Starting Day 1 of Scott... Flashcards
(373 cards)
Science Caveats
Most of what you learn in every class are abstractions
Abstraction:
1. Something that only exists as an idea
2. A simplified, generalized depiction
To Abstract:
To reduce the information content by omitting irrelevant info
EX: Map of Europe, chemical bonds
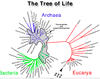
Species are Abstractions
It’s a map of biological organisms
Species is a unit of classification
Species is a taxonomic construct
Before Darwin
Mythology – Adonai/Allah/Ahura Mazda/Jehovah/Marduk/Yahweh etc. made all the organisms in the world perfect and as they are today
Aristotle – Scala Naturae (Scale of Nature)
Carl Linnaeus – “God created, Linnaeus organized.”
Linnean Organization

Traditional Darwin Story
- Darwin boards the HMS Beagle in 1832 for a five year trip around the world, collecting, and observing
- He was greatly impressed by the constantly changing variety of organisms
- ???
- “Evolution!”
Darwin’s Finches

Darwin’s Influences - Stratigraphy
Sedimentary Rock
Stratum
Stratigraphy: Study of rock layers
Sedimentary and volcanic rock is deposited in layers
These layers can be counted and compared
Sedimentary rock –formed from the deposition of material
Stratum – a layer of sedimentary rock that is internally consistent and distinguishable form other layers
Strata
Stratum – a layer of sedimentary rock that is internally consistent and distinguishable form other layers

Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy: Study of rock layers
Sedimentary and volcanic rock is deposited in layers
These layers can be counted and compared

Darwin’s Influences – Charles Lyell
Leading Geologist of the time and close friend of Darwin
He stated that the mechanisms of change are constant over time
He stated that the earth is very old
Darwin’s Influences - Paleontology
Paleontology - the study of fossils
Developed by Charles Cuvier
Cuvier noted that:
Different strata had different fossils
Species appear and disappear
The older the strata the more dissimilar the organisms are to organisms today
Darwin’s Influences – Thomas Malthus
An Essay on the Principle of Population (1798)
Populations are kept in check by their food supply
When the food supply is exhausted there is a competition for scarce resources
“In October 1838, that is, fifteen months after I had begun my systematic inquiry, I happened to read for amusement Malthus on Population, and being well prepared to appreciate the struggle for existence which everywhere goes on from long- continued observation of the habits of animals and plants, it at once struck me that under these circumstances favourable variations would tend to be preserved, and unfavourable ones to be destroyed. The results of this would be the formation of a new species. Here, then I had at last got a theory by which to work”.
Charles Darwin, from his autobiography. (1876)
Darwin’s Influences - Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Chevalier de Lamarck proposed that new species come from old species
He proposed a mechanism involving:
1) use and disuse
2) the inheritance of acquired characteristics
He also coined the word “biology”
Lamarkism: Parts of the body that are used become more developed and parts that aren’t deteriorate
These acquired characteristics are passed on to offspring

Lamarckism Today
Epigenetics - the study of changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the DNA sequence
Some epigenetic changes are heritable
Mechanisms for these changes include the methylation of DNA and vertical transmission of small RNAs
Darwin’s Influences – Alfred Russel Wallace
Came up with Natural Selection independently
Wrote Darwin about it
Had his work published w/some of Darwin’s work added
Made Darwin hurry up and publish Origin of Species before he was completely scooped
Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859)
Darwin never used the word evolution, instead he used “descent with modification”
Natural Selection is the mechanism that explains evolution
Natural Selection
One of the key mechanisms of evolution
The gradual process by which biological traits become either more or less common in a population. This is due to the differential reproduction of the organisms bearing these traits.
Different individuals in a population of organisms have slightly different traits.
These traits affect the fitness of an organism to make copies of itself.
These traits are inherited by subsequent generations of organisms.
Nature selects against organisms that are not fit, and selects for ones that are.
Nature changes over time so traits change over time.
Really long time spans result in the diversity we see today
Artificial vs. Natural Selection
Artificial – Man deliberately decides who gets to reproduce through breeding
Natural – Indifferent Nature decides who gets to reproduce and therefore what traits are maintained. A lot of luck is involved.
Artificial Selection
Wild mustard/cabbage became; broccoli, brussels sprouts, cabbage, savoy, cauliflower, kale, kohlrabi, and collard
Dog breeding

Natural Selection
It’s not about the individual
It’s not about the species or where it’s going in time
It’s mostly about which information encodes for proteins that are useful right now
Survival of the Fittest
Reproduction of the information best at reproducing right now
It’s not about the individual.
It’s not about the species.
Theory of Natural Selection
And Evidence for Evolution
Evolution is a fact
Natural selection is the theory that explains evolution
Evidence For Evolution
Direct Observations
Homologies
The Fossil Record
Biogeography
Evidence For Evolution : Direct Observations
It has been carefully observed and measured by Scientists.
We can make it happen in a controlled laboratory setting
Evolution under controlled conditions
Evolution is scale invariant – it affects molecules, organisms, ecosystems, etc.
Since bacteria can reproduce quickly, their evolution is easier to observe and measure
Techniques have been developed to evolve organisms and even molecules for desired functions
E. coli long term evolution experiment
E. coli long term evolution experiment
Started in 1988 with 12 identical populations of E. Coli
Grow E. Coli in liquid in flasks
Take a little out every day and put into fresh growth media
Take a little out every 75 days and freeze for a frozen fossil record
So far, their cultures have gone through over 56,000 generations
Some adaptations happened in all 12 cultures, some only to some of the cultures
All cultures now grow faster than the initial culture
One culture evolved the ability to consume citrate in the growth media
Sexual PCR
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a biochemical technology in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence.
A technique used to evolve molecules for specific functions
The DNA that encodes for the molecule is shuffled via PCR
The resulting gene products are screened for the desired function and the winners isolated
Subsequent rounds of shuffling are performed on the winners
Repeat
Evidence For Evolution : Fossils
Evidence For Evolution : Fossils
It is extremely rare for an organism to become a fossil
They have to die in just the right conditions to become fossilized
And yet there are so many fossils
This is due to the extreme age of the earth
Problems with the Fossil Record
Problems with the Fossil Record
The fossil record is patchy
This makes sweeping generalizations difficult
For example, “What killed the dinosaurs?”