Sports Medicine: Section 1 Knee Flashcards
(24 cards)
1
Q
ACL attachments and size
A
- Posteromedial aspect of lateral femoral condyle
- Anterior to intercondylar eminences
- 30 mm long
- 11 mm diameter
2
Q
ACL bundles
A
- Anteromedial
- tight in flexion
- anterior restraint
- LACHMANS TEST
- Posterolateral
- tight in extension
- rotational restraint
- PIVOT SHIFT TEST
3
Q
Blood supply to ACL and PCL
A
Middle geniculate artery & the fat pad
4
Q
PCL attachment and size
A
- Anterolateral medial femoral condyle
- Tibial sulcus
- 38 mm long
- 13 mm diameter
5
Q
PCL bundles
A
- Anterolateral
- tight in flexion
- Posteromedial
- tight in extension
6
Q
Meniscofemoral ligaments
A
- Origin: posterior horn of lateral meniscus (variable)
- Insertion: substance of the PCL
- HUMPHREY
- anterior
- Wrisberg
- posterior
7
Q
Superficial MCL attachments
A
- AKA tibial collateral ligament
- Origin: 3.2mm proximal and 4.8mm posterior from medial femoral epicondyle
- Insertion: proximal tibia deep to the Pes Anserinus (61.2mm distal to knee joint)
8
Q
Deep MCL attachments
A
- Capsular thickening
- Attaches to medial meniscus - Coronary ligaments
9
Q
LCL attachments
A
- AKA fibullar collateral ligament
- Origin: Posterior and superior to popliteus tendon insertion on lateral femoral epicondyle
- Insertion: fibullar head, MOST ANTERIOR STRUCTURE
- Behind axis of rotation –> tight in extension

10
Q
Posteromedial corner components
A
- Runs next to deep MCL
- Rotational restraint
- Three components
- Semimembranosus capsular thickenings
- Posterior oblique ligament
- Oblique popliteal ligament (post. capsule thickenings)
11
Q
Posterolateral corner components (PLC)
A
- Commonly injured in multiligamentour injuries
- Primary stabilizer of tibial external rotation
- 7 components
- Biceps femoris
- IT band
- Popliteus (inserts inferior, anterior to deep MCL)
- Popliteofibular ligament
- Lateral capsule
- Arcuate ligament
- Fabellofibular ligament
12
Q
Medial structures of the knee
A
- Layer I
- Sartorius
- Fascia
- Layer 2
- Superficial MCL
- Posterior oblique ligament
- Semimembranosus
- Layer 3
- Deep MCL
- Capsule

13
Q
Order of tendinous insertion:
proximal fibula
A
- Anterior to posterior
- LCL
- Popliteofibular ligament
- Biceps femorus
14
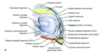
Q
Lateral structures of the knee
A
- Layer 1
- IT tract
- Biceps femorus
- Fascia
- Layer 2
- Patellar retinaculum
- Patellofemoral ligament
- Layer 3
- Arcuate ligament
- fabellofibular ligament
- capsule
- LCL
15
Q
Medial meniscus
A
- Type I collagen (because it has some vascularity)
- “C” shaped
- Intermeniscal ligament anteriorily
- Coronary ligaments peripherally
- Less mobile than lateral meniscus
16
Q
Lateral meniscus
A
- Type I collagen (because it has some vascularity)
- Circular shaped
- Intermeniscal ligament anteriorily
- Coronary ligaments peripherally
- More mobile than medial meniscus
17
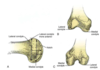
Q
Femoral condyles
A
- Lateral
- Greater AP dimensions
- Relativley straight
- Terminal sulcus
- Groove for poplitues
- Medial
- Smaller AP dimensions
- More curved –> screw home mechanism (ext rot of med tib plateau with full knee ext)
18
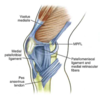
Q
Patellar restraints
A
- Restraints
- Trochlea
- Vastus medialis & lateralis
- together form patellar retinaculum
- Medial patellofemoral ligament
19
Q
Medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL)
A
-
Insertion: anterior and distal to adductor tubercle
- also just superior to the superficial MCL
- Origin: medial border of patella (jxn of prox and middle third) & undersurface of VMO
- Resposible for 50% of total medial restraint
20
Q
Common causes of acute hemarthrosis
A
- ACL tear (70%)
- Patella dislocation
- Osteochondral fracture
- Isolated meniscal tear
21
Q
What two nerves need to be protected during meniscal repair?
A
- Medial repairs
- Saphenous nerve - anterior to both the semiT and Gracilis. Posterior to inferior border of sartorius
- Lateral repairs
- Peroneal nerve - posterior to biceps femoris
22
Q
Bakers cysts
A
- Related to meniscal pathology
- Resolve with tx of primary cause
- Found between semimembranosus and medial head of gastroc
23
Q
Discoid meniscus
A
- Classification
- Incomplete
- Complete
- Wrisberg variant
- Mechanical sx of popping and locking
- Xray shows widened joint space, squaring of lateral femoral condyle
- MRI shows meniscus on 3 consecutive sagittal slices
- Tx with partial meniscectomy (saucerization)
24
Q
Bone bruises
A
- >50% of ACL injuries
- commonly near sulcus terminalis of LFC and posterolateral tibia
*


