Superficial Neck Flashcards
bones and carilage of the neck

From what pharyngeal arches do the lesser and greater cornu of hyoid come from?
lesser - second and greater - 3rd
Surface anatomy of the neck (labeled)
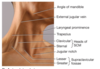
Label a, b, c, d
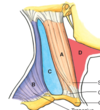
a: sternocleidomastoid
b: posterior cervical region
c: lateral cervical/posterior triangle
d: anterior cervical/anterior triangle
muscles of the neck and inn (labeled)

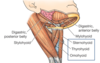
Functions of the SCM

Torticollis
2 type: 1. Fibromatosis - fibrous tissue accumulates in the muscle; most common in neonates
- muscular torticollis = “wry neck;” can be congenital - infants; birth trauma - infants; muscular or nerve injury
Fascial layers of the neck
make the neck complex; 5 compartments: superficial, investing, pretracheal, prevertebral, and alar fascia/carotid sheath

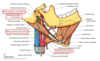
Superficial veins of the neck (know all the ones in bold*)

Cutaneous cervical branches in superficial neck

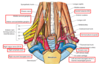
Nerves deep to investing fascia (labeled)
- accessory 2. dorsal scapular 3. nerve to levator scalpulae 4. roots of brachial plexus 5. phrenic n 6. scalene muscles 7. splenius capitis
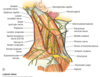
Cutaneous nerves of the neck (labeled)
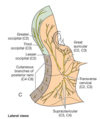
cervical plexus

Ansa Cervicalis
a loop of nerves from the cervical plexus that carry somatomotor innervation to most of the infrahyoid (below the hyoid) muscle in the neck

Anterior cervical and suprahyoid regions: superficial (labeled)

Anterior cervical and suprahyoid regoins: deep (lebeled)