Skeletal Systems 1 Flashcards
(276 cards)
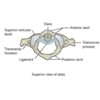
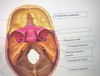
Where is the Cranial Cavity?
Top of the skull

What is the Calvaria?
Top of the skull

What does the Cranial base consist of?
The floor of the Cranial Cavity
Anterior cranial fossa
Middle cranial fossa
Posterior cranial fossa
(depression)

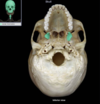
Orbits are?
Eye sockets

What is the nasal cavity?
3-D spaces
Opening of the nose

What is the bony nasal septum?
Ridge in the middle of the cavity (divides the nose)

Piriform aperture
2-D opening
Piriform- “pear-shaped”

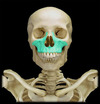
What is the hard palate?
Inferior, bottom of the skull (roof of the mouth)
Constructed from parts of the maxilla and palatine bone

What is the Zygomatic arch?
Cheek of bone
Constructed from parts of the zygomatic and temporal bones

What is the infratemporal fossa?
depression on the side of the hard palate

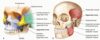
What is the Coronal suture?
Crown of the skull
Structure

What is lambdoidal?
Back of the skull

What is the sagittal suture?
Middle of skull
The line between two bones

What is the squamous suture?
Separates temporal/parietal bones

What is the supraorbital margin?
The upper half of the orbits

Feature
What is the Parietal bone?
2 sections of the skull on most superior side of the skull

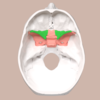
What is the External Occipital protuberance bone?
Bump on the skull

What are the occipital condyles?
Occipital Bone
Feature
Bottom of the skull
Anterior to the foramen magnum

What are Nuchal lines?
Occipital Bone
Feature
Back of the neck

What is the mastoid process?
Temporal Bone
Projection
ledge pointing straight down (breast-shaped)

What is the styloid process?
Temporal Bone
Thin-pocky stick
Projection

What is the Zygomatic process?
Temporal Bone
Projection
Horizontal line, crease
What is the Petrous portion?
Temporal Bone
Structure
Ridges, inside, back ridge

What is the mandibular fossa?
Temporal Bone
Connects jaw
Depression