Session 2 Flashcards
(26 cards)
Explain what this graph is showing

State how the enzyme CYP2D6 varies in different races. State what it metabolises and what it is inhibited by.
SSRI
typical antipsychotic
class 1 antiarrythmic

How can drugs be eliminated (processes that determine its elimination?)

State some drugs which are passively absorbed, actively secreted and filtered from the nephron

How do you work out clearance of a drug

How do you work out apparent volume of distrubution

State drugs which have a large Vd

What is first & zero order kinetics?
• 1st Order kinetics - Linear
Rate of elimination is proportional to drug level. Constant fraction of drug eliminated in unit time. Half life can be defined.
• Zero Order kinetics – Non-linear
Rate of elimination is a constant.

Given this information complete a graph showing how conc of drug in the plasma would change with increasing dose for 1st and zero order drugs
• Zero order drugs are more likely to result in toxicity
• Fixed rate of elimination per unit time
• “Small” dose changes may
– Produce large increments in [plasma]
– Lead to toxicity
• No half life is calculable
• Drug monitoring essential
Drug Monitoring
• Several PK reasons:
– Zero order kinetics
– Long half-life
– Narrow therapeutic window
– At greater risk of drug-drug interactions
• Others include:
– Know toxic effects (e.g. bone marrow suppression or
alteration in U+Es)
– Monitoring therapeutic effect (e.g. BP, glucose etc)

What is this graph showing?

Describe the pK for digoxin and how we must prescribe it
If patient becomes digitoxin -> bradycardia, xanthopsia, vomiting
If normal GFR :40hourstoreducethep[drug]to50%
• Ifrenalfailurepresent,thenclearanceisreduced–t1/2 will be increased and thus longer for [drug] to return to therapeutic values.

How do you work out loading dose?

What does k mean for elimination?

Calculating half life



What is the therapeutic index?
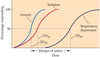
The therapeutic index is the relationship between concentrations causing adverse effects and concentrations causing desirable effects
Therapeutic index = EC50 (adverse effect) EC50 (desired effect)

Examples of drugs with narrow therapeutic windows include ?
Warfarin, Aminophylline, Digoxin and aminoglycoside antibiotics Note: peak and trough blood levels

State CYP450 inhibitors and inducers

State how codeine can be metabolised


What drugs can lead to a prolonged QT interval?


- In hepatic disease you must be careful of accumulation of ?
- What is the effect of a reduced CO
- What is the effect of grapefruit juice?
- Opiates
- Reduce hepatic and renal clearance
- Image

Use & effect of cranberry juice

What is an ADR?
Major (permanent / life threatening)
Moderate (requiring additional treatment)
Mild (trivial or unnoticeable)





