Science Flashcards
Gland/Organ: THYROID GLAND Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: THYROID GLAND Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Triiodothyronine T3 Function: Metabolism
- Hormone: Thyroxin T4 Function: Metabolism and temperature
- Hormone: Calcitonin Function: Inhibits release of Calcium from bones

Gland/Organ: ADRENAL MEDULLA Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: ADRENAL MEDULLA Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Epinephrine Function: fight
- Hormone: Norepinephrine Function: flight

Gland/Organ: Kindneys Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Kindneys Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone________________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Etyhropoietin Function: Response to cellular hypoxia
- Hormone: Renin Function: Promotes production of Angiotensin

Gland/Organ: Thymus Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Thymus Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: Thymosin Function: Stimulates T-Cell

Gland/Organ: Adrenal Cortex Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
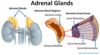
Gland/Organ: Adrenal Cortex Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Cortisol/Glucocorticoids Function: Increase blood glucose, Stress response, metabolism, Decrease immune response;
- Hormone: Aldosterone Function: Regulates Na content in blood

Gland/Organ: Pineal Gland Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Pineal Gland Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Melatonin Function: Sleep cycles; biorhythms

Gland/Organ: Ovaries (female gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Ovaries (female gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Estrogen Function: Stimulates egg maturation, controls 2ndary sex characteristics
- Hormone: Progesterone Function: Prepares uterus to receive fertilized egg

Gland/Organ: Parathyroid Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Parathyroid Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Function: Stimulates release of calcium from bones, back into blood.

Gland/Organ: Intestine Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Intestine Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Secretin Function: Response to acidity in small intestine; stimulates secretion by liver and pancreas
- Hormone: Cholecystokinin Function: Production of Bile Salts
Gland/Organ: Heart Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Heart Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) Function: Increase renal Na excretion, decrease ECF

Gland/Organ: Testes (male gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: LIVER Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Angiotensin II Function: Vasoconstriction, Increase BP

Gland/Organ: STOMACH Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: STOMACH Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone: Gastrin Function: Response to food;stimulates production of gastric juice

Gland/Organ: Hypothalamus Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Hypothalamus Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: ___________________
- Hormone: Releasing/Inhibiting hormones Function: Stimulate Pituitary

Gland/Organ: Anterior Pituitary Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Anterior Pituitary Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Function: Stimulate adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids
- Hormone: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Function: Stimulate the Thyroid gland
- Hormone: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Function: Stimulates production of ova (females) and sperm (males)
- Hormone: Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Function: Stimulates Ovaries (females) and Testes (males)
- Hormone: Prolactin Function: stimulates milk production
- Hormone: Growth Hormone (GH) Function: Stimulates growth (bones) and metabolic functions

Gland/Organ:Posterior Pituitary (back) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ:Posterior Pituitary (back) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone_______________Function: _______________
- Hormone_______________ Function: _______________
- Hormone: (ADH) Antidiuretic Hormone/ Vasopressin Function: Promotes retention of water by the kidneys
- Hormone: Oxytocin Function: Stimulates contraction of uterus and mammary gland cells

Gland/Organ: Pancreas Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: (Alpha Cells)_____________Function: _______________
- Hormone: (Beta Cells)______________ Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Pancreas Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: (Alpha Cells)_____________Function: _______________
- Hormone: (Beta Cells)______________ Function: _______________
Gland/Organ: Pancreas Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: (Alpha Cells) Glucagon Function: Increase blood glucose
- Hormone: (Beta Cells) Insulin Function: Decrease blood glucose

Gland/Organ: Testes (Male Gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: _____________Function: _______________

Gland/Organ: Testes (make gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: _____________Function: _______________
Gland/Organ: Testes (make gonads) Hormone Secreted & Function:
- Hormone: Testosterone Function: Regulates sperm production and 2ndary sex characteristics

Which of the following describes cellular respiration?
It is a reductive catabolic activity
It is an oxidative anabolic activity
It is an oxidative catabolic activity
It is a reductive anabolic activity
Answer: It is an oxidative catabolic activity
Which of the following describes cellular respiration?
It is a reductive catabolic activity
It is an oxidative anabolic activity
It is an oxidative catabolic activity
It is a reductive anabolic activity
An anabolic reaction is a reaction that uses energy to build molecules the organism needs. A catabolic reaction breaks down complex molecules into smaller molecules to create energy for the organism to use.
Oxidation is when an element loses one or more electrons to oxygen. Reduction is when an element gains one or more electrons.
Cellular respiration is the process in which a cell takes in oxygen and uses it to break down glucose to create energy in the form of ATP. In the final stage of cellular respiration (called the electron transport chain), oxygen accepts electrons and picks up protons to form water. So, because elements lose electrons to oxygen and it is a reaction in which energy is created, cellular respiration is both an oxidative and catabolic activity.
Which of the following types of tissues functions in the covering, lining, and protection of surfaces and body cavities?
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissue
Muscle tissue
Nerve tissue
Answer: Epithelial tissue
Which of the following types of tissues functions in the covering, lining, and protection of surfaces and body cavities?
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissue
Muscle tissue
Nerve tissue
Epithelial tissue functions as the lining and covering of body surfaces and cavities.
Muscle tissue functions in facilitating voluntary and involuntary movements.
Connective tissue is responsible for the support and protection of tissues and organs.
Nerve tissue is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses.
The respiratory system is composed of organs that facilitate gas exchange between the blood and the external environment. Which of the following describes the group of organs that function during ga exchange?
Organ
Organelle
Organ System
Tissue
Answer: Organ system
The respiratory system is composed of organs that facilitate gas exchange between the blood and the external environment. Which of the following describes the group of organs that function during ga exchange?
Organ
Organelle
Organ System
Tissue
Tissues are a collection of specialized cells that perform a specific functions (e.g. protection, support, nerve conduction and movement).
A group of tissues that has a specialized function is referred to as an organ.
A group of organs that work together to perform several related functions is an organ system.
Below is a model representing the hierarchy of the structure of the human body:

White blood cells contain many _________ because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Which of the following options correctly completes the statement above?
ribosomes
lysosomes
mitochondria
Golgi
Answer: lysosomes
White blood cells contain many _________ because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Which of the following options correctly completes the statement above?
ribosomes
lysosomes
mitochondria
Golgi
White blood cells contain a larger number of lysosomes because they need to dispose of harmful intruders such as bacteria and viruses. Lysosomes are responsible for digesting and removing waste from a cell. This means they can digest bacteria and viruses that are engulfed by white blood cells in order to protect the body.
Mitochondria are the organelles responsible for generating energy-rich molecules for the cell.
The Golgi apparatus collects small molecules and combines them to make more complex molecules within the cell. Then it packages up the complex molecules to either store or to send out of the cell.
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. mRNA is translated into proteins by the ribosomes.
Which of the following organ systems is correctly paired with its function?
Digestive/ waste elimination
Endocrine/ regulation of homeostasis through hormone signaling
Circulatory/ obtaining nutrients necessary for growth, energy and normal body processes
Excretory/ transport of substance to all tissues of the body
Answer: Endocrine/ regulation of homeostasis through hormone signaling
Which of the following organ systems is correctly paired with its function?
Digestive/ waste elimination
Endocrine/ regulation of homeostasis through hormone signaling
Circulatory/ obtaining nutrients necessary for growth, energy and normal body processes
Excretory/ transport of substance to all tissues of the body
The Endocrine system is responsible for regulating homeostasis through hormone signaling.
The Digestive system is responsible for obtaining nutrients through the breakdown and absorption of food.
The Circulatory system is responsible for transport of substance to all tissues of the body.
The Excretory system is primarily responsible for waste elimination.
Which of the following correctly describes anatomical position?
Upright, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Seated, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Supine, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Prone, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Answer: Upright, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Which of the following correctly describes anatomical position?
Upright, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Seated, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Supine, arms at sides, palms facing posteriorly
Prone, arms at sides, palms facing anteriorly
Anatomical position is described as standing erect, arms at sides, face and palms are facing anteriorly (facing to the front).

