Session 10 - Pathology in pictures Flashcards
The heart (1)

- Hypertrophy
- Ascentric left ventricular hypertrophy
- Aortic valve stenosis
- Hypertension (functional demand increase)
- Coronary heart disease
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

hypertrophy
increase in cell size without cell no. increase
The heart (2)
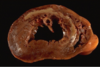
- MI with tissue necrosis (white)
- Old necrosis in this photo (coagulative)
- Due to loss of blood supply to ischaemia
- Not a fresh infarct- would see area of necrosis
- Old necrosis in this photo (coagulative)
- White infarct- no dual blood supply
- Thinner walls
- Compensatory hypertrophy of adjacent myocardium
- Fibrosis

blood vess;es

- Abdominal Aortic Aneursym
- Just above the iliac bifurcation
- Thrombus formation which fills the blood vessel
- Aneurysm- local dilation of the arterial wall due to weakening of the arterial musculature
*
why people die of an AAA
Atherosclerotic deposition on wall of vessel which weakens the medial of the wall –> starts to dilate
- rupture of AAA
- blood loss- hypovolemia
- embolism of original thrombus- goes into leg- acute ischaemia
risk factors for rupture of AAA
hypertension
the limb

- Dry gangrene- necrosis visible to the naked eye
- Dry gangrene Coagulate necrosis
- Wet gangrene - liquefactive necrosis
- Treatment- amputation
the lungs

heavy exposure to smoke or pollution
the alveoli

- These alveoli should be clear
- Neutrophils- acute inflammation affecting one lobe of the lung
- Lobile pneumonia
What is this

a saddle embolism
- commonly refers to a large pulmonary embolism that straddles the bifurication of the pulmonary trunk–> extending into the left and right pulmonary arteries
key features of thrombus vs normal clotting
- lines of zahn
- very firm and solid
features of Virchows triad
- Hypercoagulability
- Damage to the wall
- Haemostasis
pulmonary embolisms generally come from
DVTS
risk factors for DVTS
Smoking
Pregnancy
Immobility
Male
Fracture
Cancer- prothrombotic state
what is this?

Mesothelioma- due to asbestos- constant repair of pleural cells (white part surrounding lungs)
granuloma
central caseating necrosis
features of granuloma
With giant cell- langhans
- Tuberculosis

what is this?

what is this?

appendicitis
what is this?

Red infarct- haemorrhagic infarction
Dual blood supply (collateral blood supply)
what is this?

Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
- Entire mucosa covered in polyps
- All they need to do is acquire more mutations to become malignant
- Treatment- removal of damaged colon (large bowel)
what is this

Gastric biopsy showing Helicobacter pylori
- Chronic inflammation
- Stomach ulcers
- Can lead to cancer


