S3) Intracellular Signalling Pathways Flashcards
(22 cards)
What are G Proteins and what do they do?
- G-protein coupled receptors are a superfamily of receptors with an enormous diversity of cellular functions
- They alter the activities of effectors
Describe the structure of G proteins
- Heterotrimeric i.e. consist of three subunits: α, β, γ
- The β and γ subunits bind tightly to each other and function as a single unit
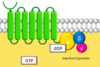
Describe the properties of the α-subunit of the G protein
- The α-subunit has a guanine nucleotide binding site
- The α-subunit possesses intrinsic GTPase activity as this site binds GTP and then slowly hydrolyses it to GDP
Describe the activity/appearance of the G protein under basal resting conditions
- G-protein is present at the inner face of the plasma membrane in its heterotrimeric form
- GDP is bound to the α subunit

Explain the effects of ligand binding on the GPCR

- The ligand binds with the GPCR and activates it
- The activated receptor has a high affinity for the G-protein
- GDP is later released and exchanged for GTP by the α-subunit

What role does the GPCR take on when GDP is exchanged for GTP?
The receptor acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF)

Describe the affinity of the GPCR for the G protein after the guanine nucleutide exchange
- The binding of GTP to the α-subunit decreases the affinity of the receptor for the G-α and Gβγ subunits
- Thus, both α and βγ subunits are released and can each can interact with effectors

Explain how the GPCR cycle is reactivated after subunit interaction with effectors
- Effector interaction is then terminated by α-subunit’s intrinsic GTPase activity which hydrolyses GTP → GDP
- Affinity of the Gα-subunit for the Gβγ-subunit then increases
- Gαβγ hetero-trimer is reformed & awaits reactivation

State the structure and function of Gs/Gαs
- Structure: Gs carries the β-adrenoceptor for adrenaline and the enzyme adenylyl cyclase
- Function: stimulates adenylyl cyclase

State the structure and function of Gi/Gαi
- Structure: an inhibitory version of G protein for the activation of adenylyl cyclase
- Function: inhibits adenylyl cyclase

Outline the mechanism of action of Gq
- Gq proteins preferentially interact with the membrane-bound enzyme phospholipase C
- This causes hydrolysis of a minor plasma membrane phospholipid (PIP2) and generates 2 messengers: IP3 and DAG

For the Gs, Gi and Gq proteins, compare and contrast the following:
- Endogenous signalling molecule
- Receptor
- Effector
- Physiological response

State the structure and function of adenylyl cyclase
- Structure: an integral plasma membrane protein
- Function: hydrolyses cellular ATP to generate cAMP

State the activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
- Activation: via Gs – noradrenaline/adrenaline at β-adrenoceptors
- Inhibition: via Gi – noradrenaline/adrenaline at α2-adrenoceptors

What does cAMP do?
Cyclic AMP interacts with protein kinase A (PKA)

What does PKA do?
PKA phosphorylates a variety of cellular proteins to increase/decrease their levels of activity:
- Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver
- Lipolysis in adipose tissue
- Smooth muscle changes
- Inotropic and chronotropic effects in the heart
State the structure and function of Phospholipase C
- Structure: an effector enzyme in the cell signalling pathway involving the hydrolysis of PIP2
- Function: generates secondary messengers – IP3, DAG

What is the role of IP3 ?
IP3 interacts with intracellular receptors on the ER to release Ca2+ from its so it can enter the cytoplasm e.g. activation of Ca2+- sensitive protein kinases

What is the role of DAG?
DAG interacts with a family of protein kinases (PKC), which are activated by this second messenger

The various intracellular signalling pathways involving GPCRs can be summarised using the mnemonic QIS.
What does this mean?
Q = PLC pathway
I = Inhibitory AC pathway
S = Stimulatory AC pathway
The various types of adrenergic receptors can be summarised using the mnemonic QISS.
What does this mean?
Q - α1
I - α2
S - β1
S - β2
(Q = PLC pathway, I = Inhibitory AC pathway, S = Stimulatory AC pathway)
The various types of muscarinic receptors can be summarised using the mnemonic QIQ
What does this mean?
Q - m1
I - m2
Q - m3
(Q = PLC pathway, I = Inhibitory AC pathway, S = Stimulatory AC pathway)


