Science A (Core): Biology (I) - The Basics Flashcards
A good diet keeps you healthy – what should it consist of?
Fats (warmth and energy)
Carbohydrates (energy)
Vitamins and minerals (health)
Protein (building cells)
Fibre (passing material)
Water
What is metabolic rate and what type of people would have different metabolic rates?
Metabolic rate is the speed of all the chemical reactions in your body
People with lots of muscle / people who do lots of exercise will have fast metabolic rates
What things can make you unhealthy?
An unbalanced diet (can make you overweight / underweight)
Not getting enough exercise
Genes play a role – some people are born with a slow metabolic rate / might have too much cholesterol which is bad for the heart
Name 2 examples of micro-organisms (pathogens) and say how they reproduce and make you feel ill
Bacteria – copy themselves damaging cells and releasing toxins
Viruses – reproduce inside your cells and damage them
How does the immune system kill pathogens?
White blood cells ingest pathogens, make antibodies and make antitoxins

What is a vaccine and how does it work?
An injection of a dead / inactive pathogen
White blood cells make antibodies to kill the ‘harmless’ pathogen which then makes you immune (you won’t get sick)
If you then do come across the real pathogen your white blood cells can make the antibodies much more quickly before you can become ill
What is MMR vaccine and what does it protect against?
Measles
Mumps
Rubella
What are antibiotics used for and what do they not help with?
Antibiotics kill bacteria
Antibiotics do not work against a virus
How can bacteria become resistant (like those resistant to antibiotics such as MRSA)
Bacteria can mutate and become resistant to the drug
Antibiotics need to be controlled (e.g. not given out for a cold) to prevent resistance

Semmelweis was a doctor who suggested people do what in hospitals?
Doctors (and visitors) to wash hands before seeing patients
This reduces bacteria spreading
What are the five sense organs which detect stimuli
*Containing different receptors
Eyes (light)
Ears (sound)
Nose (smell)
Tongue (taste)
Skin (touch)
How does the central nervous system work?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord – neurons carry messages…
*Sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors to the brain
**Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain to the effectors (muscles / glands)

What are reflexes and how do they work?
Reflexes are automatic responses (you don’t need to think about them)
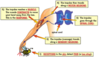
What do the synapses do?
Synapses join neurons together (chemicals take the impulse across the gap)

What are hormones?
Hormones are chemicals sent in the blood which affect specific target cells
What are the 3 hormones needed to control the menstrual cycle and what do they do?
FSH – makes the egg grow and mature
Oestrogen – stops FSH being released (for 1 egg at a time)
LH – makes the ovary release the egg
How does ‘the pill’ stop a woman from getting pregnant?
The pill stops FSH being released so no eggs mature (the pill contains oestrogen)

How can hormones help a woman get pregnant?
FSH and LH are given to stimulate egg maturation and release
IVF can join an egg and sperm ‘in a test tube’ which is put back into the woman to develop
What is an auxin and how does it work in light?
An auxin is a plant growth hormone – shoots grow towards light
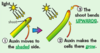
What is an auxin and how does it work in gravity?
An auxin is a plant growth hormone – roots grow down towards the soil

What 4 things does your body need to keep constant (homeostasis)
Ions
Water
Temperature
Blood sugar
How does the body keep ions constant?
Ions are absorbed through food and lost through sweat and urine