HIV is a virus that destroys the body’s defense against diseases by inserting itself into the host’s DNA. In which part of the infected host cell will HIV virus be found?
Ribosomes
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Nucleus
Answer: Nucleus
HIV is a virus that destroys the body’s defense against diseases by inserting itself into the host’s DNA. In which part of the infected host cell will HIV virus be found?
Ribosomes
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Nucleus
HIV infects a host cell by integrating its genetic material with the genetic material of the host cell. Genetic material is located in the nucleus.
Ribosomes are the sites for protein synthesis.
Peroxisomes break down fatty acids to be used for forming membranes and as fuel for respiration. They also transfer hydrogen from compounds to oxygen to create hydrogen peroxide and then convert hydrogen peroxide into water.
Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They digest excess or worn out cell parts, food, and engulfed viruses or bacteria.
Osteoblasts are specialized cells that secrete the protein collagen and other substances necessary for bone formation. Which of the following organelles is more likely to be predominant in osteoblasts?
Nucleus
Lysosomes
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Answer: Ribosomes
Osteoblasts are specialized cells that secrete the protein collagen and other substances necessary for bone formation. Which of the following organelles is more likely to be predominant in osteoblasts?
Nucleus
Lysosomes
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Ribosomes are the organelles responsible for protein synthesis, so it is expected to be predominant in protein-secreting cells such as osteoblasts.
Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They digest excess or worn out cell parts, food, and engulfed viruses or bacteria.
Mitochondria are responsible for ATP production and are considered the powerhouse of the cell.
The nucleus is the “control center” that is responsible for directing the overall activity of the cell. The nucleus contains most of the cell’s DNA
Which of the following is the correct order of structures from simple to most complex?
Brain, neurons, mitochondria, nerve tissues
Mitochondria, neurons, nerve tissues, brain
Neurons, mitochondria, nerve tissues, brain
Mitochondria, nerve tissues, neurons, brain
Answer: Mitochondria, neurons, nerve tissues, brain

Mitochondria = cell organelle
Neurons = cells
Nerve tissues = tissues
Brain = organ
Which of the following is the correct order of structures from simple to most complex?
Brain, neurons, mitochondria, nerve tissues
Mitochondria, neurons, nerve tissues, brain
Neurons, mitochondria, nerve tissues, brain
Mitochondria, nerve tissues, neurons, brain
Neurons are the basic cells that make up the nervous system. Since the mitochondria is an organelle that you would find inside a neuron, it is going to be the simplest structure in the list. Multiple neurons are needed to form nervous tissue, which in turn makes up the brain.
Below is a diagram illustrating the hierarchy of the structure of the human body:
Which of the following processes correctly describe the formation of new cells in order to replace worn-out and damaged cells during injury?
Mitosis
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Meiosis
Answer: Mitosis
Which of the following processes correctly describe the formation of new cells in order to replace worn-out and damaged cells during injury?
Mitosis
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division.
Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The major purpose of mitosis is to replace worn-out and damaged cells.
Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information. The purpose of meiosis is to create sex cells – sperm in males, eggs in females.
Exocytosis is the cellular process of transporting substances out of the cell.
Endocytosis is the cellular process of taking substance into the cell.
Which of the following is not located on the anterior region of the human body?
Mandible
Clavicle
Sternum
Vertebral column
Answer: Vertebral column
Which of the following is not located on the anterior region of the human body?
Mandible
Clavicle
Sternum
Vertebral column
The vertebral column is located posteriorly (at the back). The mandible, sternum, and clavicle are all located anteriorly (front).
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the location of various body parts.

Which of the types of tissue is responsible for providing the matrix that supports and connects other tissues of the body?
Nerve tissue
Epithelial tissue
Muscle tissue
Connective tissue
Answer: Connective tissue
Which of the types of tissue is responsible for providing the matrix that supports and connects other tissues of the body?
Nerve tissue
Epithelial tissue
Muscle tissue
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is responsible for providing the matrix that supports and connects other tissues of the the body.
Nerve tissue is responsible for transmitting nerve impulse.
Epithelial tissue functions as lining and covering of body surfaces and cavities.
Muscle tissue functions in facilitating voluntary and involuntary movements.
Which of the following is the name of the imaginary vertical plane that equally divides the body into left and right?
Horizontal
Sagittal
Coronal
Transverse
Answer: Sagittal

Which of the following is the name of the imaginary vertical plane that equally divides the body into left and right?
Horizontal
Sagittal
Coronal
Transverse
The sagittal plane is also a vertical plane but it equally divides the body into left and right.
The Coronal plane is an imaginary vertical plane that divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior).
The horizontal, or transverse, plane is an imaginary plane at right angle with coronal and sagittal planes and it divides the body into superior and inferior.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the different types of planes used to divide the body.
Which of the following steps of protein synthesis occurs in the nucleus?
Replication
Transcription to mRNA
Translation to amino acid
Elongation
Answer: Transcription to mRNA
Which of the following steps of protein synthesis occurs in the nucleus?
Replication
Transcription to mRNA
Translation to amino acid
Elongation
Protein synthesis is comprised of two main steps, transcription of DNA to mRNA and translation of mRNA codons to amino acids. In the nucleus, the mRNA transcribes the genetic instruction from the DNA. mRNA then diffuses to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pores. Translation to amino acid and elongation to a particular protein molecule occur in the cytoplasm, particularly in the ribosomes.
Which of the following describes the function of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Synthesis and transport of proteins
Intracellular digestion of damaged structures, macromolecules, and bacteria
Facilitates movement of substance in and out of the cell
Conversion of nutrients to ATP
Answer: Synthesis and transport of proteins

Which of the following describes the function of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Synthesis and transport of proteins
Intracellular digestion of damaged structures, macromolecules, and bacteria
Facilitates movement of substance in and out of the cell
Conversion of nutrients to ATP
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is studded with ribosomes and, as such, assists in the synthesis and transport of proteins.
ATP production is a function of the mitochondria while intracellular digestion is performed by lysosomes.
Entry and exit of substances is facilitated by the cell membrane.
Which of the following is the largest organ of the human body?
Skin
Kidney
Pancreas
Lung
Answer: Skin
Which of the following is the largest organ of the human body?
Skin
Kidney
Pancreas
Lung
Skin is the largest single organ of the body that is mainly responsible for covering and protection of internal structures.
The head is _________ to the neck.
Proximal
Superior
Inferior
Superficial
Answer: Superior
The head is _________ to the neck.
Proximal
Superior
Inferior
Superficial
Superficial means that the structure is closer to the surface of the body.
Superior indicates that the structure is located at a relatively higher position while inferior denotes a relatively lower position.
Proximal denotes a position that is relatively closer to the center of the body or the point of attachment.

Which of the following organ systems is not correctly paired with its function?
Circulatory/ transport of substance to all tissues of the body
Digestive/ provide defense against infectious diseases
Nervous/ collecting, analyzing and integrating information that regulates intrinsic body conditions and maintains behavioral patterns
Respiratory/ breathing and gas exchange
Answer: Digestive/ provide defense against infectious diseases
Which of the following organ systems is not correctly paired with its function?
Circulatory/ transport of substance to all tissues of the body
Digestive/ provide defense against infectious diseases
Nervous/ collecting, analyzing and integrating information that regulates intrinsic body conditions and maintains behavioral patterns
Respiratory/ breathing and gas exchange
The Immune system is responsible for providing defense and immunity against infectious diseases.
The Digestive system is responsible for the breakdown and absorption of food.
The Respiratory system facilitates breathing and gas exchange.
The Nervous system is responsible for collecting, analyzing and integrating information that regulates intrinsic body conditions and maintains behavioral patterns.
The Circulatory system is responsible for transport of substance to all tissues of the body.
Which of the following does not correctly describe a cell membrane?
Fat soluble substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and alcohol can easily pass through the membrane.
The phospholipid component has hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
It is composed of a single layer of lipids interspersed with proteins.
It is composed entirely of proteins and lipids.
Answer: It is composed of a single layer of lipids interspersed with proteins.
Which of the following does not correctly describe a cell membrane?
Fat soluble substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and alcohol can easily pass through the membrane.
The phospholipid component has hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
It is composed of a single layer of lipids interspersed with proteins.
It is composed entirely of proteins and lipids.
The cell membrane is a lipid bilayer primarily made up of lipids and proteins. The phospholipid component has hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic ends. The hydrophobic ends make up the middle portion of the membrane and this layer makes it easy for fat soluble substances, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and alcohol to pass through.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the structure of the cell membrane.

Which of the following organelles plays a vital role in the breaking down of macromolecules?
Lysosomes
Golgi Apparatus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Answer: Lysosomes
Which of the following organelles plays a vital role in the breaking down of macromolecules?
Lysosomes
Golgi Apparatus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. Ribosomes are attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, where the synthesized proteins are processed and sorted.
The Golgi Apparatus is then responsible for transporting and delivering synthesized proteins to other regions of the cell or to the plasma membrane for exocytosis into the extracellular fluid.
Lysosomes, on the contrary, are responsible for digesting molecules/ substances being transported inside the cell from the outside, such as during phagocytosis by macrophages.

Which of the following cell organelles is correctly paired with its function?
Nucleus/ Intracellular digestion
Ribosome/ Protein synthesis
Mitochondria/ Cell division
Lysosomes/ ATP production
Answer: Ribosome/ Protein synthesis
Which of the following cell organelles is correctly paired with its function?
Nucleus/ Intracellular digestion
Ribosome/ Protein synthesis
Mitochondria/ Cell division
Lysosomes/ ATP production
Ribosomes are responsible for synthesis of proteins.
The nucleus houses the genetic material and is responsible for cellular division, not intracellular digestion.
The mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, wherein ATP is generated. They are not involved in cell division.
Lysosomes contain digestive and hydrolytic enzymes which is essential for breaking down of molecules. Lysosomes are not involved in ATP

Which organelle is responsible for storing DNA?
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Nucleus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Answer: Nucleus
Which organelle is responsible for storing DNA?
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Nucleus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The genetic material, DNA, is found within the membrane-bound nucleus.
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is where synthesized proteins are processed and sorted.
The Golgi Apparatus is responsible for the transport of proteins within and out of the cell.
Lysosomes are responsible for digesting molecules/ substances being transported inside the cell from the outside.

