Shoulder, Arm, Elbow Flashcards
Label all:


The 3 bones of the shoulder region:
- Clavicle
- Scapula
- Proximal Humerus
What four muscles attach to the vertbral border of the scapula?
- rhomboid
- trapezius
- levator scapulae
- serratus anterior (subscapular side)
Label all:


Label all:


Label all:


What is the most frequent site of fracture on the proximal humerus?
surgical neck
Label all:

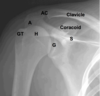
The three shoulder joints:
- sternoclavicular
- acromioclavicular
- glenohumeral
What kind of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
saddle joint
What is located within the sternoclovicular joint and what is its function?
- Articular disk; divides joint into two sections
- Allows for movements in different planes
Instead of dislocating, what does the clavicle do instead in response to excessive force?
- fractures mid-shaft
- protects the carotid artery and trachea behind the sternoclavicular joint from dislocation.
When you have a clavicle fracture mid-shaft, what pulls the lateral side downward?
gravity/weight of the limb
When you have a clavicle fracture mid-shaft, what pulls the medial side upward?
sternocleidomastoid muscle

What are the two ways to treat an overriding clavicular fracture?
- non-surgical: figure-8 bandage (BONE LUMP)
- surgical: plate and screws
The acromioclavicular joint is reinforced by:
coracoclavicular ligament

Shoulder separation is:
AC joint dislocation
Shoulder dislocation is:
glenohumeral joint dislocation
What injury and grade is this?

grade 1 shoulder separation
- AC joint dislocation with NO coracoclavicular ligament tear.
What injury and grade is this?

grade 3 shoulder separation
- AC joint dislocation with coracoclavicular ligament tear.
What kind of joint is the glenohumeral joint?
ball and socket
Label all:


Role of the subacromial bursa:
- lubrication and decrease friction
- bursitis = inflammation of the bursa
The two ligaments that support the glenhumeral joint:
- coracohumeral ligament
- glenoid labrum
MAIN SUPPORT ARE
THE ROTATOR CUFF MUSCLES


















