Spine Flashcards
Spinal History Red Flags
(3)
- Fracture
- Trauma - remember, elderly may fx c minor tx
- Compression
- Tumor/Infection
- Hx cancer
- Constitutional changes
- > 50 yo
- Neuro compromise
- Cauda Equina Syndrome
- Ask about bowel/bladder function
- **Prepare to eval rectal tone **
- Cauda Equina Syndrome
Spine-Specific Hx Questions
(5)
- Injury
- Injury type
- Mechanisms
- violence
- work related
- Pain eval (OPQRSTUVW)
- ADL’s *(think bathing) *
- Bladder/bowl function
- Attempted tx
- OTC meds
- Massage
- Chiropractory
Spine Palpation
(4 aspects)
Check all points for pn/spasm while pt is standing (if possible)
- Spinous processes
- Paraspinal muscles
- Pelvis level
- SI joint
Neurological Components, Spinal Exam
(4 general)
Conduct on upper and lower limbs
- Dermatomes
- Reflexes
- Pulse
- Sensation
Gait Protocol
- Observe gait pattern when pt walks into room
- Antalgic (limping)
- Trandelenburg
- Short leg
- Foot Drop
- Have pt toe walk (S1)
- **Heel walk (L4/5) **
Standing Evaluation
- Nerve Root Tension - pt stand c one knee bent in spite of equal leg lengths (this poisition relieves tension)
- Prolapsed Intervertebral Disc - “List” or “tilt” may be compensatory for nerve root compression
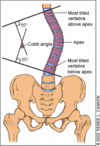
Abnml Spinal Curvature
- Spinally mediated (exaggerated curves)
- Muscle weaknesses/spasm

Spinal Landmarks
(
- T3 - spine of scapula
- T7 - just distal to inf angle of scapula
- L4 - Sacrospinalis
- S2 - Gluteus medius
These are helpful for palpating spinal tenderness - you can identify potential level of injury

Palpation Points, Spine
(5)
- Vertebral tenderness - localized vs generalized
- Paraspinal muscles - spasm/tenderness
- Sacroiliac joint - tenderness
- Groin - masses/abscesses
- Abdomen - masses/abscesses
Spinal ROM
- Flexion/extension
- Lateral flexion/extension
- Rotation L/R
Seated Inspection, Spinal Exam
(2 aspects)
- Observe movement on/off table
- Assess pt posture for obvious conditions
Straight Leg Raise (SLR)
- Lay pt supine
- Passively raise 1 leg at a time up to 60 degrees (going further may introduce hamstring tightness)
- Note the angle @ which pn radiating down leg occurs
+ exam = sciatic pn/parasthesia/discomfort/burning c ligament laxity that may be contra or ipsilateral to SC injury
- exam = 80-90 degrees s pn (potential tightness)
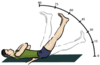
Sciatic Stretch Test
- Perform straight leg raise (passively flex leg from supine)
- Dorsiflex ankle
+ exam = additional nerve pn radiating down leg
Patrick’s/Faber’s Test
Procedure:
- Place pt supine
- Have pt place L knee just proximal to R patella
- Stabalize pelvis sharply, externally rotating hip to approach knee to table
- Repeat on other side
Results:
+ exam = hip/sacroiliac disease or injury
- exam = normal joint mobility
Spinally Relevant Reflexes
(7)
*Perform for upper and lower extremities, respectively *
- Biceps = C5
- Brachioradialis = C6
- Tricep = C7
- Knee = L4
- Ankle = S1
- Anal = S2/S3/S4 reflex arc (like cauda equina syndrome)
- Babinski = upper motor neurons