Which of the following is a heterotrophic organism with a genome stored in DNA?
Algae
Human
Virus
Plants
Answer: Human
Which of the following is a heterotrophic organism with a genome stored in DNA?
Algae
Human
Virus
Plants
Humans are heterotrophic organisms, which means that they cannot make their own food. Instead, they rely on other sources of nutrition, such as plants and animals. Humans have their genome stored in DNA.
Plants and algae are autotrophic (they can create their own food/nutrition) and have their genome stored in DNA.
A virus, on the other hand, is neither autotrophic nor heterotrophic, and has RNA as genetic material.
Which of the following organelles is responsible for digesting damaged cellular structures, as well as macromolecules and bacteria ingested by the cell?
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Answer: Lysosomes
Which of the following organelles is responsible for digesting damaged cellular structures, as well as macromolecules and bacteria ingested by the cell?
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes are responsible for intracellular digestion of damaged structures, macromolecules, and bacteria.
The Golgi Apparatus is responsible for the transport of proteins within and out of the cell.
Mitochondria are the organelles responsible for converting nutrients to energy as ATP.
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is where synthesized proteins are processed and sorted.

Which of the following anatomical terms is correctly matched with its meaning?
carpal/foot
inguinal/neck
cervical/wrist
cranial/skull
Answer: cranial/skull
Which of the following anatomical terms is correctly matched with its meaning?
carpal/foot
inguinal/neck
cervical/wrist
cranial/skull
Cranial refers to the bone comprising the skull.
Carpal refers to the bone comprising the wrist.
Cervical refers to the region of vertebrae in the neck.
Inguinal is the superior region of the thigh.

Which of the following is happening during a contraction of the diaphragm?
An increase in alveolar pressure
A decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity
Forced expiration
A decrease in alveolar pressure
Answer: A decrease in alveolar pressure
Which of the following is happening during a contraction of the diaphragm?
An increase in alveolar pressure
A decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity
Forced expiration
A decrease in alveolar pressure
When the diaphragm is contracting, it is moving downward and allowing the lungs to inflate. During inhalation, alveolar pressure is decreased because the expansion of the lungs increases the surface area or number of alveoli available for gas exchange, thus reducing the pressure at the alveoli.
Since air is being inhaled, the volume of air in the thoracic cavity is increased, not decreased.
Alveolar pressure increases during exhalation, because the lungs are slightly collapsing, reducing the surface area of the alveoli.
Forced expiration is not occurring during diaphragm contraction, because this indicates inhalation.
The ______________ is a double layered membrane that lines the lungs.
alveolus
pericardium
pleural cavity
pleura
Answer: pleura
The ______________ is a double layered membrane that lines the lungs.
alveolus
pericardium
pleural cavity
pleura
The pleura of the lungs is composed of two layers of tissue that separate the lungs from the thoracic cavity. There as an inner visceral pleura which lines all of the folds of the lungs, and an outer parietal pleura. A pleural cavity exists between the two layers of the pleura.
The pericardium is the lining of the heart.
An alveolus is a single air sac that makes up the alveoli, where the majority of gas exchange occurs in the lung.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the structures referenced in this question.

Which of the following lists the respiratory passageways in order from largest diameter to smallest diameter?
Bronchioles, bronchi, trachea
Bronchi, trachea, bronchioles
Trachea, bronchioles, bronchi
Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
Answer: Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles

Which of the following lists the respiratory passageways in order from largest diameter to smallest diameter?
Bronchioles, bronchi, trachea
Bronchi, trachea, bronchioles
Trachea, bronchioles, bronchi
Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
The trachea is the largest airway of the lower respiratory system and is composed of a single tube. It splits into two smaller tubes, a left and right bronchi. These bronchi further split into small bronchioles.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the respiratory passageways.
Which of the following terms is alternatively called the “voice box”?
Pharynx
Trachea
Larynx
Uvula
Answer: Larynx

Which of the following terms is alternatively called the “voice box”?
Pharynx
Trachea
Larynx
Uvula
The larynx is located just inferior to the pharynx and is commonly referred to as the “voice box”.
The pharynx is a shared cavity behind the nose and mouth that leads to the esophagus and trachea.
The trachea, commonly called the “windpipe”, is the large airway that receives air from the pharynx and larynx and delivers it to the lower respiratory structures.
The uvula is the soft tissue hanging in the back of the throat. When swallowing, the uvula helps prevent food from entering the nasal cavity.
Which of the following best describes the mechanical process of normal breathing during expiration?
The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles relax and move the ribs downward.
The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upward.
The diaphragm contracts and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles relax and contract upward.
The diaphragm relaxes and moves downward, while the intercostal muscles relax and move the ribs downward.
Answer: The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles relax and move the ribs downward.

Which of the following best describes the mechanical process of normal breathing during expiration?
The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles relax and move the ribs downward.
The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upward.
The diaphragm contracts and moves upward, while the intercostal muscles relax and contract upward.
The diaphragm relaxes and moves downward, while the intercostal muscles relax and move the ribs downward.
During exhalation, two primary components drive the mechanical process- the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles. During inhalation, the lungs fill with air with the help of the intercostal muscles moving up and outward to expand the chest cavity. The diaphragm contracts and pushes downward to make room for the expanded lungs.
During expiration, the opposite movements occur in order to help push air out of the lungs. Thus during exhalation, the diaphragm moves up and the intercostal muscles move the ribs downward.
Gas exchange between the blood and alveoli would be enhanced by ______________, but impeded by __________________.
increased alveolar surface area; increased membrane thickness
increased tidal volume; decreased membrane thickness
decreased respiratory rate; increased tidal volume
decreased membrane thickness; increased alveolar surface area
Answer: increased alveolar surface area; increased membrane thickness
Gas exchange between the blood and alveoli would be enhanced by ______________, but impeded by __________________.
increased alveolar surface area; increased membrane thickness
increased tidal volume; decreased membrane thickness
decreased respiratory rate; increased tidal volume
decreased membrane thickness; increased alveolar surface area
Gas exchange in the lung can be explained by Fick’s Law of Diffusion, which is represented by the following equation:
Diffusion = k * SA * ( P2 – P1)⁄T
where k represents the diffusion coefficient for the specific gas, SA represents the surface area of the tissue, P2- P1 represents the difference in the gas concentration on one side of the membrane compared to the other side, and T represents the thickness of the tissue.
Thus, any increases in gas coefficient, surface area, or difference in pressure will enhance gas exchange, while any increase in tissue thickness will impede gas exchange.
In the respiratory system, the majority of gas exchange takes place ___________________.
in the trachea
in the bronchioles
in the alveoli
in the bronchi
Answer: in the alveoli
In the respiratory system, the majority of gas exchange takes place ___________________.
in the trachea
in the bronchioles
in the alveoli
in the bronchi
When inhaling, air is taken in through the mouth and nose, and then through the larynx and pharynx. These passageways warm the air and prepare it for gas exchange. The air continues on through the trachea, commonly referred to as the “windpipe”. The trachea then splits into a right and left bronchi, with each side dividing further into smaller bronchioles. While some bronchioles may directly be involved in gas exchange, the majority of them are part of the conducting airway, which simply moves air through the respiratory system to get them to the alveoli where most of the gas exchange occurs.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the respiratory passageways.

Which of the following describes the volume of air associated with a normal breath?
Inspiratory reserve volume
Total lung capacity
Residual volume
Tidal volume
Answer: Tidal volume
Which of the following describes the volume of air associated with a normal breath?
Inspiratory reserve volume
Total lung capacity
Residual volume
Tidal volume
Tidal volume represents a normal volume of air that is inhaled and exhaled during relaxed breathing. This value is usually around 500 mL.
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) represents the total amount of air that the lungs can hold at a given time.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) represents the amount of air that can be inhaled, or inspired, in excess of the normal amount of inhaled air (tidal volume).
Residual Volume (RV) represents the amount of air remaining in the lungs after forced exhalation. This volume always remains in the lungs in order to prevent lung collapse.
Use the diagram below as a visual reference for the different volumes associated with a breath.

