S7) ECG Abnormalities Flashcards
What are the causes for abnormal rhythms?
- Abnormal impulse formation
- Abnormal conduction
What are the two types of abnormal rhythms?
- Supraventricular rhythms (SAN, Atrium, AVN)
- Ventricular rhythms
Describe 3 features of supraventricular rhythms
- Conducts impulse into and within ventricles by His-Purkinje system
- Normal ventricular depolarisation
- Normal QRS complexes (narrow)

Describe 4 features of ventricular rhythms
- Impulses arise from a focus/foci in ventricle
- Conduction not via usual His-Purkinje system
- Depolarisation takes longer
- Wide/bizarre QRS complexes

What is the best way to interpret rhythm from an ECG?
- Look at the ‘rhythm strip’ at the bottom of 12 lead ECG
- Some machines record Lead II, V1 and V5 rhythm strips

What is atrial fibrillation?
- Atrial fibrillation is a condition where impulse arise from multiple atrial foci, leading to chaotic atrial depolarisation wherein atria quiver rather than contract
- It carries risk of thrombosis

In 4 steps, explain the electrical activity in atrial fibrillation
⇒ Chaotic impulses from multiple atrial foci
⇒ Impulses arrive at AVN at rapid irregular rate
⇒ Only some conducted to ventricles (at regular intervals)
⇒ Ventricles depolarise and contract normally
What are two characteristic features of atrial fibrillation?
- No p waves (wavy baseline)
- Pulse and heart rate irregularly irregular

What are AV conduction blocks?
A heart block is a delay/ failure of conduction impulses from the atrium to the ventricles via the AVN and bundle of His
What are the causes of AV conduction blocks?
- Acute myocardial infarction (commonest)
- Degenerative changes
What are the three different types of AV conduction blocks?
- First degree heart block
- Second degree heart block
- Complete Heart Block
What are the characteristic features of first degree heart block (1o HB)?
- P wave normal
- QRS normal
- PR interval prolong > 5 small squares (slow conduction in AV and Bundle of His)

What are the characteristic features of Mobitz Type I (2o HB)?
- Progressive lengthening of PR interval
- Until one P is not conducted (this allows time for AVN to recover),
- Cycle begins again

What are the characteristic features of Mobitz Type II (2o HB)?
- PR interval normal
- Sudden non-conduction of a beat
- Dropped QRS
- High risk of progression to complete heart block

What causes complete heart block?
- Normal atrial depolarisation but impulses not conducted to ventricle
- Ventricular pacemaker takes over (ventricular escape rhythm)

What are the characteristic features of third degree heart block (CHB)
- Rate is very slow (30-40 bpm)
- Wide QRS complexes
- HR often too slow to maintain BP and perfusion

Identify three causes of ventricular rhythms
- Ventricular premature beats
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular fibrillation
What are ventricular ectopic beats?
- Ventricular ectopic beats are when an ectopic focus in the ventricle muscle prevents the spread of impulse via the fast His -purkinje system
- Hence, much slower depolarisation of ventricle (wide & bizzare QRS complex)

What is ventricular tachycardia?
- Ventricular tachycardia involves a run of ≥ 3 consecutive ventricular ectopics producing broad QRS complexes
- Persistent VT is a dangerous rhythm, requires urgent treatment and has a high risk of ventricular fibrillation

What is ventricular fibrillation?
- Ventricular fibrillation is the abnormal, chaotic and fast ventricular depolarisation due to impulses from multiple ventricular ectopic foci
- The ventricles quiver as there is no co-ordinated contraction, no cardiac output and is a state of cardiac arrest

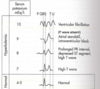
Compare and contrast ventricular and atrial fibrillation

Why are there ECG changes in ischaemia and myocardial infarction?
- Due to reduced perfusion of myocardium
- Changes seen in leads facing affected area
Explain how reduced myocardial perfusion due to coronary atherosclerosis impacts the heart
- Major coronary arteries lie on epicardial surface hence sub-endocardial muscle is furthest away & most vulnerable
- Flow is during diastole, so if diastole is short (rapid HR) there is less time for blood flow e.g. exercise
The sub endocardial region is the most vulnerable.
What are the ischaemic changes observed in an ECG?
Leads facing affected area show:
- ST segment depression
- T wave inversion

What is STEMI?
- ST segment elevation myocardial infarction is a condition occurring due to complete occlusion of lumen by thrombus
- Muscle injury extends ‘full thickness’ from endocardium to epicardium and ST segment elevation is observed in leads facing area
Describe the evolving changes in a STEMI (6 stages)

How do we identify pathological Q waves?
- > 1 small square (width)
- > 2 small squares (length)

Describe the ECG changes observed in hyperkalaemia
- In hyperkalaemia, the RMP less negative
- Heart becomes less excitable as hyperkalaemia worsens
Describe the ECG changes observed in hypokalaemia
In hypokalaemia, the RMP more negative:



