S2 Electricity COPY Flashcards
- Describe what is meant by a complete circuit.
A complete circuit starts at one end of a power supply and continues to the other end with no gaps.
- Define series and parallel circuits.
Series circuits only have one route.
Parallel circuits have more than one branch.

- State the basic properties of series circuits:
What happens when more bulbs are added?
What happens when one bulb breaks?
As more bulbs are added, existing bulbs get dimmer.
(If the bulbs are identical they will have the same brightness as each other.)
If one bulb breaks, the rest go out.
- State the basic properties of parallel circuits:
What happens when more bulbs are added?
What happens when one bulb breaks?
As more bulbs are added, there is no change in the brightness of existing bulbs.
(If the bulbs are identical they will have the same brightness as each other.)
If one bulb breaks, the rest are unaffected.
- Draw the circuit symbols for a battery, cell, switch, lamp, voltmeter, ammeter and resistor.

- Identify the following circuit symbols.

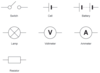
- What are the rules for drawing neat circuit diagrams?
Neat circuit diagrams should be drawn with a pencil and a ruler, making sure the symbols are correct and that there are no gaps. The wires are drawn as straight lines with right angles. Symbols are not placed in corners. e.g.
- Define what a conductor is and give 2 examples.
A conductor is a material which allows electricity to flow
e.g. copper, iron
- Define what an insulator is and give 2 examples.
An insulator is a material which does not allow electricity to flow
e.g. rubber, glass.
- Describe what electrical current is.
Electrical current is a flow of charge.
Usually the charges are electrons, which flow away from the negative end of a battery and towards the positive.
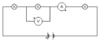
- Draw circuit diagrams to show the correct positions of an ammeter and voltmeter in a circuit.
An ammeter (to measure current) is always added in series and a voltmeter (to measure voltage) in parallel. E.g.
- State the rule for current in series circuits.
In a series circuit the current is the same at all positions.
- State the rule for voltage in series circuits.
The sum of the voltages across components in series is equal to the supply voltage.
9.&10. Example
A 5.5V battery is connected across 2 bulbs in series.
Bulb 1 has a voltage of 2V. What is the voltage across bulb 2?
The current through bulb 1 is 2A. What is the current through bulb 2?
V<sub>S</sub> = 5.5V (s for supply) V<sub>1</sub> = 2V V<sub>2</sub> = ?
V<sub>S</sub> = V<sub>1 </sub>+ V<sub>2</sub> 5.5 = 2 + V<sub>2</sub> V<sub>2</sub> = 5.5 - 2 = 3.5V
I2 = I1 = 2A
- State the rule for current in parallel circuits.
The sum of the currents in parallel branches is equal to the supply current.
- State the rule for voltage in parallel circuits.
The voltage across components in parallel is the same as the supply voltage for every component.
11.&12. Example
What will the voltmeter and ammeter in this circuit read?

The voltmeter will read 3V since the voltage across every component is the same as the supply voltage.
I<sub>S</sub> = 0.6A (s for supply) I<sub>1</sub> = 0.1A I<sub>2</sub> = ? I<sub>3</sub> = 0.2A
IS = I1 + I2 + I3
0.6 = 0.1 + I2 + 0.2 = 0.3 + I2
I2 = 0.6 – 0.3 = 0.3A
The ammeter will read 0.3A
- Explain the function of switches connected in series.
When more than one switch is connected in series they all have to be closed to complete the circuit and allow current to flow.
- Explain the function of switches connected in parallel.
When more than one switch is connected in parallel, any one (or more) can be closed to complete the circuit and allow current to flow.
- Describe what is meant by electrical resistance.
Electrical resistance is the ability of an object to reduce (or oppose) the flow of current.
- Describe the relationship between voltage and current
and what a V-I graph looks like for a resistor.
Voltage and current are directly proportional for a resistor.
OR The voltage divided by the current will always give the same answer for a resistor.
A graph of V versus I will be a straight line through the origin:

- Define the numerical value of resistance.
Resistance is defined as R=V/I
- Define the symbols and their units in the equation
V = IR
V - Voltage (V)
I - Current (A)
R - Resistance (Ω Ohms)
- Example:
Calculate the voltage across a 6 Ω resistor when 2 A of current flow.
R = 6 Ω I = 2 A V = ?
V = IR V = 2x6 V = 12 V
- Example:
Calculate the current flowing when a 200 V supply is connected across a 4 kΩ resistor.
R = 4 kΩ = 4,000 Ω I = ? V = 200 V
V = IR 200 = Ix4,000 Ix4,000 = 200 I = 200/4,000 V = 0.05 A
- Example:
Calculate the resistance if a 40 V supply produces 2 mA of current.
R = ? I = 2 mA = 0.002 A V = 40 V
V = IR 40 = 0.002xR 0.002xR = 40 R = 40/0.002 V = 20,000 Ω
- Example of calculations involving the relationship RT = R1 + R2 + R3 for resistors in series:
The total resistance of a series circuit is 70 Ω, and the value of the 1st resistor is 10 Ω and the 3rd is 20 Ω. Calculate the value of the 2nd resistor in this circuit.
R<sub>T</sub> = 70 Ω R<sub>1</sub> = 10 Ω R<sub>2</sub> = ? R<sub>3</sub> = 20 Ω
R<sub>T</sub> = R<sub>1</sub> + R<sub>2</sub> + R<sub>3</sub> 70 = 10 + R<sub>2</sub> + 20 70 = 30 + R<sub>2</sub> R<sub>2</sub> = 70 – 30 = 40 Ω
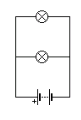
- Example (see image)
a. Calculate the total resistance.
b. Calculate the current flowing in the circuit.
c. Calculate the voltage across the 12 Ω resistor.
d. Calculate the voltage across the 8 Ω resistor.

a. Use the rule for resistance in series
RT = ? RT = R1 + R2
R1 = 12 Ω RT = 12 + 8
R2 = 8 Ω RT = 20 Ω
b. Apply V=IR to the whole circuit
V = 30 V V = IR
R = 20 Ω 30 = I x 20
I = ? I x 20 = 30
I = 30/20 = 1.5 A
c. Apply V=IR to resistor 1
R = 12 Ω V = IR
I = 1.5 A V = 1.5 x 12
V = ? V = 18 V
d. Use the rule for voltage in series (NB there are other ways. You could apply V=IR to resistor 2)
VT = 30 V VT = V1 + V2
V1 = 18 Ω 30 = 18 + V2
V2 = ? Ω V2 = 30 – 18 = 12 V