Which of the following conditions would exhibit an increase in lung compliance?
Emphysema
Bronchitis
Asthma
Lung cancer
Answer: Emphysema
Which of the following conditions would exhibit an increase in lung compliance?
Emphysema
Bronchitis
Asthma
Lung cancer
Lung compliance is the property of the lung that allows it to stretch and recoil. Both appropriate stretch and recoil are necessary for proper lung function, thus compliance that is too high or too low can negatively affect function. Emphysema increases lung compliance due to the damaged lung tissue. In this condition, the lung will be able to inflate, but the recoil is delayed, thus exhalation is impaired.
Asthma and bronchitis may be associated with some increase in lung compliance however this is less likely with these conditions. These conditions typically demonstrate reduced lung function due to inflammation or airway obstructions as opposed to damaged alveoli.
Lung cancer usually causes a decrease in lung compliance due to the presence of more fibrotic tissue, which makes the lung stiffer and harder to inflate.
Which of the following substances is produced by the lung for the purpose of reducing surface tension?
Sodium bicarbonate
Oxidase
Carbon dioxide
Surfactant
Answer: Surfactant
Which of the following substances is produced by the lung for the purpose of reducing surface tension?
Sodium bicarbonate
Oxidase
Carbon dioxide
Surfactant
The primary purpose of surfactant is to prevent lung collapse. The secondary purpose is to reduce surface tension. Additionally, the compliance of the lung is increased, meaning it can inflate more easily.
Sodium bicarbonate is a chemical buffer that reduces acidity to maintain the proper acid-base balance.
Oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a hydrogen to an oxygen molecule.
Carbon dioxide is the gas byproduct that forms as a result of metabolism and is exhaled through the lungs.
As air is inhaled, the sequence in which it passes through the respiratory tract is best described by which of the following choices?
Pharynx, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
Nasal cavity, bronchi, bronchioles, trachea, pharynx, larynx
Nasal cavity, trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchioles, bronchi
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
Answer: Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
As air is inhaled, the sequence in which it passes through the respiratory tract is best described by which of the following choices?
Pharynx, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
Nasal cavity, bronchi, bronchioles, trachea, pharynx, larynx
Nasal cavity, trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchioles, bronchi
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
When inhaling, air is taken in through the mouth and nose, and then through the larynx and pharynx. These passageways warm the air and prepare it for gas exchange. The air continues on through the trachea, commonly referred to as the “windpipe”. The trachea then splits into a right and left bronchi, with each side dividing further into smaller bronchioles. While some bronchioles may directly be involved in gas exchange, the majority of them are part of the conducting airway, which simply moves air through the respiratory system to get them to the alveoli where most of the gas exchange occurs.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the structures of the respiratory system.

Which of the following anatomical structures prevents food from entering the respiratory system?
Pharynx
Pleura
Epiglottis
Larynx
Answer: Epiglottis
Which of the following anatomical structures prevents food from entering the respiratory system?
Pharynx
Pleura
Epiglottis
Larynx
The epiglottis is a cartilage flap located at the top of the larynx that is responsible for closing during swallowing. This flap covers the opening to the trachea so that food does not enter the lower respiratory airways.
The pharynx is a shared cavity behind the nose and moth that leads to the esophagus and trachea.
The pleura are a double layered membrane that line the lungs.
The larynx is located just inferior to the pharynx and is commonly referred to as the “voice box”.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for structures described in this question.

Which of the following terms correctly describes the movement of air in and out of the lungs?
Diffusion
Respiration
Ventilation
Oxidation
Answer: Ventilation
Which of the following terms correctly describes the movement of air in and out of the lungs?
Diffusion
Respiration
Ventilation
Oxidation
Ventilation is the physical movement of air in and out of the lungs.
Respiration is the use of oxygen by a cell or organism to make energy.
Oxidation refers to a chemical process in which a molecule loses electrons.
Diffusion is the passive movement of a substance from high concentration to low concentration.
Voluntarily holding your breath will eventually result in:
an innate reflex to start breathing due to low oxygen levels.
brain damage or death to due to lack of oxygen.
an innate reflex to start breathing due to increased carbon dioxide levels.
temporary unconsciousness and risk of stroke.
Answer: an innate reflex to start breathing due to increased carbon dioxide levels.
Voluntarily holding your breath will eventually result in:
an innate reflex to start breathing due to low oxygen levels.
brain damage or death to due to lack of oxygen.
an innate reflex to start breathing due to increased carbon dioxide levels.
temporary unconsciousness and risk of stroke.
When someone holds their breath, two things are happening: there is a lack of oxygen being taken in and delivered to the body’s tissues, and there is a buildup of carbon dioxide that is not being exhaled as it normally would. Since the chemoreceptors in the body can’t detect the lack of something (i.e oxygen), they instead detect the unsafe increase in something: carbon dioxide. These sensors then override the voluntary breath-holding and force an exhalation to rid the body of carbon dioxide and stimulate oxygen intake.
While a temporary lack of oxygen does occur, it will not cause brain damage because breathing will occur before that happens.
Breathing will re-start due to an innate reflex, but it is due to increased carbon dioxide levels, not low oxygen levels.
Unconsciousness and stroke are unlikely to occur as breathing will re-start due to the reflex to rid the body of carbon dioxide.
A lung with a low level of compliance could be best described as _____________.
a lung with normal function.
A lung with a high elasticity but with damaged alveoli.
a stiff lung requiring extra work to accomplish normal breathing.
a highly elastic lung allowing breathing occur with reduced work.
Answer: a stiff lung requiring extra work to accomplish normal breathing.
A lung with a low level of compliance could be best described as _____________.
a lung with normal function.
A lung with a high elasticity but with damaged alveoli.
a stiff lung requiring extra work to accomplish normal breathing.
a highly elastic lung allowing breathing occur with reduced work.
Lung compliance is the property of the lung that allows it to stretch and recoil. Both appropriate stretch and recoil are necessary for proper lung function, thus compliance that is too high or too low can negatively affect function. In a lung with low compliance, or a stiff lung, extra work will be required to overcome the stiffness of the lung and breathe sufficient air in.
A stiff lung will not operate normally as sufficient air will not be able to be taken in without extra effort to overcome the resistance of the lung.
The low compliance of the lung indicates that it’s elastic properties are reduced, thus it will not be highly elastic.
A lung with low compliance will not have high elasticity; instead it will be stiff. There may be damaged alveoli but this may not always be the case.
Which of the following is not a function of pulmonary surfactant?
Increase in lung compliance
Reduction of surface tension
Decrease in lung compliance
Prevention of lung collapse
Answer: Decrease in lung compliance
Which of the following is not a function of pulmonary surfactant?
Increase in lung compliance
Reduction of surface tension
Decrease in lung compliance
Prevention of lung collapse
The purpose of surfactant is to prevent lung collapse and to reduce surface tension. Additionally, it increases the compliance of the lung, meaning it can inflate more easily.
A decrease in lung compliance would make it more difficult to inflate the lungs. This is the opposite effect of surfactant.
______________ is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the alveolar membrane.
Exocytosis
Osmosis
Diffusion
Active transport
Answer: Diffusion
______________ is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the alveolar membrane.
Exocytosis
Osmosis
Diffusion
Active transport
Answer: Diffusion
Diffusion is the passive movement of a substance from high concentration to low concentration. During inhalation, oxygen in the alveoli has to make its way into the blood, and this occurs via diffusion. A high oxygen concentration in the alveoli drives the movement of oxygen into the pulmonary capillaries where oxygen content is low. Conversely, carbon dioxide is also exchanged this way, but is unloaded, or moved from the blood to the alveoli for exhalation.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the structures of the respiratory system.

Diastole is the term that describes _________, while systole represents_____________.
receiving of the electrical impulse from the SA node; ventricular contraction
contraction and ejection; relaxing and filling
relaxing and filling; contraction and ejection
contraction and filling; relaxing and ejection
Answer: relaxing and filling; contraction and ejection
Diastole is the term that describes _________, while systole represents_____________.
receiving of the electrical impulse from the SA node; ventricular contraction
contraction and ejection; relaxing and filling
relaxing and filling; contraction and ejection
contraction and filling; relaxing and ejection
One cardiac cycle consists of one period of diastole, and one period of systole. During diastole, the heart relaxes allowing the chambers to fill with blood. During systole, a large portion of that blood is pumped out of the ventricle. During periods of rest, diastole is usually longer than systole to allow more time for filling.
Before any contraction or systolic phase can occur, there must be an electrical signal coming from the SA node. However, this is not referred to as diastole.
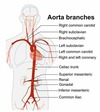
The primary function of the ________________ is to deliver blood to the brain.
aorta
brachial artery
subclavian artery
carotid artery
Answer: carotid artery
The primary function of the ________________ is to deliver blood to the brain.
aorta
brachial artery
subclavian artery
carotid artery
The carotid artery is located on the lateral aspect of the neck area and is actually a pair of arteries. Thus we have a right and a left carotid artery. The left carotid artery branches directly off of the aorta, while the right carotid artery branches off of the brachiocephalic artery (this split creates the right carotid artery and the right subclavian artery). Each of the carotid arteries eventually split into an internal and internal carotid, which supply blood to different regions of the head and brain. This split is the location of the carotid sinus, a widening of the artery that contains receptors that detect blood pressure changes.
While the aorta is an extremely important artery, it is not specific to supplying blood to the brain, but to the entire body.
The brachial artery is found in the upper arm.
The subclavian arteries (right and left) account for 2 of the 3 primary branches extending from the aorta. The subclavian arteries give rise to the arteries in the upper extremities.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the different arteries.

