Separate Biology - B6 Inheritance, Variation and Evolution Flashcards
(112 cards)
Which type of cell division leads to identical cells being formed?
Mitosis
Name the gametes (sex cells) in animal reproduction.
Sperm (male) and egg (female)
Which type of reproduction leads to a variety in the offspring as there is mixing of genetic information?
Sexual reproduction
What is a clone?
Genetically identical offspring (a result of asexual reproduction)
Which type of cell division leads to non-identical cells being formed?
Meiosis
Name the gametes (sex cells) in plant reproduction.
Pollen (male) and egg cells (female)
Which type of reproduction leads to genetically identical offspring?
A-sexual reproduction
Before meiosis, there are 46 chromosomes in a human body cell. How many are there in each gamete after meiosis?
23
Describe the structure of DNA
A polymer made up of two strands forming a double helix.
What is the name for a specific section of DNA that codes for a particular protein?
A gene
What is the genome of an organism?
The entire genetic material of that organism
Give three reasons why understanding the human genome is important.
- Genes linked to different types of disease can be searched for
- Inherited disorders can be understood / treated
- Migration patterns of the past can be traced
Before cell division, what does the DNA in the cell get stored in?
Chromosomes
What does a gene code for?
A particular sequence of amino acids, which make specific proteins
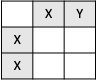
Complete the Punnett square for the % chance of having a mouse with black fur.
F = brown fur, f = black fur

0% chance of having a mouse with black fur

What is embryo screening?
Removing a cell from an embryo and analysing its DNA to look for genetic disorders
Explain what is meant by a ‘dominant allele’
The characteristic is expressed if one or two copies of the allele is present
What name is given to two of the same alleles (e.g TT or tt)?
homozygous
What does ‘genotype’ mean?
What alleles an organism has, e.g. Tt, TT or tt
What is an allele?
A version of a gene
Explain what is meant by a ‘recessive allele’
The characteristic is only expressed if two copies of the allele are present.
What name is given to two different alleles (e.g Tt)?
heterozygous
What does ‘phenotype’ mean?
The characteristics an organism has, e.g. ‘long hair’, ‘black fur’, ‘blue eyes’ e.t.c
Give an example of characteristics controlled by a single gene
Fur colour in mice / red-green colour blindness in humans