Secretory pathway 2 Flashcards
How are vesicles transported in the cell?
—-cytoskeletol transport
The selectivity of vesicular transport is key to maintaining the functional organization of a cell.
Note how topology is maintained.

What initiates formation of coated vesicles and how is vesicle binding regulated?
—-GEF’s and G proteins (ARF1 and Sar1)

ARF1 and Sar1 are related to Ras and Ran.
Sar1 G protein involved in formation of COPII vesicles, whereas ARF1 is involved in the formation of COPI and clathrin-coated vesicles.
What activates ARF1 and what happens to ARF1?
—-ARF-GEF and it embeds in the membrane
In the figure, ARF-GEF activates ARF1 by stimulating it to exchange GDP for GTP. Activation embeds ARF1 in the membrane to form a focal point for vesicle assembly.

Describe the improtance of transmembrane receptors and adaptors?
Not all cargo may have a sorting signal. Some highly abundant secretory proteins travel to various cellular destinations in transport vesicles by bulk flow – they enter the transport vesicle at the same concentration that they occur in the organelle.

What are the 4 sorting signals need to know and what do they do?
Certain sorting signals have been worked out, such as the KDEL and the KKXX, or the di-acidic. The mannose-6-phosphate signal is the best characterized in terms of mediating specific delivery of specific cargo.
Know: KDEL, mannose-6-phosphate, KKXX, di-acidic

What is the purpose of coat proteins and what is a specific one?
—Form basket like lattice structures and Dynamin (a G protein that forms a ring around the neck of the bud pinching it off)

What are the 3 families of vesicle coat proteins and what are their functions?
—–COPII, COPI, Clathrin
There may be other coat proteins that are not yet characterized.

What directs polymerization of clathrin?
—–adaptins

What two things help vesicles dock to the membrane?
—-rab and tethering factors
Vesicles move along microtubules or actin filaments.

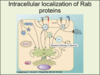
What do Rab proteins do?
Rab proteins mark different organelles and transport vesicles, so their localization on the correct membrane is key to establishing the specificity of vesicular transport.
You don’t need to know specific Rab proteins

T or F? The Rab trafficking control system complex.
Rab trafficking control system is complex – there are Rabs for each route!
AP, autophagosome; ERGIC, ER-Golgi intermediate compartment; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; EE, early endosome; LD, lipid droplet; LE, late endosome (multivesicular body); L/V, lysosome/vacuole; PAS, preautophagosomal structure; RE, recycling endosome; SV, secretory vesicle/granule.
What transmembrane proteins facilitate fusion of vesicles with membrane?
—-SNAREs

Describe the process of fusion?

What guides Rab proteins to their appropriate membranes?
—–GDI’s

What activates Rab’s and what stimulates hydrolysis of GTP on them?
—–GEF’s activate them and GAP’s stimulate hydrolysis

Discuss Cranio-lenticulo-sultural dysplasia?
Defects in Rabs or associated proteins often lead to disease when mutated.

Discuss Griscelli Syndrome Type II?
—-No Rab is produced with this disease

Discribe CEDNIK sydrome?

Describe autosoma recessive Hemophilia?

Describe choroiderma?
—-mutation on REP1 gene