Using the provided image, choose the anatomical structure designated by letter B.
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Right atrium

Answer: Left atrium

Which blood vessel delivers blood directly into the right atrium?
Vena cava
Aorta
Brachial artery
Coronary artery
Answer: Vena cava

Which blood vessel delivers blood directly into the right atrium?
Vena cava
Aorta
Brachial artery
Coronary artery
The largest vein, the vena cava, dumps blood directly back into the heart at the right atrium.
When blood is pumped out from the heart, the left ventricle ejects blood to the body through the aorta (the body’s largest artery), and then through the branching of arteries. As blood travels throughout the body, it travels through various arteries. The arteries get smaller, becoming arterioles, as they get closer to the tissues. At the tissues, oxygen and nutrients are exchanged through capillary beds. Capillaries act as transition vessels between the arteries and veins. Once the oxygen and nutrients are unloaded to the tissue, the remaining blood enters the venous circulation and travels back to the heart. Smaller veins closer to the capillary beds are called venules, becoming larger veins as they get closer to the heart. The largest vein, the vena cava, dumps blood directly back into the heart at the right atrium.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for how blood flows through the heart.
Which of the following conditions occurs when a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked?
Myocardial infarction
Migraine
Aneurysm
Stroke
Answer: Stroke
Which of the following conditions occurs when a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked?
Myocardial infarction
Migraine
Aneurysm
Stroke
A stroke can result if a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked, either by a clot or other type of embolism. When this occurs, blood flow to the affected area of the brain is stopped, and that area of the brain loses function, sometimes permanently.
A myocardial infarction (heart attack) also occurs as a result of a blocked vessel, however this occurs in the heart, not the brain.
An aneurysm is the enlargement and weakening of a blood vessel, and is susceptible to rupture. While this can occur in the brain, causing a hemorrhagic stroke, it is not due to a blockage in the blood vessel.
Migraines are painful headaches that can last for several hours to days. The causes of migraines are not fully understood, but there are several environmental and physiological factors that may contribute to their onset. While migraines can be severely painful, they are not associated with blocked blood vessels in the brain.
One of the primary functions of blood is to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues. This is accomplished by ________________, which contain the oxygen-carrying protein called ___________________.
platelets; hemoglobin
erythrocytes; hemoglobin
leukocytes; myoglobin
plasma; albumin
Answer: erythrocytes; hemoglobin
One of the primary functions of blood is to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues. This is accomplished by ________________, which contain the oxygen-carrying protein called ___________________.
platelets; hemoglobin
erythrocytes; hemoglobin
leukocytes; myoglobin
plasma; albumin
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, (“eryth” meaning red, and “cyte” meaning cell) are the cells found in blood that bind and deliver oxygen. They are able to carry oxygen because of a protein they contain called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-based protein and is actually what gives blood its red pigment.
Platelets are small cells which are also found in blood but have a different job. Their role is to form blood clots and stop excessive bleeding by flocking together when there is an injury to the blood vessel. They do not contain hemoglobin.
Leukocytes are also found in blood, but these are a group of white blood cells that have various specific functions relating to immune function. Leukocytes do not contain myoglobin, which is an oxygen-carrying protein found in muscle, not blood.
Plasma makes up the watery component of blood and serves to help transport various substances throughout the body. The protein albumin is found in plasma and binds substances such as hormones and electrolytes. While this is an important function, oxygen binding and transport is not a function of plasma or albumin.
Which of the following comparisons between arteries and veins is true?
Veins have valves, and arteries do not.
Veins have thick, muscular walls, while arteries have thin, more compliant walls.
Veins carry freshly oxygenated blood from tissue back to the heart, while arteries carry oxygen-depleted blood away from the heart.
Veins have a smaller diameter than arteries.
Answer: Veins have valves, and arteries do not.
Which of the following comparisons between arteries and veins is true?
Veins have valves, and arteries do not.
Veins have thick, muscular walls, while arteries have thin, more compliant walls.
Veins carry freshly oxygenated blood from tissue back to the heart, while arteries carry oxygen-depleted blood away from the heart.
Veins have a smaller diameter than arteries.
Due to the lower pressure in the venous system and the fact that most blood is trying to return back to the heart against the force of gravity, veins have valves that prevent blood from moving backwards.
Veins do not contain thick, muscular walls like arteries do. If venous walls were thick like arterial walls, there would be more resistance for blood flowing into veins. Since blood in the venous side is already under a lower pressure, this would create a problem for blood to return to the heart. Arteries have thick muscular walls due to the higher pressure of blood flow in the arterial side of circulation.
Veins carry blood that is leaving tissue after it has unloaded oxygen, therefore they carry oxygen-depleted blood, along with metabolic waste back towards the heart. Venous blood carries oxygen-deficient blood back to the heart. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to tissues where oxygen can be delivered and used for cellular respiration.
Due to the higher pressure in which arterial blood must flow, arteries have thicker walls and smaller lumen, or diameter, as compared to veins. Veins are often considered to be capacitance vessels as they carry a larger volume of blood, and have thinner walls, and greater wall compliance to accommodate the higher volume of blood.
A decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood would result in __________________.
increased oxygen-carrying capacity
decreased oxygen-carrying capacity
decreased blood pressure
increased blood viscosity
Answer: decreased oxygen-carrying capacity
A decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood would result in __________________.
increased oxygen-carrying capacity
decreased oxygen-carrying capacity
decreased blood pressure
increased blood viscosity
The function of hemoglobin is to bind oxygen molecules in order to transport oxygen in the blood. If hemoglobin levels are decreased, this would directly result in a limited ability to carry and deliver oxygen.
Blood viscosity may increase if the number of red blood cells increases. However, if hemoglobin is decreased, blood viscosity would likely not change.
Blood pressure may also increase if the number of red blood cells was increased. However, decreased hemoglobin would not affect blood pressure.
Which of the following correctly describes the flow of blood through the heart’s primary chambers?
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle
right atrium, left atrium, aorta, and vena cava
right ventricle, right atrium, vena cava, and aorta
right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta, and vena cava
Answer: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle
Which of the following correctly describes the flow of blood through the heart’s primary chambers?
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle
right atrium, left atrium, aorta, and vena cava
right ventricle, right atrium, vena cava, and aorta
right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta, and vena cava
The heart is composed of four primary chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right side of the heart, which includes the right atrium and the right ventricle receive blood from the body and send it to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart at the left side, specifically the left atrium, and then the left ventricle. The left ventricle then ejects the now oxygenated blood to the body. The atria act as collection chambers, while the ventricles are the primary pumps of the heart.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for how blood moves through the heart.

Which of the following lists the heart’s primary valves in the order in which blood passes through them?
Bicuspid, tricuspid, aortic semilunar valve, pulmonary semilunar valve
Tricuspid, pulmonary semilunar valve, bicuspid, aortic semilunar valve
Tricuspid, aortic semilunar valve, bicuspid, pulmonary semilunar valve
Tricuspid, bicuspid, aortic semilunar valve, pulmonary semilunar valve
Answer: tricuspid, pulmonary semilunar valve, bicuspid, aortic semilunar valve
Which of the following lists the heart’s primary valves in the order in which blood passes through them?
Bicuspid, tricuspid, aortic semilunar valve, pulmonary semilunar valve
Tricuspid, pulmonary semilunar valve, bicuspid, aortic semilunar valve
Tricuspid, aortic semilunar valve, bicuspid, pulmonary semilunar valve
Tricuspid, bicuspid, aortic semilunar valve, pulmonary semilunar valve
When the blood returns to the heart from the body, it is collected by the vena cava, which then delivers blood directly to the right atrium. Blood passes through the tricuspid valve as it moves from the right atrium to the right ventricle, and is then ejected into the lungs, passing through the pulmonary semilunar valve. Once the blood has been oxygenated, it returns to the heart at the left atrium. When the blood moves from the left atrium to the left ventricle, it passes through the bicuspid valve. The left ventricle will eject blood through the aortic semilunar valve, then send it through the systemic circuit.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for how blood moves through the heart.

