Stem cell biology Flashcards
How can we experimentally demonstrate self-renewal of stem cells?
serial transplantation:
- remove lacZ labelled sperm stem cells from a mouse donor
- inject cells into recipient mouse into endogenous non-lacZ recipient
- visualize that spermatogonia are repopulated into blue colonies from stem cells from the donor

experimental demonstration of stem cell differentiation?
ability to form colonies in soft agar (in vitro) assay
Which types of cells can form teratomas?
pluripotent ES cells
what factors promote plurpotency of stem cells?
oct4, nanog, sox2
HSCs have what type of potency?
multipotent, because they can make all lineages of cells within an organ system
what do transit-amplifying cells do?
go-between for stem cells and differentiated cells
amplifies pool of progenitor cells to replace organ system faster
How is potency determined experimentally?
lineage tracing: process of identifying all progeny of a single cell (in vivo)
- visualize cell lneage by reporter gene expression in stem cells that is passed onto progeny
- label starting stem cell with the reporter and see which cells end up containing the marker
What is the effect of destroying the niche on a stem cell population?
Because the niche helps cells maintain stemness, it will cause them to differentiate.
describe drosophila testis stem cell niche.
signaling from hub cells is proximity-based
- hub cell binds to germ SC and secreted “unpaired” protein
- unpaired miantains committed state of stem cells, so differentiated gonialblast cells divide away from the hub cell

Describe the drosophila ovarian stem cell niche.
stemness maintained by proximity effect to cap cells
- cryoblasts divide and differentiate horizontally, so there is no TGF-beta from cap cells that reaches them to maintain them as stem cells
- in stem cells, TGFB signaling from cap cells activates BMP signal transduction
- BMP activates MAD which turns off expression of bam, which is required for differentiation into an oocye.

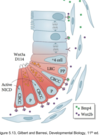
Describe the adult intestinal stem cell niche.
- base of crypt houses ISCs. Here, Wnt2b is high, and Bmp4 is low.
- traveling up the crypt are the transit-amplifying (progenitor) cells, followed by more differentiated cells
- at the tip of the villi, cells die by anoikis (loss of contact)

Describe the ISC types.
two types of ISCs:
- crypt base columnar cells (CBCC): Lgr5+, divide every 9-12 hours, maintained for life (possible because they are next to paneth cells)
- +4 cells: fourth stem cell in from the base, Bmi1+, quiescent
(stromal cells also contribute to stem cell maintenance via Bmp4 and Wnt2b by signaling)
Describe the clonogenic nature of the ISC niche.
An entire crypt and villus can be populated from a single ISC at the very base of the crypt. Know this thanks to lineage tracing (single cell marked with lacZ).
Describe the neutral competition model in the context of ISC niche.
If many CBCCs are placed in the base of a crpyt, one will win out as the ancestor to an entire crypt and villus.
Describe the hematopoietic stem cell niche.
- endosteal niche HSCs are quiescent
- perivascular niche HSCs are rapidly dividing

Which stem cells can function before they have a niche?
hair follicle
How can we recreate the SC niche in vitro?
organoids
-a single SC will grow in soft agar (with signaling from niche cells, with ECM) and will generate the microenvironment consistent with its normal tissue type
How can we study stem cells in vivo?
- can study how long they live via label retention of DNA – will maintain in tissues for a long time because the cells are not dividing too much (stem cells often become quiescent so they don’t divide too much so they are protected from DNA damage and remain viable). Works by pulsing the cells with a nucleotide analog during S phase
How is DNA damage repaired in quiescent stem cells?
Via NHEJ. Though this is error-prone, it is still better than rapidly dividing cells that accumulate much more DNA damage.
Describe in vivo lineage tracing.
Can track progeny over time using a specific marker/reporter:
-Can use cre/lox to recombine a visual marker such as lacZ or GFP into a stem cell specific promotor
Describe this model for lineage tracing.

in vivo, small intestine

Define dedifferentiation and transdifferentiation.
dedifferentiation: terminally differentiated cells revert back to dedifferentiated cell within the same lineage (allows for regeneration of limbs in some organisms!)
transdifferentiation: one differentiated cell gives rise to another differentiated cell in an entirely different lineage (mammalian pancreas, ductal cell induces beta-cell)
Describe regeneration in the mammalian intestine.
Loss of Lgr5+ CRCC stem cells can be replaced through the plasticity of their enterocyte-lineage Alpi+ daughter cells. These move down to the crypt, dedifferentiate, and are now multipotent and able to self-renew.

Application and utility of IPS cells?
- disease modeling
- gene correction, differentiation, and transplantation


