanol use
- HIV
from a systemic standpoint, what are 5 implications of periodontics for practice?
- emphasize the importance of oral health to overall well-being
- reducing inflammatory burden
- recognize systemic signs and symptoms and be prepared to refer patients to a physician
- clearer links between oral health and systemic health may necessitate practice adjustments
- all patients should be screened for periodontal disease
clearer links between oral health and systemic health may necessitate practice adjustments for what 4 types of patients?
- people with diabetes
- pregnant women
- patients at risk for cardiovascular disease
- elderly patients
can SBE prophylaxis prevent infective endocarditis?
- only in an extremely small number of cases
- it is still recommended for patients with underlying conditions associated with highest risk for infective endocarditis
- recommendations based on “prevention of infective endocarditis - guidelines from the American Heart Association 2007”
“prevention of infective endocarditis - guidelines of the american heart association - 2007” recommends that patients at high risk for infective endocarditis who are receiving any of what 3 types of care should also receive SBE prophylaxis?
- manipulation of gingival tissues
- manipulation of the periapical region
- perforation of the oral mucosa
according to “prevention of infective endocarditis: guidelines from the american heart association - 2007”, antibiotic prophylaxis with dental procedures is recommended only for patients with cardiac conditions associated with the highest risk of what 2 adverse outcomes from endocarditis?
- prosthetic cardiac valce
- previous endocarditis
according to the “prevention of infective endocarditis: guidelines from the american heart association - 2007”, patients with congenital heart disease from which 4 categories should receive antibiotic prophylaxis?
- Unrepaired cyanotic congenital heart disease, including those with palliative shunts and conduits
- Completely repaired congenital heart disease with prosthetic material or device, whether placed by surgery or catheter intervention, during the first six months after the procedure
- Repaired congenital heart disease with residual defects at the site or adjacent to the site of a prosthetic patch or prosthetic device (which inhibit endothelialization)
- Cardiac transplantation recipients with cardiac valvular disease
how many people in the US have diabetes?
how many diagnosed, undiagnosed, and pre-diabetes cases are there in the US?
how many deaths were associated with diabetes in 2007 in the US?
diabetes is the ___ leading cause of death in the US
- 25.8 million people - 8.3% of the US population
- diagnosed: 18.8 million people
- undiagnosed: 7 million people
- pre-diabetes: 57 million people
- 231,404 deaths in 2007
- 7th leading cause of death
how many people in the following categories have diabetes?
age 20 years or older
age 65 years or older
men age 20 or older
women age 20 or older
non-hispanic whites
non-hispanic blacks
- age 20 years or older: 25.6 million, or 11.3%
- age 65 years or older: 10.9 million, or 26.9%
- men: 13 million, or 11.8%
- women: 12.6 million, or 10.8%
- non-hispanic whites: 15.7 million, or 10.2%
- non-hispanic blacks: 4.9 million, or 18.7%
what are 3 main characteristics of diabetes?
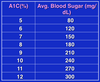
- fasting blood glucose levels >126 mg/dL after overnight fast
- 2-hr blood glucose level >200 mg/dL after a 2-hr oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
- an HbA1c level >6.5%
- *the first 2 are 2 of 3 methods used to diagnose diabetes*
what are the 4 main classifications of diabetes, and what percentage of the population has each type?
- type 1 (IDDM); 5-10%
- type 2 (NIDDM); 90-95%
- gestational diabetes (due to pregnancy); 3-5% of all preg.
- secondary diabetes; 1-2%
- impaired glucose tolerance/impaired fasting glucose
describe causes of secondary diabetes
- recurrent pancreatitis, pancreatectomy endocrine disorders
- steroid drug therapy/misuse
describe diabetes
- a metabolic disorder in which the body does not produce or use insulin properly
- affects approxmiately 7% of people int he united states - almost 21 million people
- 6th* leading cause of death among americans
*earlier slide claims that it is the 7th leading cause
describe type 1 diabetes
- insulin is not created at all
- accounts for about 5-10% of diabetes cases
- requires daily insulin supplementation
describe type 2 diabetes
- insulin is produced, but use ineffectively
- accounts for 90-95% of diabetes cases
- occurs most often in people who are overweight
- may or may not require modificaiton
describe gestational diabetes
- glucose intolerance that is diagnosed during pregnancy
- requires treatment to normalize maternal blood glucose levels to avoid complications in the infant
- frequency varies among the female population
gestational diabetes is more frequent among what members of the female population?
- african americans, hispanic/latino americans, and american indians
- obese women and women with family history during pregnancy