The condition ________________ can often lead to ________________ due to buildup and blockage of coronary arteries, preventing blood flow to the myocardium.
atherosclerosis; myocardial infarction
atherosclerosis; stroke
arteriosclerosis; myocardial infarction
arteriosclerosis; stroke
Answer: atherosclerosis; myocardial infarction
The condition ________________ can often lead to ________________ due to buildup and blockage of coronary arteries, preventing blood flow to the myocardium.
atherosclerosis; myocardial infarction
atherosclerosis; stroke
arteriosclerosis; myocardial infarction
arteriosclerosis; stroke
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque inside the arteries. If the plaque buildup is severe, a blockage can result, preventing blood flow to the associated heart tissue. This is a myocardial infarction, or heart attack. This can also occur if a plaque ruptures, travels through the vessels, and becomes lodged in a coronary artery.
Arteriosclerosis is the hardening and narrowing of the blood vessels and though blood flow can be restricted, this is not the cause of buildup or blockage.
A stroke can occur if a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked by an embolism (embolism is the word we use for any material that blocks a blood vessel).
Blood pressure is recorded as two numbers, for example 110/70. The top number (110) represents
___________ blood pressure which is ____________________________.
Diastole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is ejecting blood
Systole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is filling
Systole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is ejecting blood
Diastole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is filling
Answer: Systole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is ejecting blood
Blood pressure is recorded as two numbers, for example 110/70. The top number (110) represents ___________ blood pressure which is ____________________________.
Diastole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is ejecting blood
Systole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is filling
Systole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is ejecting blood
Diastole; the pressure in the blood vessels while the heart is filling
One cardiac cycle consists of one period of diastole, and one period of systole. During diastole, the heart relaxes allowing the chambers to fill with blood. During systole, a large portion of that blood is pumped out of the ventricle. During periods of rest, diastole is usually longer than systole to allow more time for filling.
In a blood pressure recording the top number represents systole, while the bottom number represents diastole.
In order for the heart to contract, an action potential must be generated at the sinoatrial node. If this signal fails to reach the Purkinje fibers, what will be the result?
The systolic period will be elongated
The ventricles will not contract and blood will pool within the heart
The Purkinje fibers will act as pacemaker cells but fire at a slower rate
The diastolic period will be shortened
Answer: The Purkinje fibers will act as pacemaker cells but fire at a slower rate
In order for the heart to contract, an action potential must be generated at the sinoatrial node. If this signal fails to reach the Purkinje fibers, what will be the result?
The systolic period will be elongated
The ventricles will not contract and blood will pool within the heart
The Purkinje fibers will act as pacemaker cells but fire at a slower rate
The diastolic period will be shortened
Just like skeletal and smooth muscle, cardiac muscle must have an electrical signal, or action potential, in order to contract. This means that the heart can contract on its own without the brain telling it to contract. This is possible due to the sinoatrial (SA) node, which can spontaneously initiate an action potential. This action potential is initiated in the right atrium where the SA node is located and disperses throughout the heart allowing muscle contraction to occur.
Purkinje fibers are networks of fibers that are involved in relaying the electrical signal to the ventricles. If an electrical discharge does not reach the Purkinje fibers, they will take over as pacemaker cells to allow the continued contraction of the ventricles. However, the Purkinje fibers are only able to fire between 20-40 beats per minute, while the SA node is capable of firing 60-100 beats per minute.
Note: If the Purkinje fibers were not able to fire, then the ventricles would not contract at all.
Which of the following lists the blood vessels in the order of blood flow from the left ventricle back to the heart at the right atrium?
Aorta, arterioles, arteries, capillaries, veins, venules, vena cava
Arterioles, arteries, aorta, vena cava, veins, venules, capillaries
Vena cava, veins, venules, capillaries, arterioles, arteries, aorta
Aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, vena cava
Answer: Aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, vena cava
Which of the following lists the blood vessels in the order of blood flow from the left ventricle back to the heart at the right atrium?
Aorta, arterioles, arteries, capillaries, veins, venules, vena cava
Arterioles, arteries, aorta, vena cava, veins, venules, capillaries
Vena cava, veins, venules, capillaries, arterioles, arteries, aorta
Aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, vena cava
When blood is pumped out from the heart, the left ventricle ejects blood to the body through the aorta (the body’s largest artery), and then through the branching of arteries. As blood travels throughout the body, it travels through various arteries. The arteries get smaller, becoming arterioles, as they get closer to the tissues. At the tissues, oxygen and nutrients are exchanged through capillary beds, Capillaries act as transition vessels between the arteries and veins. Once the oxygen and nutrients are unloaded to the tissue, the remaining blood enters the venous circulation and travels back to the heart. Smaller veins closer to the capillary beds are called venules, becoming larger veins as they get closer to the heart. The largest vein, the vena cava, dumps blood directly back into the heart at the right atrium.
Using the provided image, choose the anatomical structure designated by letter J.
Aorta
Superior Vena cava
Pulmonary Vein
Pulmonary Artery

Answer: Aorta
Using the provided image, choose the anatomical structure designated by letter J.
Aorta
Superior Vena cava
Pulmonary Vein
Pulmonary Artery

The _________________ carries oxygen depleted blood away from the heart, while the ________________ carries oxygen-rich blood back towards the heart.
pulmonary vein; pulmonary artery
pulmonary artery; pulmonary vein
aorta; pulmonary artery
vena cava; pulmonary artery
Answer: pulmonary artery; pulmonary vein
The _________________ carries oxygen depleted blood away from the heart, while the ________________ carries oxygen-rich blood back towards the heart.
pulmonary vein; pulmonary artery
pulmonary artery; pulmonary vein
aorta; pulmonary artery
vena cava; pulmonary artery
The pulmonary artery carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, where it can pick up oxygen. Therefore, oxygen-depleted blood is carried in the pulmonary artery. This is contrary to most arteries, which typically carry oxygen-rich blood. Once the blood is oxygenated in the lungs, it returns to the heart at the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
Once blood has been oxygenated and returns to the left side of the heart, it can be ejected by the left ventricle throughout the body via the aorta.
The vena cava returns oxygen depleted blood to the right atrium.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the structure of the heart.

Which of the following is not true about the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system transports a fluid called lymph throughout the body.
The lymphatic system transports both white blood cells and red blood cells.
The lymphatic system includes the spleen, thymus, and tonsils.
The lymphatic system facilitates the filtering of fluid at the lymph nodes.
Answer: The lymphatic system transports both white blood cells and red blood cells.
Which of the following is not true about the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system transports a fluid called lymph throughout the body.
The lymphatic system transports both white blood cells and red blood cells.
The lymphatic system includes the spleen, thymus, and tonsils.
The lymphatic system facilitates the filtering of fluid at the lymph nodes.
______________ is a condition in which red blood cells are poorly functioning and have reduced ability to carry oxygen.
Hypokalemia
Hypertension
Leukemia
Anemia
Answer: Anemia
______________ is a condition in which red blood cells are poorly functioning and have reduced ability to carry oxygen.
Hypokalemia
Hypertension
Leukemia
Anemia
Anemia is a general term for different conditions that can affect a red blood cell’s ability to carry oxygen. A common type of anemia can be caused from low iron, resulting in a lack of hemoglobin, which would directly limit the oxygen-carrying capacity.
Hypokalemia is a condition in which blood potassium levels are low; this does not influence the oxygen carrying capacity.
Hypertension is the condition of having high blood pressure.
Leukemia is a type of cancer which usually involves the white blood cells and bone marr
Which of the following arteries has the primary responsibility of supplying blood to the reproductive system?
Common iliac artery
Femoral artery
Gonadal artery
Inguinal artery
Answer: Gonadal artery
Which of the following arteries has the primary responsibility of supplying blood to the reproductive system?
Common iliac artery
Femoral artery
Gonadal artery
Inguinal artery
The gonadal artery is a branch off of the abdominal aorta that supplies the reproductive organs with blood. There are actually two gonadal arteries (a right and a left branch).
The term “inguinal” refers to the groin area of the body, however there is no inguinal artery.
The femoral artery is a major artery supplying the lower extremities however it does not supply the reproductive organs with blood.
The common iliac artery is found at the splitting of the inferior aorta, and supplies blood to the lower extremities.
You may use the diagram below as a visual reference for the different branches of the aorta.
In order for blood to be delivered to the body (i.e. the systemic circuit), enough pressure must be developed by the ___________ to push open the ________________.
left ventricle; pulmonary semilunar valve
right ventricle; pulmonary semilunar valve
right ventricle; aortic semilunar valve
left ventricle; aortic semilunar valve
Answer: left ventricle; aortic semilunar valve
In order for blood to be delivered to the body (i.e. the systemic circuit), enough pressure must be developed by the ___________ to push open the ________________.
left ventricle; pulmonary semilunar valve
right ventricle; pulmonary semilunar valve
right ventricle; aortic semilunar valve
left ventricle; aortic semilunar valve
Which of the following describes what would happen during a period of hyperventilation?
Increased carbon dioxide levels result in an increase in pH
Increased oxygen uptake results in greater tissue perfusion
Decreased carbon dioxide levels result in an increase in pH
Decreased carbon dioxide levels result in a decrease in pH
Answer: Decreased carbon dioxide levels result in an increase in pH
Which of the following describes what would happen during a period of hyperventilation?
Increased carbon dioxide levels result in an increase in pH
Increased oxygen uptake results in greater tissue perfusion
Decreased carbon dioxide levels result in an increase in pH
Decreased carbon dioxide levels result in a decrease in pH’’
Hyperventilation is the increase in breathing rate beyond the normal rate. When this happens, more carbon dioxide than needed is exhaled lowering the carbon dioxide levels in the blood. As a compensatory mechanism to increase carbon dioxide levels, hydrogen ions are used, creating more bicarbonate as a byproduct and increasing the pH.
Which of the following is not typically a result of an embolus?
Myocardial infarction
TIA
Pulmonary embolism
Atherosclerosis
Answer: Atherosclerosis
Which of the following is not typically a result of an embolus?
Myocardial infarction
TIA
Pulmonary embolism
Atherosclerosis
An embolus is a blood clot that often forms in the lower extremities and travels to another location.This can be lodged in the heart causing a myocardial infarction; in the brain, a TIA (transient ischemic attack), sometimes called a mini-stroke can occur; and in the lungs, a pulmonary embolism can prevent blood flow and breathing.
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque in the arteries and is not caused by an embolus. However, plaque from atherosclerosis could potentially cause an embolism.
Of the following organs, which has both endocrine and digestive functions?
Pancreas
Duodenum
Gallbladder
Colon
Answer: Pancreas
Of the following organs, which has both endocrine and digestive functions?
Pancreas
Duodenum
Gallbladder
Colon
The pancreas has both endocrine and digestive functions because it secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon, as well as various digestive proteases, amylases and lipases.
The duodenum is a part of the small intestine and does not secrete any hormones or have any endocrine function.
The colon is a part of the large intestine and does not secrete any hormones or have any endocrine function.
The gallbladder is connected to the liver and does not secrete any hormones or have any endocrine function.
The term _________________ refers to the contraction of smooth muscle in the digestive system that moves food along the GI tract.
retroperistalsis
peristalsis
vasoconstriction
segmentation
Answer: peristalsis
The term _________________ refers to the contraction of smooth muscle in the digestive system that moves food along the GI tract.
retroperistalsis
peristalsis
vasoconstriction
segmentation
Peristalsis is the contraction of smooth muscle that lines the esophageal walls. The smooth muscle has a circular layer as well as a longitudinal layer of muscle that allows a “wringing” action of the smooth muscle to push food down the esophagus.
Vasoconstriction refers to the constriction of blood vessels and is not directly related to digestive function.
Segmentation is the muscular contraction of the smooth muscle layers of the stomach that moves food around to ensure its interaction with digestive juices.
Retroperistalsis is the countermovement to peristalsis where the smooth muscle contracts pushing esophageal contents back towards the mouth. This usually occurs just prior to vomiting.
Which of the following is not part of the small intestine?
Ileum
Colon
Duodenum
Jejunum
Answer: Colon
Which of the following is not part of the small intestine?
Ileum
Colon
Duodenum
Jejunum
The small intestine is composed of three main parts: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum.
The colon makes up the majority of the large intestine.

