Session 6: Regulation of Serum Potassium Flashcards
Normal serum K+
3.5 - 5.5 mmol/l
Where can most of the K+ be found in the body?
Intracellularly (Around 140 mmol/l)
In which foods can you find potassium?
Bananas Avocado Cocoa/chocolate Coconuts Potatoes Tomatoes
How much of a male’s total body mass consist of fluid?
Around 60%
How much of a female’s total body mass consist of fluid?
Around 55%
Why do males consist of more fluid than females?
Because males generally have more muscle. More muscle -> more water
Rough fraction of fluid in elderly.
45-50%
Rough fraction of fluid in infants
73-75%
ECG changes of hyperkalaemia.
Tall T wave Prolonged PR interval Widened QRS duration Absent P wave Sinus wave
ECG changes of hypokalaemia.
Depressed ST segment T wave inversion Prominent U wave
Complications of hyperkalaemia
Nerve dysfunction, muscle weakness. Ventricular fibrillation, asystole.
Complications of hypokalaemia
Atrial fibrillation Muscle weakness Muscle cramps Constipation Cardiac arrest
Initial concentration of K+ in ultrafiltrate
3.5 - 5.5 mmol/l
Where is potassium reabsorbed in the nephron?
PCT Thick ascending limb of loop of Henle
What happens to K+ in the DCT and collecting duct
It can be secreted into the lumen of the tubule again.
Where is most of potassium reabsorbed?
In the PCT
How much potassium is reabsorbed in the PCT?
Roughly 67%
State the names of the drugs acting on each part of the nephron.
1
2
3
4
5
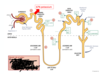
1 - Acetazolamide
2 - Osmotic diuretics like Mannitol
3 - Loop diuretics like furosemide
4 - Thiazides
5 - Spironolactone
Causes of raised potassium (Broad)
Lack of excretion
Release from cells
Excess administration
Causes of raised potassium due to lack of excretion
Acute kidney injury
Chronic kidney disease
Potassium sparing diuretics like Spironolactone
ACE - inhibitors, ARBS
Aldosterone deficiency
Causes of raised potassium due to release from cells.
Acidosis
Cellular breakdown like in ischaemia, toxins, chemo or rhabdomyolysis
Give examples of excess K+ administration causing hyperkalaemia.
Potassium containing fluids or medications
Blood transfusions
Immediate hyperkalaemia treatment
Insulin to shift K+ into cells. This last for 6 hours
Salbutamol has same action as insulin - 6 hours
Calcium which stabilisis cardiac membrane potential.
Calcium gluconate is a common treatment
Long-standing hyperkalaemia treatments
Low K+ diet
Calcium resonium to bind potassium in gut
Stop medications causing raised K+
Furosemide
Dialysis


