Skin, Hair, Nails Flashcards
What is a macule?
Lesion is flat, nonraised, and <1 cm.

What is a patch?
Lesion is flat and >1 cm.
What is a papule?
Papule: Lesion is raised, <1 cm, and not fluid filled.
What is a plaque?
Plaque: Lesion is raised, >1 cm, but not fluid filled.
What is a vesicle?
Vesicle: Lesion is raised, <1 cm, and filled with fluid.
What is a bulla?
Bulla: Lesion is raised, >1 cm, and fluid filled.
What does an annular shape entail?
ring-like, with central clearing
Describe a nummular lesion
coin-like, no central clearing
What are the important characteristics to include with skin lesions?
- number
- size
- color
- shape
- texture
- primary lesion
- location
- configuration.
What does confluent mean?
Lesions that tend to run together
Describe a morbilliform drug eruption
Multiple 3–8-mm erythematous confluent round macules on chest, back, and arms

Describe benign melanocytic nevi
Multiple scattered 2–4-mm round and oval brown macules, symmetrically pigmented, on back and chest with reticular pattern on dermoscopy

Describe benign melanocytic nevus
Solitary 6-mm dark brown round symmetric macule on upper back

What is the ABCDE rule for detecting melanoma?
-
Asymmetry - Of one side of mole compared to the
other - Border irregularity - Especially if ragged, notched, or blurred
-
Color variations - More than two colors, especially blue-black, white (loss of pigment due to regression), or
red (inflammatory reaction to abnormal cells) - Diameter >6 mm - Approximately the size of a pencil eraser
- Evolving - Changing rapidly in size, symptoms, or morphology
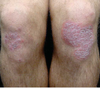
Describe plaque psoriasis
Scattered erythematous to bright pink well-circumscribed flat-topped plaques on extensor knees and elbows, with overlying silvery scale
Describe atopic dermatitis
- Bilateral erythematous, lichenified (thickened from rubbing) poorly circumscribed plaques on flexor wrists, antecubital fossae, and popliteal fossae
- Usually beginning in infancy, this red, itchy rash most commonly occurs where the skin flexes — inside the elbows, behind the knees and the front of the neck. When scratched, the rash can leak fluid and crust over. People with atopic dermatitis may experience improvement and then flare-ups.

Describe herpes simplex virus vessicles
Multiple 2–4-mm vesicles and pustules on erythematous base
Describe a herpes zoster (shingles) lesion distribution
Grouped 2–5-mm vesicles on erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution that does not cross the midline
Describe how contact dermatitis presents
Scattered 2–5-mm erythematous papules and vesicles with transudate crust, some with linear arrays
Describe a pustule
Small palpable collection of neutrophils or keratin that appears white
What is a Furuncle?
Inflamed hair follicle; multiple furuncles together form a carbuncle
What is a wheal?
Area of localized dermal edema that evanesces (comes and goes) within a period of 1–2 days; this is the essential primary lesion of urticaria

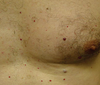
What are cherry angiomas?
A cherry angioma is often bright red, circular or oval in shape, and small — usually ranging in size from a pinpoint to about one-fourth of an inch in diameter. Some cherry angiomas appear smooth and even with your skin, while others appear slightly raised. They most often grow on the torso, arms, legs, and shoulders.
What are epidermal cysts?
- Epidermoid cysts are noncancerous small bumps beneath the skin. They can appear anywhere on the skin, but are most common on the face, neck and trunk.
- Epidermoid cysts are slow growing and often painless, so they rarely cause problems or need treatment

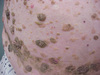
What is seborrheic keratosis?
- A seborrheic keratosis usually appears as a brown, black or light tan growth on the face, chest, shoulders or back.
- The growth has a waxy, scaly, slightly elevated appearance. Seborrheic keratoses don’t become cancerous and aren’t thought to be related to sun exposure, but they can look like skin cancer.
- Seborrheic keratoses are normally painless and require no treatment. You may decide to have them removed if they become irritated by clothing or for cosmetic reasons.
What does lichenified mean?
- Lichenified means the skin has become thickened and leathery. This often results from continuously rubbing or scratching the skin.
- Chronic irritation due to conditions such as eczema can cause lichenified skin

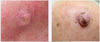
What are some characteristics of squamous cell carcinoma?
- Keratoacanthomas are SCCs that arise rapidly and have a crateriform center
- Often have a smooth but firm border
- SCCs can become quite large if left untreated (Note: highest Sites of metastasis are the scalp, lips, and ears)
Describe petechia/purpura
- Deep red or reddish purple round, sometimes irregular, flat lesions that fade away over time;
- petechia, 1–3 mm; purpura are larger
Describe Ecchymosis
- COLOR & SIZE: Purple or purplish blue, fading to green, yellow, and brown with time; ariable size, larger than petechiae, >3 m
-
SHAPE: Rounded, oval, or irregular; may have a central
subcutaneous flat nodule (a hematoma
What is Onycholysis?
A painless separation of the whitened opaque nail plate from the pinker translucent nail bed. Fingernails that extend past the fingertip are more likely to result in the traumatic shearing forces that produce onycholysis. Starts distally and progresses proximally, enlarging the free edge of the nail.

What causes Onycholysis?
- Local causes: Trauma from excess manicuring,
- psoriasis, fungal infection, and allergic reactions to nail cosmetics.
- Systemic causes: Diabetes, anemia, photosensitive drug reactions, hyperthyroidism, peripheral ischemia, bronchiectasis, and syphilis.
What is anonchia?
The absence of the fingernails and toenails.

Describe Koilonychia
It is a nail disease that can be a sign of hypochromic anemia, especially iron-deficiency anemia. It refers to abnormally thin nails (usually of the hand) which have lost their convexity, becoming flat or even concave in shape
Describe the hairloss seen in male pattern hairloss
- In men, look for frontal hairline regression and thinning on the posterior vertex
- The hair pull test is normal or only pulls a few hairs.

Describe the hairloss seen in female pattern hairloss
- In women, look for thinning that spreads from the crown down without hairline regression
- The hair pull test is normal or only pulls a few hairs.

Describe Alopecia Areata
There is sudden onset of clearly demarcated, usually localized, round or oval patches of hair loss leaving smooth skin without hairs, in children and young adults. There is no visible scaling or erythema.

Describe Tinea Capitis (“Ringworm”)
- There are round scaling patches of alopecia, mostly seen in children. There may be “black dots” of broken hairs and comma or corkscrew hairs on dermoscopy.
- Usually caused by Trichophyton tonsurans from humans, and less commonly, Microsporum canis from dogs or cats. Boggy Paques are called kerions.