Which of the following statements is true about protein digestion?
The majority of protein absorption occurs in the large intestine.
Chemical digestion of protein initially occurs in the mouth.
Absorption of protein occurs primarily in the small intestine.
The majority of mechanical protein digestion occurs in the stomach.
Answer: Absorption of protein occurs primarily in the small intestine.
Which of the following statements is true about protein digestion?
The majority of protein absorption occurs in the large intestine.
Chemical digestion of protein initially occurs in the mouth.
Absorption of protein occurs primarily in the small intestine.
The majority of mechanical protein digestion occurs in the stomach.
The absorption of protein, as well as all other nutrients, occurs primarily in the small intestine.
The large intestine facilitates the absorption of water and some electrolytes, but typically protein has already been absorbed by the time it reaches the large intestine.
Chemical digestion of protein does not begin until protein reaches the stomach where protease enzymes are available.
Mechanical digestion of proteins occurs in the mouth through chewing, while the majority of chemical digestion of proteins occurs in the stomach.
Which of the following statements regarding digestion is false?
The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin to regulate blood sugar levels.
The presence of fiber in the esophagus promotes peristalsis.
Villi and microvilli increase surface area for absorption.
The hormone glucagon is secreted from the pancreas and stimulates mechanical digestion.
Answer: The hormone glucagon is secreted from the pancreas and stimulates mechanical digestion.
Which of the following statements regarding digestion is false?
The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin to regulate blood sugar levels.
The presence of fiber in the esophagus promotes peristalsis.
Villi and microvilli increase surface area for absorption.
The hormone glucagon is secreted from the pancreas and stimulates mechanical digestion.
Glucagon is a hormone that is released from the pancreas and helps regulate blood sugar by breaking down stored carbohydrate and releasing glucose into the bloodstream when blood glucose levels are low. Glucagon does not stimulate mechanical digestion.
It is true that the pancreas secretes insulin, which is a hormone used to regulate blood sugar by promoting the uptake of sugar into cells.
Villi and microvilli are folds or convolutions in the intestinal membrane that help to increase surface area so more absorption can occur.
When an adequate amount of fiber, or any significant bolus of food, is present in the esophagus, peristalsis will occur to move the food towards the stomach.
Gastric reflux occurs as a result of an improper closing of the ________________.
pyloric sphincter
lower esophageal sphincter
epiglottis
Upper esophageal sphincter
Answer: lower esophageal sphincter
Gastric reflux occurs as a result of an improper closing of the ________________.
pyloric sphincter
lower esophageal sphincter
epiglottis
Upper esophageal sphincter
The lower esophageal sphincter is located at the bottom end of the esophagus where food will move from the esophagus to the stomach. When this muscular sphincter does not close properly, acidic contents from the stomach can leak back up into the esophagus causing gastric reflux.
The pyloric sphincter is located at the distal portion of the stomach, allowing food to pass from the stomach into the small intestine. While there may be some instances of improper closing of this sphincter, this is not the cause of gastric reflux.
The epiglottis is the flap of cartilage that covers the trachea when swallowing food. This prevents food from entering the lungs.
The upper esophageal sphincter is located at the top of the esophagus, between the pharynx and the esophagus. Improper closing would not cause gastric reflux.
If villi in the small intestine were to become damaged, which of the following would likely occur?
Segmentation of the stomach would be negatively affected leading to reduced digestion.
Malnutrition would result due to a decreased ability to absorb nutrients.
A reduced ability to breakdown fat due to the inability of villi to secrete bile.
Gastric reflux disease would result due to the increased production of stomach acid.
Answer: Malnutrition would result due to a decreased ability to absorb nutrients.
If villi in the small intestine were to become damaged, which of the following would likely occur?
Segmentation of the stomach would be negatively affected leading to reduced digestion.
Malnutrition would result due to a decreased ability to absorb nutrients.
A reduced ability to breakdown fat due to the inability of villi to secrete bile.
Gastric reflux disease would result due to the increased production of stomach acid.
The function of villi and microvilli is to increase surface area of the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs. If these are damaged, it could interfere with the ability of the small intestine to absorb nutrients, potentially leading to malnutrition.
Gastric reflux would not be caused by damage to villi, as this will be occurring in the small intestine, whereas gastric reflux is related to regurgitation of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Since the villi and microvilli are located in the small intestine, stomach segmentation would not be affected.
Villi do not secrete bile, therefore there would be no effect on bile secretion or fat breakdown.
The ______________ is an extension off of the large intestine that is often referred to as a vestigial organ.
appendix
gall bladder
cecum
spleen
Answer: appendix
The ______________ is an extension off of the large intestine that is often referred to as a vestigial organ.
appendix
gall bladder
cecum
spleen
The appendix is a small finger-like extension off of the large intestine that has no definite function. It has been theorized to have some influence on gut bacteria, however this has not been widely confirmed. Thus the appendix is often referred to as a vestigial organ, having no known function.
The gall bladder has a defined function, which is to store bile made by the liver.
The cecum is the part of the large intestine in which the appendix is attached.

