Skillstorm Intro to Coding - Data Structures in Java Flashcards
In Java, every Object has two comparison methods. What are they?
equals and hashCode Methods
The equals and hashCode methods must be _________ to work properly.
Why?
Overridden
Without them, you would have to create very large “if” comparisons, comparing every field from an object, making code really confusing and hard to read.
Fill in the Blanks of the attached image
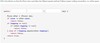
boolean equals Object
Fill in the blanks of the following code:
public _____ _____ () {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + size;
if (topping == null) {
result = prime * result + 0;
}else {
result = prime * result + topping.hashCode();
}
return result;
}
int hashCode
A List is an _________ collection that may contain _________ elements.
Ordered
duplicate
What are the two types of general-purpose list implementations?
ArrayList and LinkedList
Are Java LinkedList automatically Doubly LinkedList?
Yes
ArrayLists are resizable. But by what size do they increase when they are full?
50%
ArrayList and LinkedList are both ordered by ________ position.
index
Because you can add and remove from the heads and tails of LinkedList, this makes them perfect for __________ and __________.
Stacks (and) Queues
What is Last In First Out? Stacks or Queues
Stacks
What is First In First Out? Stacks or Queues
Queues
Manipulating LinkedList. See image…
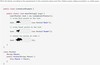
add
add
remove
Manipulating ArrayList. See attached image…

< String >
add
get
size
What is a Queue?
A collection for holding elements prior to processing
A ________ is a double-ended queue.
Deque
A Deque supports ________, removal, and __________ of elements at both end-points!
insertion,
examination
Deque interface implements both ______ and ______ at the same time.
Stacks
Queues
Queue Manipulation. See attached images…

queue. offer
queue. peek
queue. poll
Stack Manipulation. See attached images…

push
push
pop
peek
- Is a Map an object that maps equal keys?
- What are mapped to unique keys?
- Do Maps include methods for basic operations?
- Do Maps include methods for non-bulk operations?
- Do Maps includes methods for collection views?
- False: They map unique keys
- Values
- True
- False: They include methods for bulk operations
- True
Java contains three general-purpose Map implementations. What are they?
HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap
HashMap Manipulation. See attached image…

