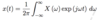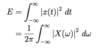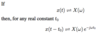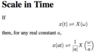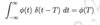Signal Representation and Analysis Flashcards
(36 cards)
What are the two main categories of signal? (What-time?)
What two classifications do these then fall into?
Continuous-time and Discrete-time
Periodic or Non-periodic
What length of time do we assume the four classes of signal all have?
Infinite-duration
What does it mean if a continuous-time signal x(t) is said to be an energy signal?
If the total energy, E, dissipated by the signal over all time is both nonzero and finite.
Thus the magnitude of the signal must tend to 0 as time heads to infinity.
What is the equation for E, the energy dissipated by a signal over all time?

What does it mean for a signal to be a power signal?
If the average power delivered by the signal over all time is both nonzero and finite.
What is the equation for P, the power of a signal?
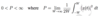
Name a type of signal which is not an example of an energy signal.
A periodic signal has finite energy over one period, so consequently has infinite energy. However has a finite average power and is therefore a power signal and not an energy signal
How do we convert our abstract signal energy and power values to real values for use in circuits?
Divide by the resistance in Ohms
What is the simplified equation for power for a periodic signal?
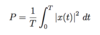
Using the Fourier Series (trignometric form) how can we represent any finite-power periodic signal x(t) with period T ?

What is the fundamental frequency of a periodic signal x(t), with relation to the Fourier series of that signal.

The fundamental frequency is the inverse of the fundamental period

How do we find the fourier coefficients An and Bn in the trignometric Fourier Series of a signal?

How can a complex phasor of amplitude A and frequency ω0 be split into real and imaginary trignometric parts?
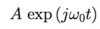

Using the Complex Fourier Series how can we represent a periodic signal x(t)?

How do we calculate Xn , the complex fourier coefficient?
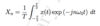
Define how the complex coefficient of the fourier series Xn relates to the trignometric coefficients An and Bn. Consider the cases:
(i) . n >0
(ii) . n=0
(iii) . n<0
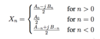
Write the equation for xn(t), the nth harmonic of a complex fourier series

If the product of two periodic signals is integrated over one period and the result is zero then what can we say about those signals?
They are orthogonal (at 90o)
How do we calculate the power of a signal from its complex fourier coefficients?
Use Parseval’s Theorem

What is Parsevak’s Theorem for complex Fourier coefficients?
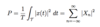
What is Parseval’s theorem for trignometric fourier coefficients?
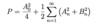
How do we use the principles of the Fourier Series for a non-periodic signal; ie: T→∞
We instead use the forward Fourier Transform
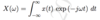
Give the formula for the forward Fourier transform
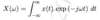
Give the formula for the inverse Fourier transform