In the digestive system, bile is manufactured by the ______________ and stored in the ______________.
liver; gallbladder
gallbladder; stomach
gallbladder; liver
stomach; gallbladder
Answer: liver; gallbladder
In the digestive system, bile is manufactured by the ______________ and stored in the ______________.
liver; gallbladder
gallbladder; stomach
gallbladder; liver
stomach; gallbladder
The liver makes bile and sends it to the gallbladder for storage until it is needed for fat digestion.
The majority of nutrient absorption occurs in the _________________.
large intestine
small intestine
pancreas
liver
Answer: small intestine
The majority of nutrient absorption occurs in the _________________.
large intestine
small intestine
pancreas
liver
The small intestine is the site of the majority of nutrient absorption. The folds in the lining along with the length of the small intestine allows ample time for nutrients to travel through the small intestine to allow maximum absorption.
The large intestine facilitates the absorption of water and some electrolytes, but typically protein has already been absorbed by the time it reaches the large intestine.
The liver has several functions, with a few functions related to digestion such as bile secretion, but there is no absorption occurring by the liver.
The pancreas secretes many digestive enzymes and hormones, but it does not absorb nutrients in the digestive tract.
The function of the pyloric sphincter is to ______________.
prevent reflux of digestive juices into the esophagus
produce chyme
release stomach enzymes
control the entry of food into the duodenum
Answer: control the entry of food into the duodenum
The function of the pyloric sphincter is to ______________.
prevent reflux of digestive juices into the esophagus
produce chyme
release stomach enzymes
control the entry of food into the duodenum
The pyloric sphincter is located at the distal portion of the stomach, allowing food to pass from the stomach into the small intestine, specifically the duodenum, which is the proximal segment of the small intestine.
The pyloric sphincter does not release stomach enzymes or produce chyme.
Also, because of the location of the pyloric sphincter, it can not prevent the reflux of digestive juices into the esophagus.
In the digestive system, the function of the ____________ is to ______________.
liver; secrete insulin for glucose uptake.
gall bladder; secrete lipase for fat emulsification
pancreas; secrete bile for starch digestion
stomach; secrete pepsinogen for protein digestion
Answer: stomach; secrete pepsinogen for protein digestion
In the digestive system, the function of the ____________ is to ______________.
liver; secrete insulin for glucose uptake.
gall bladder; secrete lipase for fat emulsification
pancreas; secrete bile for starch digestion
stomach; secrete pepsinogen for protein digestio
The stomach secretes the enzyme pepsinogen, which is a precursor to the enzyme pepsin. Pepsin is an enzyme used for digesting protein.
The liver does not secrete insulin; insulin is used for glucose uptake but it is secreted by the pancreas.
The gallbladder is a small organ associated with the liver. The gallbladder does not secrete any substance, but is used to store bile that the liver produces.
The pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon; it does not secrete bile. Furthermore, bile is not used for protein digestion-it is used for fat emulsification.
The primary function of _____________ is _____________________.
Chyme; carbohydrate breakdown in the mouth
bile; fat emulsification in the small intestine
Amylase; fat breakdown in the stomach
Saliva; protein breakdown in the mouth
Answer: bile; fat emulsification in the small intestine
The primary function of _____________ is _____________________.
Chyme; carbohydrate breakdown in the mouth
bile; fat emulsification in the small intestine
Amylase; fat breakdown in the stomach
Saliva; protein breakdown in the mouth
Bile is secreted by the liver and sent to the gallbladder for storage. The primary function of bile is to facilitate the breakdown and emulsification of fat, which occurs in the small intestine.
Chyme is a mixture of partially broken-down food and digestive juices that moves from the stomach to the small intestine. It is not able to breakdown any nutrients.
Saliva is found in the mouth and contains salivary enzymes, specifically amylases and lipases, that break down carbohydrates and fats. However, protein enzymes are not present in saliva.
Amylase is found in digestive enzymes in the mouth and stomach; however, the purpose of amylase is to break down carbohydrates, not fats.
The folds that make up the shape of the villi and microvilli:
Help push food along the intestinal tract.
Create a barrier to block absorption of fats.
Increase enzyme secretions due to greater surface area.
Facilitate absorption due to an increased surface area.
Answer: Facilitate absorption due to an increased surface area.
The folds that make up the shape of the villi and microvilli:
Help push food along the intestinal tract.
Create a barrier to block absorption of fats.
Increase enzyme secretions due to greater surface area.
Facilitate absorption due to an increased surface area.
The function of villi and microvilli is to increase surface area of the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs.
Villi and microvilli do not help push food along the intestinal tract, nor do they block fat absorption.
Villi and microvilli do not secrete enzymes
Which of the following correctly pairs structure and function?
mouth / nutrient absorption
stomach / chemical digestion
duodenum / reabsorption of water
colon / absorption of glucose
Answer: stomach / chemical digestion
Which of the following correctly pairs structure and function?
mouth / nutrient absorption
stomach / chemical digestion
duodenum / reabsorption of water
colon / absorption of glucose
The stomach is responsible for chemical digestion. As food contents enter the stomach, it mixes with digestive enzymes and hydrochloric acid to break down food. The muscular contractions, or segmentation, that the stomach muscles produce helps to move the food around and ensure it thoroughly mixes with the chemicals.
While mechanical digestion (i.e. chewing) and chemical breakdown begins in the mouth, nutrient absorption does not occur until the food particles are small enough for absorption and this happens in the small intestine.
The duodenum is a segment of the small intestine (where most nutrient absorption takes place). However, reabsorption of water happens in the large intestine, not the small intestine.
The colon is a segment of the large intestine which is primarily responsible for reabsorption of water and some electrolytes. The absorption of glucose occurs mainly in the small intestine.

Which of the following describes the contraction of the smooth muscle in order to move food down the esophagus to the stomach?
Mastication
Deglutition
Peristalsis
Pharyngeal constriction
Answer: Peristalsis
Which of the following describes the contraction of the smooth muscle in order to move food down the esophagus to the stomach?
Mastication
Deglutition
Peristalsis
Pharyngeal constriction
Peristalsis is the contraction of smooth muscle that lines the esophageal walls. The smooth muscle has a circular layer as well as a longitudinal layer of muscle that allows a “wringing” action of the smooth muscle to push food down the esophagus.
Mastication refers to the chewing actions carried out by the mouth that mechanically breaks down food.
Deglutition is the process of swallowing, where food is pushed from the mouth to the esophagus through the pharynx.
Pharyngeal constriction refers to the muscular action of the throat that allows food to be pushed towards the esophagus.
Which of the following digestive organs contains vitamin-producing bacteria?
Small intestine
Large intestine
Liver
Stomach
Answer: Large intestine
Which of the following digestive organs contains vitamin-producing bacteria?
Small intestine
Large intestine
Liver
Stomach
The large intestine contains healthy gut bacteria that are responsible for producing Vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a role in blood clotting. Often-times newborns are given a Vitamin K shot to aid in blood clotting due to any trauma during the birthing process. This is done because the gut bacteria has not yet populated and synthesized Vitamin K.
Which of the following is not a function of pancreatic juice?
Increase acidity of stomach contents
Chemically digest carbohydrates
Neutralize the pH of chyme
Chemically digest proteins
Answer: Increase acidity of stomach contents
Which of the following is not a function of pancreatic juice?
Increase acidity of stomach contents
Chemically digest carbohydrates
Neutralize the pH of chyme
Chemically digest proteins
Pancreatic juice is composed of several digestive enzymes as well as a high concentration of bicarbonate ions, making it an alkaline solution. Since the pH of this fluid is high (not acidic), it is unlikely that it would increase the acidity of the stomach.
Due to the various digestive enzymes, pancreatic juice does break down carbohydrates and proteins. And due to its high pH, it neutralizes the acidity of stomach chyme.
Gastric reflux occurs as a result of an improper closing of the ________________.
pyloric sphincter
lower esophageal sphincter
epiglottis
Upper esophageal sphincter
Gastric reflux occurs as a result of an improper closing of the ________________.
pyloric sphincter
lower esophageal sphincter
epiglottis
Upper esophageal sphincter
lower esophageal sphincter
The lower esophageal sphincter is located at the bottom end of the esophagus where food will move from the esophagus to the stomach. When this muscular sphincter does not close properly, acidic contents from the stomach can leak back up into the esophagus causing gastric reflux.
The pyloric sphincter is located at the distal portion of the stomach, allowing food to pass from the stomach into the small intestine. While there may be some instances of improper closing of this sphincter, this is not the cause of gastric reflux.
The epiglottis is the flap of cartilage that covers the trachea when swallowing food. This prevents food from entering the lungs.
The upper esophageal sphincter is located at the top of the esophagus, between the pharynx and the esophagus. Improper closing would not cause gastric reflux.

Which of the following digestive organs contains vitamin-producing bacteria?
Stomach
Liver
Large intestine
Small intestine
Which of the following digestive organs contains vitamin-producing bacteria?
Stomach
Liver
Large intestine
Small intestine
Large intestine
The large intestine contains healthy gut bacteria that are responsible for producing Vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a role in blood clotting. Often-times newborns are given a Vitamin K shot to aid in blood clotting due to any trauma during the birthing process. This is done because the gut bacteria has not yet populated and synthesized Vitamin K.
If villi in the small intestine were to become damaged, which of the following would likely occur?
Gastric reflux disease would result due to the increased production of stomach acid.
Malnutrition would result due to a decreased ability to absorb nutrients.
A reduced ability to breakdown fat due to the inability of villi to secrete bile.
Segmentation of the stomach would be negatively affected leading to reduced digestion.
If villi in the small intestine were to become damaged, which of the following would likely occur?
Gastric reflux disease would result due to the increased production of stomach acid.
Malnutrition would result due to a decreased ability to absorb nutrients.
A reduced ability to breakdown fat due to the inability of villi to secrete bile.
Segmentation of the stomach would be negatively affected leading to reduced digestion.
Malnutrition would result due to a decreased ability to absorb nutrients.
The function of villi and microvilli is to increase surface area of the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs. If these are damaged, it could interfere with the ability of the small intestine to absorb nutrients, potentially leading to malnutrition.