put
put
get
size
containsKey
Can a Set contain duplicate elements?
No
Sets add a stronger contract on the behavior of the _______ and _______. It allows Set instances to be compared meaningfully even if their implementation types differ.
equals (and) hashCode
What are the three general-purpose Set implementations?
HashSet, TreeSet, and LinkedHashSet
HashSet Manipulation. See attached images…
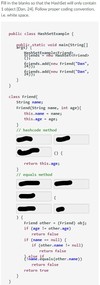
public int hashCode
public boolean equals Object obj
LinkedList is a(n) ______ collection.
Ordered
LinkedList has an underlying array that changes size as needed? True or False
False
Two objects with the same hashCode must be equal? True or False
False
A Queue is a first-in last-out collection? True or False
False
Two objects that are equal must have the same hashCode? True or False
True
The equals method in java.lang.Object compares two objects and returns a(n)______.
boolean
A LinkedList in Java is _______ by default.
Doubly-linked
The performance of accessing a value in a HashMap is ______________.
Constant Time
An ArrayList will grow ___ in size when it reaches its maximum capacity.
50%
A Stack is a ______________ collection
last-in first-out
A HashSet will maintain duplicate values. True or False….
False
In Java with Object Equality, you can decide when two objects are equivalent, but with what method and how is it written in Java?
- The method is ==> java.lang.Object.equals method
- In Java it is written as ==> public boolean equals(Object other)
In Object Equality, does it check the memory location by default?
Yes
In Object equality what must you override to compare object state?
The method
True or False, in Object Equality, some data structures require unique objects…
True
True or False, the hashcode isn’t used to give a consistent integer that represents the object…
False
How is the hashCode method written in code?
public int hashCode()
Is hashCode loved by HashMap, HashSet, and others?
Yes
True or False, HashCode puts objects into a smaller group to optimize searching…
True
Fill in the blanks of this code:
public _____ _____ ( _____ obj) {
Pizza other = (Pizza) obj;
if (size != other.size)
return false;
if (topping == null)
if (other.topping != null)
return false;
} else if (!topping.equals(other.topping))
return false;
return true;
}
boolean equals ( Object obj)
True or False, ArrayList is a class in the Collections API in Java…
True
What does ArrayList do in Java?
- Creates an array
- Provides methods for working with ArrayList
What is the ArrayList default size when it is created?
16
True or False, ArrayList is not mutable…
False
What happens if an ArrayList fills up?
It grows 50% larger to accommodate more elements
True or False, ArrayList does not allow for duplicate elements…
False
True or False, in ArrayList order of insertion is preserved…
True
LinkedList is a Class in the Collections API in Java, True or False?
True
What is the LinkedList a series of?
Nodes
What are Nodes in LinkedList?
A Node wraps up a value (String, Pizza, etc.)
How are Nodes in LinkedList connected?
They are “Linked” by a reference to the next Node
Are LinkedList singly-linked or doubly-linked?
Doubly-linked
How are doubly-linked Nodes connected?
The Nodes have a previous and next reference.
LinkedLists allow duplicate elements, True or False?
True
Order of insertion is not preserved in LinkedList, True or False?
False
Fill in the blanks of the following code:
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new LinkedList();
// write Dill pickle to the list
list.______ (new Pickle(“Dill”));
// write Sweet pickle to the list
list.______ (new Pickle(“Sweet”));
// delete the pickle at index 1
list.______ (1);
}
}
class Pickle{
String flavor;
public Pickle(String flavor) {
this.flavor = flavor;
}
}
- add
- add
- remove
Fill in the blanks in the following code:
// create an ArrayList of Strings
ArrayList _____ list = new ArrayList<>();
// add XYZ to the list
list.______ (“XYZ”);
// print element at index 2
System.out.println(list.______ (2));
// print how many Strings are in the list
System.out.println(list.______ ());
- add
- get
- size
Is the Queue an interface in the Collections API in Java?
Yes
True or False, the queue is First-in/First-out…
True
- When you Push in a Queue, what happens?
- What you Pop in a Queue, what happens?
- Node goes to the tail
- Node goes to the head
True or False, the Queue doesn’t allow for duplicate elements…
False
True or False, in a Queue, the order of insertion is preserved…
True
True or False, the Stack is a Class in the Collections API in Java…
True
Stack is Last-in/First-out, True or False?
False and True, it can be First-in/Last-out and Last-In/First-Out!
- In a Stack what happens when we Push?
- In a Stack what happens when we Pop?
- Data/Node goes to the tail
- Data/Node comes from the tail
True or False, Stacks don’t allow for duplicate elements…
False
In Stacks order of insertion is preserved, True or False?
True
Fill in the following blanks in the code:
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
// add new Person to tail ‘push’
______._____ (new Person());
// check what’s at the head of the queue
______._____();
// ‘pop’ the head of the queue
System.out.println( _____._____ ());
}
}
class Person{}
- queue.offer
- queue.peek
- queue.poll
Fill in the blanks in the following code:
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
// add two cards to the stack
stack. _____ (new Card(“A of Spades”));
stack. _____ (new Card(“K of Diamonds”));
// remove the top of the stack
System.out.println(stack._____ ());
// look at (but not remove) top of the stack
System.out.println(stack._____ ());
}
}
class Card {
String value;
public Card(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
- push
- push
- pop
- peek
A HashMap is not a class in a Collections API that stores key-value pairs, True or False?
False
In HashMaps, how do you identify the value?
By the Key
For example, a Social Security Number maps to a U.S. Citizen.
True or False, Keys do not have to be unique whereas values must be unique…
False, keys must be unique while values have no restriction
What happens if a key already has a value and then you add a different value?
It updates the value for that key.
For example, if the key is 79 and the value assigned to it is “Joe Rogan takes horse dewormer!” and then you change the value of 79 to “Joe Rogan actually takes Soolantra (generic brand for Ivermectin for humans for the last 16 years),” then the value for the key 79 updates to the last quote!
In a HashMap, stores “Entry” objects in a Queue, True or False?
False, the “Entry” objects are stored in an array.
What does the Object’s HashCode do?
It helps calculate the array index to store the object in.
In HashMaps, if the calculation for 2 indices yields the same value, what is the outcome?
HashMap collisions occur and then Java appends the Entry in a a LinkedList.
In HashMaps, if the LinkedList gets too long, what problem occurs?
Read operations are much slower.
What is the time complexity of HashMap Reads?
O(1) - Constant Time
In HashMaps, when LinkedLists get too long, what happens?
When the LinkedList is 8+, it is converted to a red-black tree.
Fill in the blanks of the following code for HashMap:
public class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap citizens = new HashMap<>();
// add two entries to the map
citizens. _____ (“5001”, new Citizen(“Brian”));
citizens. _____ (“4524”, new Citizen(“Diane”));
// retrieve the value for the key 5001
System.out.println(citizens._____ (“5001”));
// print how many entries are in the map
System.out.println(citizens._____ ());
// print if the key 5001 is in the map
citizens._____ (“5001”);
}
}
class Citizen{
String name;
Citizen(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
put
put
get
size
containsKey
True or False, HashSet is a class in the Collections API…
True
In the HashSet, are duplicates are allowed?
No, HashSets only store unique objects.
True or False, in HashSets order of elements is guaranteed…
False, Order of elements is not guaranteed.
Do HashSets have indices available?
No, there is no index available unlike in Lists.
Where do HashSets store values?
HashSets store values inside of a HashMap.
Use set.add();
to store values tied to a key in a HashMap.
Fill in the blanks of the following HashSet Code:
public class HashSetExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSetExample friends = new HashSet();
friends. add(new Friend(“Dan”, 24));
friends. add(new Friend(“Dan”, 24));
}
}
class Friend{
String name;
Friend(String name, int age){
this. name = name;
this. age = age;
}
// hashcode method
_____ _____ _____ () {
return this.age;
}
// equals method
_____ ______ ______ ( _____ ______ ) {
Friend other = (Friend) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false
return true
}
}
- public int hashCode
- public boolean equals ( Object obj )
LinkedList is a(n) ______ collection
Ordered
True or False, LinkedList has an underlying array that changes size as needed…
False
True or False, Two objects with the same hashcode must be equal…
False
True or False, A Queue is a first-in last-out collection…
False
True or False, Two objects that are equal must have the same hashcode…
True
The equals method in java.lang.Object compares two objects and returns a(n) _____ .
boolean
A LinkedList in Java is _____ by default.
Doubly-linked
The performance of accessing a value in a HashMap is _____ .
Constant time
An ArrayList will grow _____ in size when it reaches its maximum capacity.
50%
A Stack is a _____ collection.
last-in first-out
A HashSet will maintain duplicate values, True or False?
False
Why does the main method have the static modifier?
Because the static modifier allows us to call all members in main without having to create an Object!


